Data Structures & Algorithms(second:sort)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-23
排序:對一種抽象資料型別按照其自然規律或邏輯規律排序(eg:從小到大,從前到後…)
sort:sorting is the processing of rearranging a sequence of objects so as to put them in a logical order.
There are three reasons to study sorting algorithms :
1: A easy start to start all kinds of other algorithms
2:Exercise a ability to compare with other algorithms
3: Similar techniques in other problems
Seven kinds of sorting algorithms :
| algorithm | stable? | in place? | order of running time | extra space | notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 演算法 | 穩定性? | 是否在原陣列中操作? | 時間複雜度 | 額外空間大小 | 注意 |
| selection sort | no | yes | N^2 | 1 | none |
| insertion sort | yes | yes | N~N^2 | 1 | time depends on original order of items |
| shellsort | no | yes | NlogN or N^(6/5) | 1 | none |
| quicksort | no | yes | NlogN | lgN | probabilistic (概率性的) |
| 3-way quicksort | no | yes | N~NlogN | lgN | probabilistic and depends on what kinds of intput source |
| mergesort | yes | no | NlogN | N | none |
| heapsort | no | yes | NlogN | 1 | none |
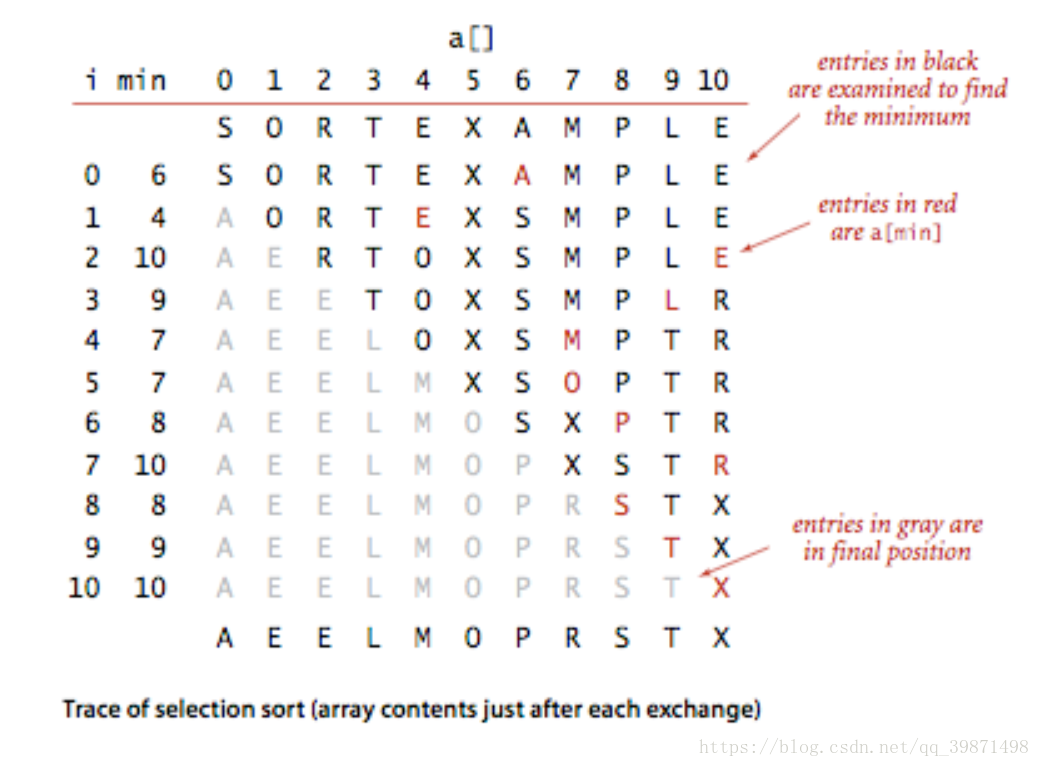
一:selection sort
It is the simplest sorting algorithms .
Its core logic is a for-loop.
core codes :
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N=a.length;
for (int i = 0; i <N; i++) {
int min =i;
for(int j=i+1;j<N;j++) {
if(less(a[j], a[min]))
min=j;
}
exch(a, i,min);
}
}
complete codes:
package algorithms_4th_chapter2_1;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In;
/**
* 2.1
* O(time)=N^2
* @author Enzo
*
*/
public class Selection {
public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
int N=a.length;
for (int i = 0; i <N; i++) {
int min =i;
for(int j=i+1;j<N;j++) {
if(less(a[j], a[min]))
min=j;
}
exch(a, i,min);
}
}
public static boolean less (Comparable v,Comparable w) {
return v.compareTo(w)<0;
}
public static void exch (Comparable[] a,int i,int j) {
Comparable t=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=t;
}
public static void show(Comparable [] a) {
for(int i=0;i<a.length;i++) {
System.out.print(a[i]+"");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static boolean is_sorted (Comparable [ ] a) {
for (int i = 0; i < a.length-1; i++) {
if(less(a[i+1], a[i]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String[] a =new In("tiny.txt").readAllStrings();
sort(a);
assert is_sorted(a);
show(a);
}
}
Nodes:
Use Comparable interface
Every loop to find the minimum item in array and decrease 1 of needed to retrieval array items ,also put this min item in a[i].
Features:
1: Running time is insensitive to input
2: Data move is minimal