linux之檔案描述符
寫在前面,linux的描述符有程序描述符、檔案描述符、記憶體描述符。首先標題想了很久linux的描述符從哪裡說起,看了幾份資料後還是決定從程序描述符說起。但是此文章還是重點說的是檔案描述符。知識深度有限,如有錯誤,請指出。
程序描述符:linux為了管理程序,核心必須對每個程序所作的事情進行清楚的描述,例如核心必須知道程序的優先順序,它是正在cpu上執行還是因某事而被堵塞?給它分配了什麼樣的地址空間(記憶體描述符),可訪問哪些檔案(檔案描述符),程序描述符存放很多資訊,如下圖:
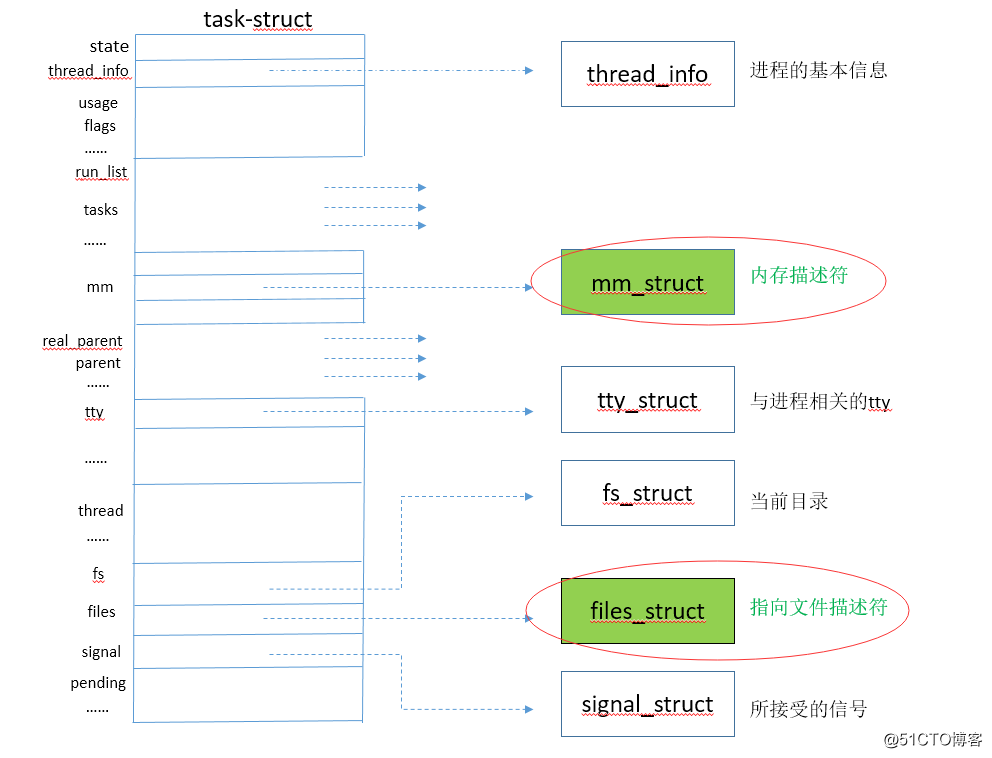
files_struct 如下圖:
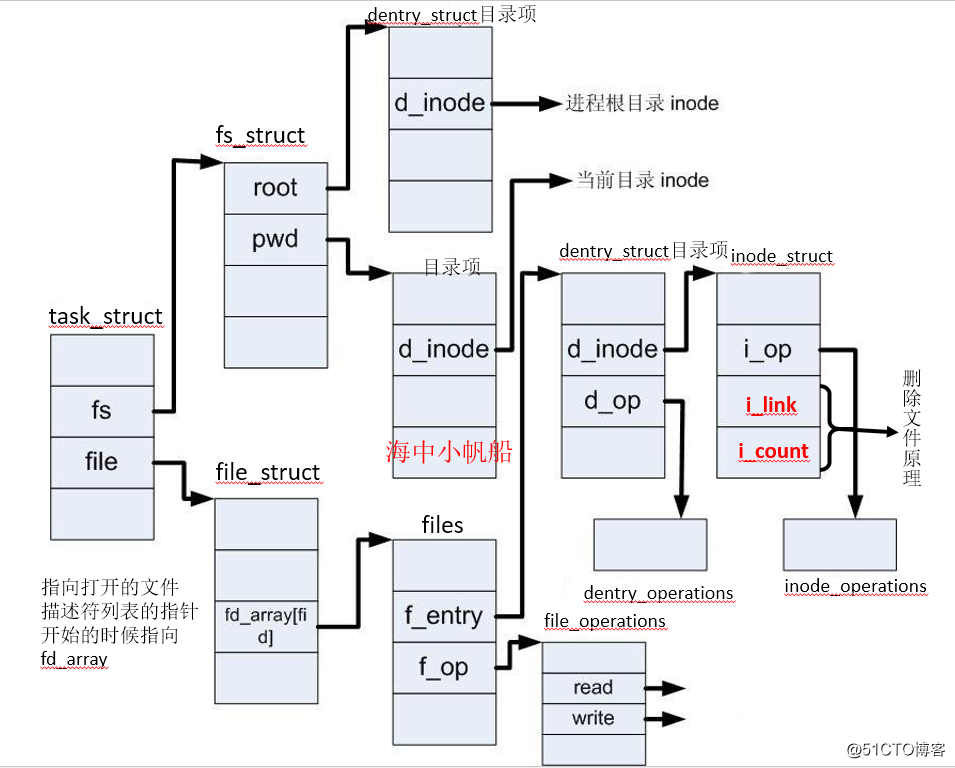
從上圖可得:
task_struct -----> file_struct(fd) -----> find opened file list -----> 被開啟檔案的資訊(dentry) -----> 檔案本身資訊(inode) -----> 磁碟
檔案描述符fd:
檔案描述符是linux核心為了高效管理已被開啟的檔案所建立的索引,所有的IO作業系統呼叫都是使用檔案描述符。
每開啟一個檔案都會建立檔案描述符,並將檔案指標指向這個檔案描述符,檔案描述符由非負整數表示,系統預設的3個檔案描述符是0,1,2,即標準輸入、標準輸出、標準錯誤輸出。
此時開啟一個檔案即從3開始,寫入到檔案描述符表中。每個程序在PCB(Process Control Block)即程序控制塊中都儲存著一份檔案描述符表。
能開啟多少檔案描述符?理論來說記憶體有多大就可以開啟多少檔案描述符,但核心進行管理 一般是記憶體的10%(系統限制)。
檢視系統限制可以建立多少檔案描述符:
方法1. [[email protected]WebA-136 ~]# sysctl -a | grep fs.file-max fs.file-max = 98622 方法2. [[email protected] ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 98622 [[email protected] ~]#
核心為了不讓某個程序消耗掉所有檔案資源,會對單個程序最大開啟檔案個數做限制:
檢視使用者級別的使用ulimit
[[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n#列出每個程序可以開啟的檔案數,此值不能超過1024*1024,核心限制,若要超過此值需要重新編譯核心。從核心2.6.25可以動態修改此值vim /proc/sys/fs/nr_open 1024 [[email protected] ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/nr_open 1048576 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n 1048577 -bash: ulimit: open files: cannot modify limit: Operation not permitted [[email protected] ~]# echo '1048577' > /proc/sys/fs/nr_open [[email protected] ~]# cat /proc/sys/fs/nr_open 1048577 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n 1048577
