Java集合---LinkedList(3)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-03
用途與特點
可用於儲存有序資料,底層使用連結串列形式進行資料儲存。
該集合理論上只要記憶體可以存放資料,就可以一直新增,是無限擴容的。
實現演算法
底層使用Node的自定義物件進行儲存,該物件中包含當前儲存的數item、上一個節點prev、和下一個節點next 這三個屬性來實現。但該連結串列是非環形,第一個first的prev為null,最後一個last的next為null,這樣就形成了一下非閉環手拉手的效果。
LinkedList有3個主要屬性size、first、last。
新增
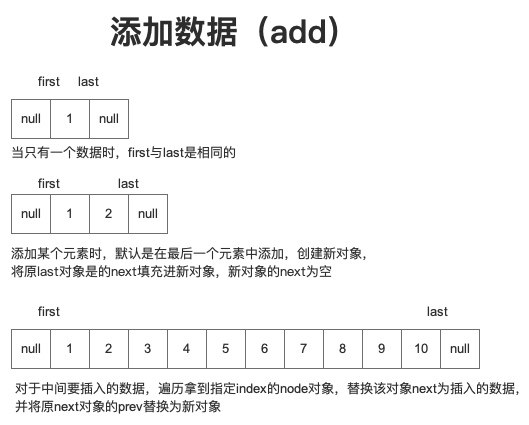
新增與刪除的操作邏輯基本相同,不再贅述。
/** * Links e as first element. */ private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; else f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; } /** * Links e as last element. */ void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } /** * Inserts element e before non-null Node succ. */ void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
查詢

/** * Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index. */ Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //根據傳入index大小,判斷從連結串列的開始搜尋,還是結尾搜尋 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
擴容機制
擴容時機:每次新增、刪除都在擴容
是否執行緒安全,為什麼?
非執行緒安全,因為在原始碼中未對資料的新增、刪除、讀取等做鎖操作
根據jdk1.8版本原始碼解讀
