python 入門第五課 模組module
1 模組介紹
1.1 模組定義:
模組:用來從邏輯上組織python程式碼(變數,函式,類,邏輯:實現一個功能),本質就是.py結尾的python檔案(檔名:test.py,對應模組名是test)
包:本質是一個目錄(必須帶一個__init__.py的檔案),從邏輯上組織模組
1.2 匯入:
import test1,test2
from test import *
from test import name,def1
from test import def1 as def1_imp
1.3 import的本質:()
匯入模組的本質就是把python檔案解釋一遍
(import test ---> test = 'test.py all code')
(from test import name -->name = 'code')
匯入包的本質執行該包下面的__init__.py檔案
1.4 匯入優化
from test import def1 as fun1
1.5 模組的分類:
1.5.1 標準庫
1.5.2 三方開源模組
1.5.3 自定義模組
2 內建模組
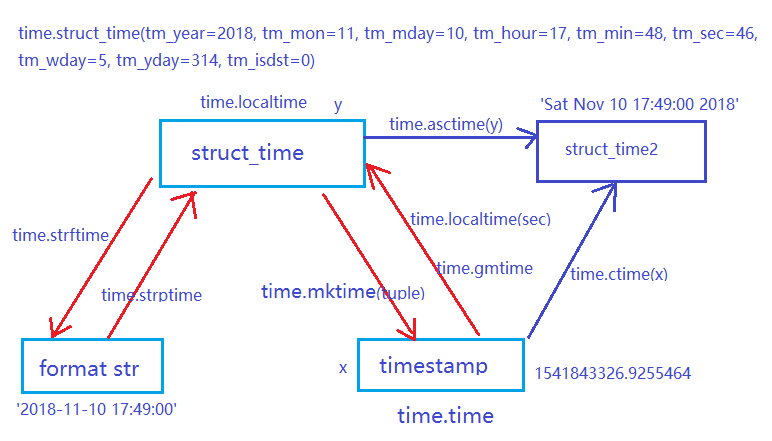
2.1 time 模組
struct_tuple:
time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=17, tm_min=49, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=314, tm_isdst=-1)
strftime():
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61].
%z Time zone offset from UTC.
%a Locale's abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale's full weekday name.
%b Locale's abbreviated month name.
%B Locale's full month name.
%c Locale's appropriate date and time representation.
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM.
2.2 datetime
datetime.datetime.now()---->
datetime.datetime(2018, 11, 10, 18, 23, 42, 407988)
timedelta():
+datetime.timedelta(3)
+datetime.timedelta(hours = 5)
練習程式碼:
__author__ = 'admin' import time,datetime x = time.time() y = time.localtime() print(x,'\n',y) # 1541846184.9383597 ; time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=18, tm_min=36, tm_sec=24, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=314, tm_isdst=0) print(time.mktime(y)) #1541846184.0 print(time.gmtime(x)) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=10, tm_min=36, tm_sec=24, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=314, tm_isdst=0) print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',y)) #2018-11-10 18:39:18 print(time.strptime('2018-11-10 18:39:18','%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')) #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=11, tm_mday=10, tm_hour=18, tm_min=39, tm_sec=18, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=314, tm_isdst=-1) print(time.ctime(x)) #Sat Nov 10 18:41:24 2018 print(time.asctime(y)) #Sat Nov 10 18:41:24 2018 print(y.tm_year,y.tm_yday) #2018 314 z = datetime.datetime.now() print(z) #2018-11-10 18:51:47.737317 w = z +datetime.timedelta(hours = 10) print('***',w) #*** 2018-11-11 04:51:47.737317 rez = z.replace(minute=20) print(rez) # 2018-11-10 18:20:47.737317 print(datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(time.time())) #2018-11-10 18:51:47.737317 print(time.time())
3 random模組
3.1 random練習
__author__ = 'admin'
import random
print(random.random()) ## float between 0 -1
print(random.uniform(1,9)) # float between 1 -9
print(random.randint(2,10)) #inter from 2 -10
print(random.randrange(2,10)) # not include the last element
print(random.choice('hello')) # choice one element
print(random.sample('hello',2)) # pick x elements
lz =[2,4,6,8,9,10,15]
random.shuffle(lz) # disorder the order
print(lz)3.2 隨機驗證碼
__author__ = 'admin'
import random
'''
lz ='32455656fsafhghfdhr7896'
checkcode = ''
listc = random.sample(lz,4)
print(listc)
for i in range(len(listc)):
checkcode += listc[i]
print(checkcode)
'''
checkcode = ''
for i in range(5):
current = random.randint(0,5)
if current == i :
temp = chr(random.randint(65,90))
else:
temp = random.randint(0,9)
checkcode += str(temp)
print(checkcode)4 os 模組
os.getcwd() 獲取當前工作目錄,即當前python指令碼工作的目錄路徑
os.chdir("dirname") 改變當前指令碼工作目錄;相當於shell下cd
os.curdir 返回當前目錄: ('.')
os.pardir 獲取當前目錄的父目錄字串名:('..')
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多層遞迴目錄
os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目錄為空,則刪除,並遞迴到上一級目錄,如若也為空,則刪除,依此類推
os.mkdir('dirname') 生成單級目錄;相當於shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir('dirname') 刪除單級空目錄,若目錄不為空則無法刪除,報錯;相當於shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目錄下的所有檔案和子目錄,包括隱藏檔案,並以列表方式列印
os.remove() 刪除一個檔案
os.rename("oldname","newname") 重新命名檔案/目錄
os.stat('path/filename') 獲取檔案/目錄資訊
os.sep 輸出作業系統特定的路徑分隔符,win下為"\",Linux下為"/"
os.linesep 輸出當前平臺使用的行終止符,win下為"\t\n",Linux下為"\n"
os.pathsep 輸出用於分割檔案路徑的字串
os.name 輸出字串指示當前使用平臺。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
os.system("bash command") 執行shell命令,直接顯示
os.environ 獲取系統環境變數
os.path.abspath(path) 返回path規範化的絕對路徑
os.path.split(path) 將path分割成目錄和檔名二元組返回
os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目錄。其實就是os.path.split(path)的第一個元素
os.path.basename(path) 返回path最後的檔名。如何path以/或\結尾,那麼就會返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二個元素
os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是絕對路徑,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一個存在的檔案,返回True。否則返回False
os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一個存在的目錄,則返回True。否則返回False
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 將多個路徑組合後返回,第一個絕對路徑之前的引數將被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的檔案或者目錄的最後存取時間
os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的檔案或者目錄的最後修改時間
5 sys模組
sys.argv 命令列引數List,第一個元素是程式本身路徑
sys.exit(n) 退出程式,正常退出時exit(0)
sys.version 獲取Python解釋程式的版本資訊
sys.maxint 最大的Int值
sys.path 返回模組的搜尋路徑,初始化時使用PYTHONPATH環境變數的值
sys.platform 返回作業系統平臺名稱
sys.stdout.write('please:')
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]
6 shutil 檔案複製
shutil練習:
import shutil,os
# f1 = open('TEXTpy2',encoding='utf-8')
# f2 = open('testpy3','w',encoding='utf-8')
# shutil.copyfileobj(f1,f2) # opened f1 and f2
#shutil.copyfile('testpy3','testpy4') #new testpy4
#shutil.copymode('testpy3','test5') #existed test5
#shutil.copystat('testpy3','test5')
#shutil.copytree('module_test','module22')
#shutil.rmtree('module22')
shutil.make_archive('module_test','gztar')
#os.remove('module_test.tar.gz')