spring mvc中DispatcherServlet如何得到ModelAndView的
首先看下面這種張圖,這張圖說明了spring mvc整體的流程。
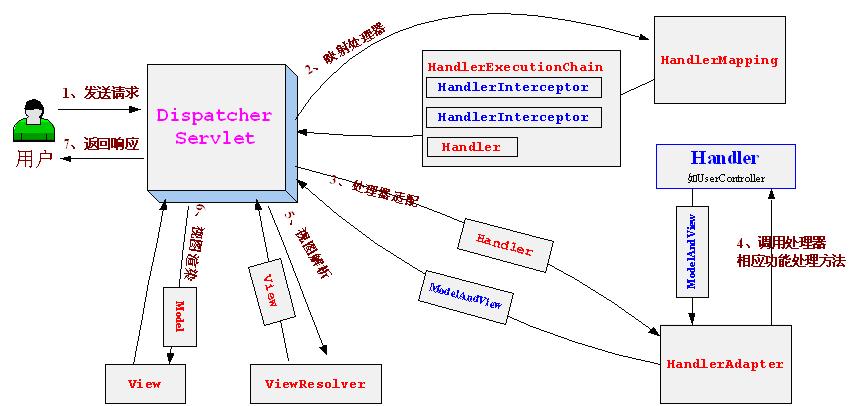
本文講的就是如何從DispatcherServlet中得到ModerAndView的過程。
首先看DispatherServlet這個類的doService方法,學過servlet的人都知道,它是web容器處理請求的入口。
1 protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 2 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {3 String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; 4 logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + 5 " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");6 } 7 8 // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, 9 // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. 10 Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null; 11 if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { 12 attributesSnapshot = newHashMap<String, Object>(); 13 Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); 14 while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { 15 String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); 16 if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { 17 attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 22 // Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects. 23 request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); 24 request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); 25 request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); 26 request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); 27 28 FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); 29 if (inputFlashMap != null) { 30 request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); 31 } 32 request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); 33 request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); 34 35 try { 36 doDispatch(request, response); 37 } 38 finally { 39 if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 40 return; 41 } 42 // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. 43 if (attributesSnapshot != null) { 44 restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); 45 } 46 } 47 }
可以看到,doService做的事情一共就兩件,一是儲存request的Attribute並在框架處理完之後恢復回去,以防止attribute在框架處理的過程中被迫壞;第二件事就是在第36行呼叫doDispatch,進入真正的spring mvc流程中。我們來看doDispatch函式,這個函式是DispatchServlet控制整個spring mvc流程的核心,文章開始的那張圖所描述的流程都是在這個函式中完成的。我們來看一下這個函式。
1 /** 2 * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. 3 * <p>The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. 4 * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters 5 * to find the first that supports the handler class. 6 * <p>All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers 7 * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. 8 * @param request current HTTP request 9 * @param response current HTTP response 10 * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure 11 */ 12 protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { 13 HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; 14 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; 15 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; 16 17 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 18 19 try { 20 ModelAndView mv = null; 21 Exception dispatchException = null; 22 23 try { 24 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); 25 multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); 26 27 // Determine handler for the current request. 28 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); 29 if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { 30 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); 31 return; 32 } 33 34 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. 35 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); 36 37 // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. 38 String method = request.getMethod(); 39 boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); 40 if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { 41 long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 42 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 43 logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); 44 } 45 if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { 46 return; 47 } 48 } 49 50 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { 51 return; 52 } 53 54 try { 55 // Actually invoke the handler. 