Linux核心初始化步驟(三)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-01
在start_kernl函式的最後呼叫了reset_init函式進行後續的初始化
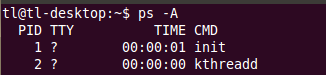
static noinline void __init_refok rest_init(void) { int pid; rcu_scheduler_starting();//核心RCU鎖機制排程啟動 /* * We need to spawn init first so that it obtains pid 1, however * the init task will end up wanting to create kthreads, which, if * we schedule it before we create kthreadd, will OOPS. */ /*我們必須先建立init程序以便於使它獲得程序號1,然而init程序將會被掛起來等待建立kthreads 執行緒,如果我們在建立kthreadd執行緒前排程它,將會導致OOPS錯誤*/ /*rest_init()函式最主要的歷史使命就是啟動核心執行緒kernel_init*/ kernel_thread(kernel_init, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_SIGHAND); numa_default_policy(); /*啟動核心執行緒kthreadd,執行kthread_create_list全域性連結串列中的kthread 1.它迴圈執行一個叫做kthreadd的函式,該函式的作用是執行ktheard_create_list全域性連結串列中 維護的核心執行緒; 2.呼叫kthread_create建立一個kthread,它會被加入到kthread_create_list連結串列中; 3.被執行過的kthread會從kthread_create_list連結串列中刪除 4.且kthreadd會不斷呼叫scheduler函式讓出CPU,此執行緒不可關閉 上面兩個執行緒就是我們平時在Linux系統中用ps命令看到: */ pid = kernel_thread(kthreadd, NULL, CLONE_FS | CLONE_FILES); rcu_read_lock(); kthreadd_task = find_task_by_pid_ns(pid, &init_pid_ns); rcu_read_unlock(); complete(&kthreadd_done); /*1.獲取kthreadd的執行緒資訊,獲取完成說明kthreaddd已經建立成功。並通過一個complete 變數(kthreadd_done)來通知kernel_init執行緒*/ /* * The boot idle thread must execute schedule() * at least once to get things moving: */ init_idle_bootup_task(current); preempt_enable_no_resched(); schedule(); /* Call into cpu_idle with preempt disabled */ preempt_disable(); cpu_idle(); }