修改系統限制
臨時修改 [[email protected] ~]# sysctl -w fs.file-max=400000 fs.file-max = 400000 You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root [[email protected] ~]# echo 350000 >/proc/sys/fs/file-max [[email protected] ~]# sysctl -a | grep fs.file-max fs.file-max = 350000 [[email protected] ~]# 永久修改 將fs.file-max=400000新增到/etc/sysctl.conf配置檔案中。
ulimit命令:限制程序對系統資源的使用情況。常用限制有:
核心檔案大小限制
程序資料塊大小限制
shell程序建立檔案大小限制
可加鎖記憶體大小限制
常駐記憶體集大小限制
開啟檔案描述符數量限制
分配堆疊的最大大小限制
cpu佔用時間限制使用者最大可用的程序數限制
shell程序所能使用的最大虛擬記憶體限制
常用選項:
-a 顯示當前系統所有的limit資源資訊
-H 設定硬資源限制,一旦設定不能增加
-S 設定軟資源限制,設定後可以增加,但是不能超過硬資源設定
-c 最大的core檔案的大小,以 blocks 為單位
-f 程序可以建立檔案的最大值,以blocks 為單位
-d 程序最大的資料段的大小,以Kbytes 為單位
-m 最大記憶體大小,以Kbytes為單位
-n 可以開啟的最大檔案描述符的數量
-p 管道緩衝區的大小,以Kbytes 為單位
-s 執行緒棧大小,以Kbytes為單位
-u 使用者最大可用的程序數
-v 程序最大可用的虛擬記憶體,以Kbytes 為單位
-t 最大CPU佔用時間,以秒為單位
-l 最大可加鎖記憶體大小,以Kbytes 為單位
修改使用者級別
臨時修改,重啟失效 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -SHn 10240#修改可以開啟的檔案描述符數量限制 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n 10240 永久修改,所有使用者都生效。將hard,soft寫入檔案中,此檔案格式是#<domain>使用者或@組名或* <type>限制類型hard soft <item>限制的資源名稱 <value> 值 [[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/security/limits.conf 永久修改,所有使用者都生效。