56 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); 57 } 58 finally { 59 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 60 return; 61 } 62 } 63 64 applyDefaultViewName(request, mv); 65 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); 66 } 67 catch (Exception ex) { 68 dispatchException = ex; 69 } 70 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); 71 } 72 catch (Exception ex) { 73 triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); 74 } 75 catch (Error err) { 76 triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); 77 } 78 finally { 79 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 80 // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion 81 mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); 82 return; 83 } 84 // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. 85 if (multipartRequestParsed) { 86 cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); 87 } 88 } 89 }
這個方法的核心工作內容包括這麼幾件:處理http請求得到模型和檢視(存在一個ModelAndView物件中)、處理攔截器、渲染檢視、解除安裝multipart內容,以及獲取用於處理模型所需的處理器HanderExecutionChain和介面卡HandlerAdapter。
http的請求具體會被怎麼處理將取決於處理器執行器HanderExecutionChain和介面卡HandlerAdapter,所以我們先看這兩個物件是怎麼得到的。方法註釋的已經大致說明了這兩個物件是如何得到的:HanderExecutionChain是通過應用servlet所擁有的HanderMapping生成的,HandlerAdapter是通過依次查詢servlet所擁有的介面卡中能夠支援執行器的介面卡得到的。
那麼我們就來看一下HanderExecutionChain和HandlerAdapter到底是怎麼得到的。
看28行的getHandler,HanderExecutionChain是從這裡獲取的,跟進去看:
1 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { 3 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 4 logger.trace( 5 "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); 6 } 7 HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); 8 if (handler != null) { 9 return handler; 10 } 11 } 12 return null; 13 }
看第7行,真的是通過DistpacherServlet的HandlerMappings得到的,跟進去看怎麼得到的:
發現這個servlet擁有的一個HM是AbstractHanderMethondMapping物件,跟進他的方法,發現它在第3行獲取了一個HandlerMethod(名為handler的object物件)。
1 @Override 2 public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 3 Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request); 4 if (handler == null) { 5 handler = getDefaultHandler(); 6 } 7 if (handler == null) { 8 return null; 9 } 10 // Bean name or resolved handler? 11 if (handler instanceof String) { 12 String handlerName = (String) handler; 13 handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); 14 } 15 return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request); 16 }
這個HandlerMethod物件存的是什麼呢?我們看看:

原來是它封裝了我們對映到的控制器,包括bean,以及map到的方法。有了這個封裝物件,剩下的事情就好辦了。
繼續往下看便到了第15行,跟進去getHandlerExecutionChain方法:
1 protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) { 2 HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ? 3 (HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler)); 4 chain.addInterceptors(getAdaptedInterceptors()); 5 6 String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); 7 for (MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor : this.mappedInterceptors) { 8 if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) { 9 chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor()); 10 } 11 } 12 13 return chain; 14 }
可以看到,這個方法new了HandlerExecutionChain物件,並且把HM的攔截器和使用者的攔截去都加進去了。至此HandlerExecutionChain的獲取過程就講完了。
接下來看介面卡HandlerAdapter是怎麼來的。
1 protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { 2 for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { 3 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 4 logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); 5 } 6 if (ha.supports(handler)) { 7 return ha; 8 } 9 } 10 throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + 11 "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); 12 }
真的就是看servlet有那些介面卡,然後一個個查詢是否支援,最後返回。
HanderExecutionChain和HandlerAdapter都有了,那麼接下來就要看它們是怎麼獲取到模型和檢視了。
跟進去dispatch方法的56行,一路下去,來到了 ModelAndView invokeHandleMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) 方法,這個方法是HandlerAdapter介面卡的方法啊, 來看看這個方法:
