瘋狂Java學習筆記(023)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-02
位元組流:
抽象基類:
InputStream:
實現子類:
FileInputStream:
構造方法:
FileInputStream(File file):
FileInputStream(String name):
方法:
int read():
int read(byte[] bys):
緩衝位元組輸入流:
BufferedInputStream:
構造方法:
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in):
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in,
一、資料操作流
針對不同資料型別操作的流,屬於位元組流.底層包裝的是基本的位元組流,在讀寫資料的次數上進行了增強!
DataOutputStream:
DataOutputStream(OutputStream out):
方法:
void writeInt(int i):
void writeLong(long l):
void writeDouble(double d):
void writeFloat(float f):
void writeUTF(String s):
1.寫出方法的原始碼
通過檢視writeInt方法的原始碼:

發現實際上就是呼叫了底層位元組流的四次write方法,依次將一個int型資料的四個位元組寫出到底層流中!!!寫出的順序是高位在前!!!其它方法原理相同!
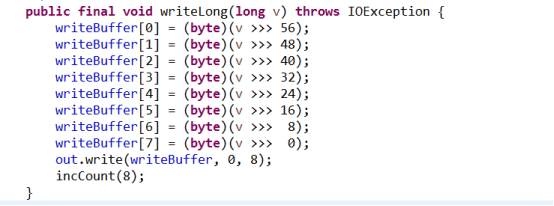
long型資料是先寫到一個位元組陣列中,然後一次性將整個陣列寫出到底層的流中。
2.writeUTF(String s):
- 使用的是修改版的UTF-8編碼:
- 先寫出兩個位元組的控制位元組:表示真實字串編碼後的位元組數!!
- 然後寫出的是字串真實的位元組陣列!
- 即:寫出資料的長度:最短:2+字串長度
- 最長:2+字串長度*3!
3.DateInputStream:
屬於位元組流,在讀取不同資料型別的時候,進行了次數上的控制。
構造方法:
DataInputStream(InputStream in):
方法:
int read();
int readInt();
long readLong();
........
二、讀取方法的原始碼
舉例:以readInt方法為例,檢視如何還原資料:

實際上,就是一次從底層流中讀取四個位元組,並按照高位在前的順序,將int值還原。
1. readLong( ):方法

依次從底層的流中讀取八個位元組,並做相應的移位運算,將long型資料還原!!
三、自定義工具類
例如:實現int型資料和long型資料的原生陣列的轉換操作:
/*
* 資料操作的工具類:
*
* 方便int型long型資料和位元組陣列之間的轉換!
*/
public class DataTools {
//私有構造方法
private DataTools(){}
//獲取int型資料的陣列:高位在前
public static byte[] int2Bytes(int i){
//建立一個數組,存放int型資料的四個位元組
byte[] bys = new byte[4];
//將int型資料轉換成四個位元組
bys[0] = (byte)(i >> 24);
bys[1] = (byte)(i >> 16);
bys[2] = (byte)(i >> 8);
bys[3] = (byte)(i >> 0);
return bys;
}
//從陣列還原int資料:高位在前
public static int bytes2Int(byte[] bys){
int i0 = (bys[0] & 0xFF) << 24;
int i1 = (bys[1] & 0xFF) << 16;
int i2 = (bys[2] & 0xFF) << 8;
int i3 = (bys[3] & 0xFF) << 0;
return i0 + i1 + i2 + i3;
}
//long -> byte[] : 高位在前
public static byte[] long2Bytes(long l){
byte[] bys = new byte[8];
bys[0] = (byte)(l >> 56);
bys[1] = (byte)(l >> 48);
bys[2] = (byte)(l >> 40);
bys[3] = (byte)(l >> 32);
bys[4] = (byte)(l >> 24);
bys[5] = (byte)(l >> 16);
bys[6] = (byte)(l >> 8);
bys[7] = (byte)(l >> 0);
return bys;
}
//byte[] -> long : 高位在前
public static long bytes2Long(byte[] bys){
long l0 = ((long)bys[0] & 0xFF) << 56;
long l1 = ((long)bys[1] & 0xFF) << 48;
long l2 = ((long)bys[2] & 0xFF) << 40;
long l3 = ((long)bys[3] & 0xFF) << 32;
long l4 = ((long)bys[4] & 0xFF) << 24;
long l5 = ((long)bys[5] & 0xFF) << 16;
long l6 = ((long)bys[6] & 0xFF) << 8;
long l7 = ((long)bys[7] & 0xFF) << 0;
return l0 | l1 | l2 | l3 | l4 | l5 | l6 | l7;
}
//通過封裝jdk提供的資料流寫出指定型別的資料
public static void writeInt(OutputStream out,int value) throws Exception{
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(out);
dos.writeInt(value);
dos.close();
}
}
- 使用場景:凡是需要寫出超過一個位元組的場景,都可以使用!
- 使用系統提供的資料操作流或者使用位元組定義的工具類!
- 自定義工具類的優點:不用開流和關流!直接使用即可!
四、列印流
按位元組操作的位元組流列印流和按字元操作的字元列印流,都是隻有輸出,沒有輸入。
1.位元組列印流
PrintStream: 構造方法: PrintStream(File file): PrintStream(String name): PrintStream(OutputStream out): PrintStream(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush): 方法: print():不換行輸出 println():換行輸出 都是把引數轉換成字串再輸出!!!
如:以printin(int value)為例:

2.System.out的本質
/* * System.out 實際上就是一個位元組列印流!!! * */ public class PrintStreamDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //相當於獲取了控制檯的引用! PrintStream ps = System.out; ps.println("abc"); ps.println(300); ps.close(); } }
五、字元列印流
PrintWriter: 構造方法: PrintWriter(File file): PrintWriter(String name): PrintWriter(OutputStream out): PrintWriter(OutputStream out,boolean autoFlush): PrintWriter(Writer out): PrintWriter(Writer out,boolean autoFlush):