在/etc/security/limits.d/90-nproc.conf 中,系統會先讀取這個檔案,此檔案中的專案會覆蓋/etc/security/limits.conf中的專案,建議將其一內容註釋。 永久修改,修改單一使用者,寫入使用者環境變數中 .bash_profile 寫入ulimit -SHn 10240. [[email protected] ~]# echo "ulimit -SHn 10240" >>/root/.bash_profile [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n #已修改 10240 [[email protected] ~]# 或者在應用程式的啟動指令碼寫入ulimit -n 10240
ulimit -a顯示當前使用者所有系統限制
[[email protected] ~]# ulimit -a core file size (blocks, -c) 0 data seg size (kbytes, -d) unlimited scheduling priority (-e) 0 file size (blocks, -f) unlimited pending signals (-i) 7802 max locked memory (kbytes, -l) 64 max memory size (kbytes, -m) unlimited open files (-n) 1024 pipe size (512 bytes, -p) 8 POSIX message queues (bytes, -q) 819200 real-time priority (-r) 0 stack size (kbytes, -s) 10240 cpu time (seconds, -t) unlimited max user processes (-u) 7802 virtual memory (kbytes, -v) unlimited file locks (-x) unlimited [[email protected] ~]#
ulimit -SHn 修改硬限制、軟限制和檔案描述符數
[[email protected] ~]# ulimit -SHn 11223 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n 11223 [[email protected] ~]# . /root/.bash_profile#我這裡已經對當前使用者所有程序都設定開啟檔案描述符數為10240了 [[email protected] ~]# ulimit -n 10240 [[email protected] ~]#
檢視使用者可以建立的程序數量限制
[[email protected] ~]# ulimit -u 7802 [[email protected] ~]#
檢視所有使用者建立的程序數量
[[email protected] ~]# ps h -Led -o user | sort | uniq -c | sort -n 2 dbus 2 postfix 193 root
注:ulimit 生效後,若是web伺服器。需要重啟web服務。