1 private ModelAndView invokeHandleMethod(HttpServletRequest request, 2 HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { 3 4 ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); 5 6 WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); 7 ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); 8 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod requestMappingMethod = createRequestMappingMethod(handlerMethod, binderFactory); 9 10 ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); 11 mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); 12 modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, requestMappingMethod); 13 mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); 14 15 AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); 16 asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); 17 18 final WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); 19 asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); 20 asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); 21 asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); 22 asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); 23 24 if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { 25 Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); 26 mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; 27 asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); 28 29 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 30 logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]"); 31 } 32 requestMappingMethod = requestMappingMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); 33 } 34 35 requestMappingMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); 36 37 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { 38 return null; 39 } 40 41 return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); 42 }
終於知道為什麼需要介面卡了,原來這個介面卡的方法中,就適配了spring mvc和servlet,還有幾個適配物件,其中最重要的是ServletWebRequest webRequest ,它適配了request。另外還有ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,通過它持有模型和檢視。
另外看這三行,這三行採用了工廠模式。
第一行獲取了資料繫結的工廠,最重要的是它有handlerMethod。然後它會傳給第三行,得到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod requestMappingMethod 。這個 requestMappingMethod 就是我們進入控制器呼叫的關鍵。
第二行獲取了模型工廠,有了它,就可以建立模型了。
值得注意的是,這三個物件,每個裡面都有handlerMethod的資訊。
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); ServletInvocableHandlerMethod requestMappingMethod = createRequestMappingMethod(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
看第35行,requestMappingMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer),這裡開始真正的填充模型了,怎麼填充呢?其實猜都能猜到,首先它自己有handlermethod,又傳入了webRequest和mavContainer,很容易想到,它肯定是根據請求,通過反射獲取控制器的requestMap方法,將引數傳入並呼叫方法,最後得到控制器處理後的模型,並得到控制器指定的檢視。至於傳入的引數是如何得到的,我在另一篇文章李有比較詳細的描述,請看spring mvc中的控制器方法中的引數從哪裡傳進來這篇文章。
看起來貌似已經把整個流程講完了,但是等等,有個很重要的問題,生成處理器執行器HandlerExecutionChain的時候需要從HM裡get到一個真正的處理器傳入給HandlerExecutionChain的構造器。這個處理器怎麼來的?這個帶著這個疑問,我們繼續來看他們是怎麼得到的。
前面已經說了,這個handler是在HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) 的第三行呼叫HM的Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request)得到的,我們看一看getHandlerInternal這個函式:
1 protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); 3 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 4 logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath); 5 } 6 HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request); 7 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 8 if (handlerMethod != null) { 9 logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]"); 10 } 11 else { 12 logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]"); 13 } 14 } 15 return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); 16 }
可以看到,getHandlerInternal是通過請求的路徑來查詢得到那個關鍵的處理器(在這裡是一個HandlerMethod,它含有控制器的requestMap方法簽名),再看一下第6行,它是怎麼通過路徑查詢到處理器的,跟進去lookupHandlerMethod函式:
1 protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { 2 List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>(); 3 List<T> directPathMatches = this.urlMap.get(lookupPath); 4 if (directPathMatches != null) { 5 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); 6 } 7 if (matches.isEmpty()) { 8 // No choice but to go through all mappings... 9 addMatchingMappings(this.handlerMethods.keySet(), matches, request); 10 } 11 12 if (!matches.isEmpty()) { 13 Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request)); 14 Collections.sort(matches, comparator); 15 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 16 logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" + lookupPath + "] : " + matches); 17 } 18 Match bestMatch = matches.get(0); 19 if (matches.size() > 1) { 20 Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1); 21 if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { 22 Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); 23 Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); 24 throw new IllegalStateException( 25 "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" + request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + 26 m1 + ", " + m2 + "}"); 27 } 28 } 29 handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request); 30 return bestMatch.handlerMethod; 31 } 32 else { 33 return handleNoMatch(handlerMethods.keySet(), lookupPath, request); 34 } 35 }
