關於java物件陣列(全)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-29
文章目錄
1 簡單物件陣列的構造與使用
1.1 Practice類
//Practice.java
package Object;
/**
把5個學生的資訊儲存到陣列中,並遍歷陣列,獲取得到每一個學生資訊。
* 學生:Student
* 成員變數:name,age
* 構造方法:無參,帶參
* 成員方法:getXxx()/setXxx()
* 分析:
* A:建立學生類。
* B:建立學生陣列(物件陣列)。
* C:建立5個學生物件,並賦值。
* D:把C步驟的元素,放到陣列中。
* E:遍歷學生陣列。
**/ 1.2 Student.java
//Student.java
package Object;
public class Student {
//成員變數
private String name;
private int age;
//構造方法
public Student(){
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age){
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//成員方法
//getXxx()/setXxx()
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Student [name=" + name + ",age=" + age + "]";
}
}
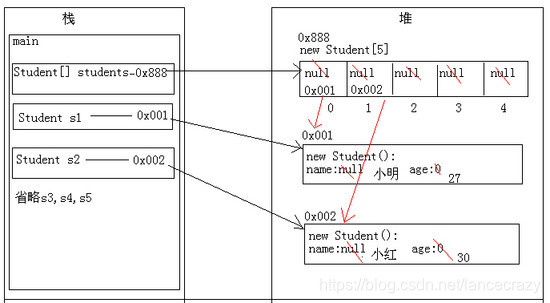
1.3 關於簡單物件陣列的記憶體圖解
2 高階物件陣列::集合簡介
2.1 集合的由來及陣列的區別
- 由來:面嚮物件語言都是以物件的形式, 為方便對多個物件的操作,java提供了集合類
- 區別:
- 陣列可以儲存同一型別的基本資料也可以儲存.同一型別的物件,但長度是固定的
- 集合可以儲存不同型別的物件,集合長度可變,可以儲存不同型別的物件
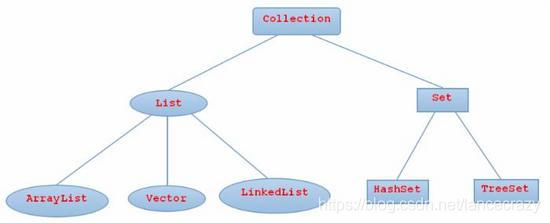
2.2 框架的頂層Collection介面
2.3 Collection集合的功能概述
- Collection是層次結構中的根介面。
- Collection 表示一組物件,這些物件也稱為 collection 的元素。
- 一些 collection 允許有重複的元素,而另一些則不允許。
- 一些 collection 是有序的,而另一些則是無序的。
- JDK 不提供此介面的任何直接實現:它提供更具體的子介面(如 Set 和 List)實現。
- 此介面通常用來傳遞 collection,並在需要最大普遍性的地方操作這些 collection。
2.4 Collection集合的基本功能測試
2.4.1 成員方法介紹
//確保此Collection包含指定的元素(可選操作)
boolean add(E e)
//從此lollection中移除指定元素的單個例項,如果存在的話(可選操作)
boolean remove(Object o)
//移除此collection中的所有元素(可選操作)
void clear()
//如果此collection包含指定的元素,則返回true
boolean contains(Object o)
//如果此collection不包含元素,則返回true
boolean isEmpty()
//返回此collection中的元素數
int size()
2.4.2 基本功能測試
//
package Collection_1;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class test_collection {
public static void main(String[] args){
// 建立集合物件
//Collection c = new Collection();
//錯誤,因為介面不可以例項化
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
//c.clear();
//移除所有元素
System.out.println("remove:" + c.remove("hello"));
System.out.println("remove:" + c.remove("javaee"));
//判斷集合中是否包含指定的元素
System.out.println("contains:" + c.contains("hello"));
System.out.println("contains:" + c.contains("android"));
//判斷集合是否為空
System.out.println("isEmpty:" + c.isEmpty());
//元素的個數
System.out.println("size:" + c.size());
System.out.println("c:" + c);
}
}
2.5 Collection集合的高階功能測試
2.5.1 成員方法介紹
//將指定 collection 中的所有元素都新增到此 collection 中(可選操作)。
boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E>c):
//移除此 collection 中那些也**包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素**(可選操作)。
boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c):
//如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,則返回 true。
boolean containsAll(Collestion<?> c):
//僅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection 的元素(可選操作)。換句話說,移除此 collection 中未包含在指定 collection 中的所有元素。
boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c):
2.5.2 基本功能測試
c1.addAll(c2);//將c2集合中的所有元素新增到c1集合中,c1變c2不變
c1.removeAll(c2);//將c1集合中與c2集合相同的所有元素刪除,只要有一個相同的就返回true
c1.containsAll(c2);//判斷c1集合中的元素是否包含c2中的全部元素,全部包含則返回true
c1.retainAll(c2);//將c1集合中與c2集合相同的元素保留,刪除其他元素,返回值表示c1集合是否發生變化,發生變化返回true,沒有變化返回false
還有一些沒補充完整,先這樣,夠寫專案了,待補充