lookupHandlerMethod函式把獲取的處理器包裝成一個個Match,並對Match進行了排序(因為一個path可能不僅僅對應一個處理器,比如存在兩個requestMap路徑相同的函式,那麼一個path就會對應兩個處理器)之後取最匹配的那個。在這個過程中甚至還做了重複性檢測,如果有兩個一模一樣的處理器存在,那說明我們的控制器寫的有歧義了,直接丟擲異常。我們看到第5行 addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request); ,這裡是真正獲取HandlerMethod的地方,跟進去看:
1 private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) { 2 for (T mapping : mappings) { 3 T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request); 4 if (match != null) { 5 matches.add(new Match(match, this.handlerMethods.get(mapping))); 6 } 7 } 8 }
直接看到第5行 matches.add(new Match(match, this.handlerMethods.get(mapping))) ,這裡傳入了一個重要的this.handlerMethods.get(mapping),this.handlerMethods 是一個LinkedHashMap,存放了此HM所有的處理器,根據mapping物件進行索引(mapping物件標識了唯一的請求對映),看一看這個handlerMethods 裡有啥:
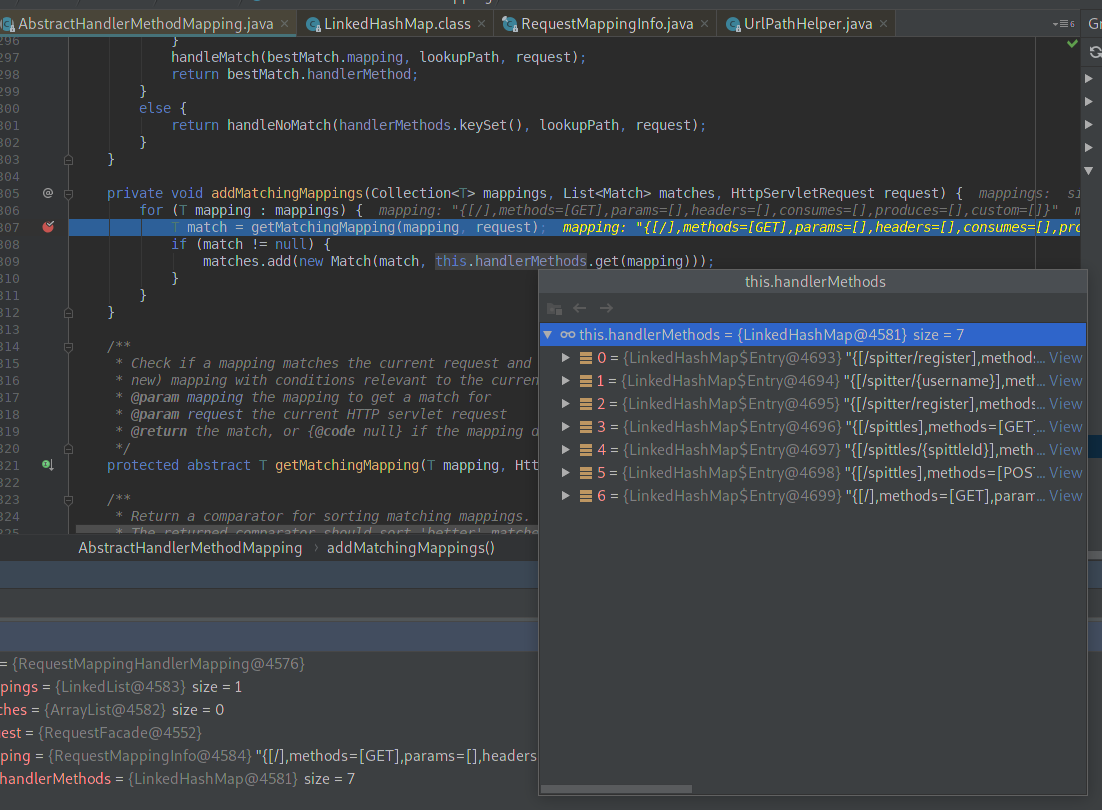
果然我們寫的控制器方法對應的handler,都在這裡頭儲存著。
接下來我們看看,這些handler是怎麼儲存到HM中的。我們在HM中找到了一個initHandlerMethods方法,從名字中就可以看出來這個方法是初始化methods用的,我們看看這個方法的內容:
1 protected void initHandlerMethods() { 2 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 3 logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); 4 } 5 6 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? 7 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : 8 getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); 9 10 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 11 if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX) && 12 isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ 13 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); 14 } 15 } 16 handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); 17 }
它從ApplicationContext中獲取了bean的名字,然後根據名字,在第13行中通過 detectHandlerMethods(beanName) 得到真正的bean:
1 protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { 2 Class<?> handlerType = 3 (handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); 4 5 // Avoid repeated calls to getMappingForMethod which would rebuild RequestMappingInfo instances 6 final Map<Method, T> mappings = new IdentityHashMap<Method, T>(); 7 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); 8 9 Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { 10 @Override 11 public boolean matches(Method method) { 12 T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType); 13 if (mapping != null) { 14 mappings.put(method, mapping); 15 return true; 16 } 17 else { 18 return false; 19 } 20 } 21 }); 22 23 for (Method method : methods) { 24 registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mappings.get(method)); 25 } 26 }
看第24行,在這裡註冊HM所持的HandlerMethod,跟進去:
1 protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { 2 HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); 3 HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = this.handlerMethods.get(mapping); 4 if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) { 5 throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() + 6 "' bean method \n" + newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '" + 7 oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped."); 8 } 9 10 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod); 11 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 12 logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + newHandlerMethod); 13 } 14 15 Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); 16 for (String pattern : patterns) { 17 if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { 18 this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping); 19 } 20 } 21 }
看第10行 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod) ,一個個Put 進去了,這樣,就完成了HandlerMethod的註冊。在第18行 this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping) ,完成了路徑到mapping的對映。
最後只要框架在啟動是呼叫initMethod方法,就可以完成處理器的註冊了。
自此,DispatcherServlet如何得到ModelAndView的過程就講完了。
