Android 6.0撥號介面響應工程碼流程
背景
最近看到一個需要在撥號介面輸入工程碼,彈出指定介面的功能。類似輸入”*#06#”彈出手機IMEI號,當然根據具體需求可以彈出隱藏在手機裡面不針對終端使用者使用的功能。下面就具體分析一下該功能的流程。
具體分析
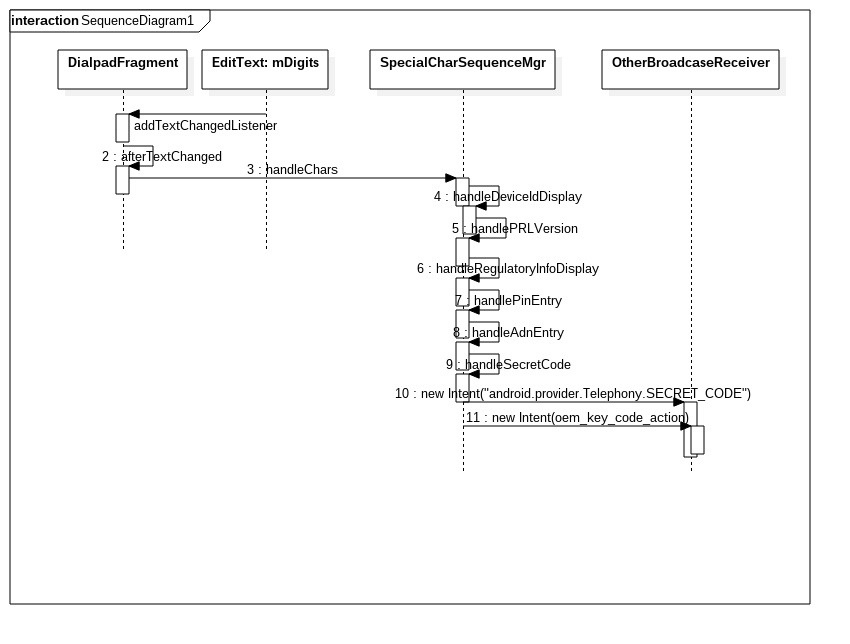
在6.0中,撥號介面的顯示和響應邏輯在DialpadFragment中。這個介面有一個TextEdit物件mDigits,裡面容納我們撥號的時候,輸入的號碼。
這個介面在初始化這個mDigits的時候就在上面添加了一個監聽字元變化的監聽器:
mDigits.addTextChangedListener(this);這個監聽器是一個TextWatcher型別的物件,當你輸入字元之後,會觸發下面的響應函式:
public void afterTextChanged(Editable input) {
// When DTMF dialpad buttons are being pressed, we delay SpecialCharSequenceMgr sequence,
// since some of SpecialCharSequenceMgr's behavior is too abrupt for the "touch-down"
// behavior.
if (!mDigitsFilledByIntent && SpecialCharSequenceMgr.handleChars(getActivity(), input.toString(), mDigits)) {
// A special sequence was entered, clear the digits 從而觸發SpecialCharSequenceMgr的靜態成員函式handleChars。
public static boolean handleChars(Context context, String input, EditText textField) {
//get rid of the separators so that the string gets parsed correctly
String dialString = PhoneNumberUtils.stripSeparators(input);
if 注意看if裡面的這些函式,可以看到一些是處理”*#06#”之類硬編碼進程式碼裡面的工程碼。如果自己要自定義的話,那麼就會呼叫最後一個函式handleSecretCode。在這個函式裡面,邏輯就很清晰了。
/**
* Handles secret codes to launch arbitrary activities in the form of *#*#<code>#*#*.
* If a secret code is encountered an Intent is started with the android_secret_code://<code>
* URI.
*
* @param context the context to use
* @param input the text to check for a secret code in
* @return true if a secret code was encountered
*/
static boolean handleSecretCode(Context context, String input) {
// Secret codes are in the form *#*#<code>#*#*
int len = input.length();
if (len > 8 && input.startsWith("*#*#") && input.endsWith("#*#*")) {
final Intent intent = new Intent(SECRET_CODE_ACTION, Uri.parse("android_secret_code://" + input.substring(4, len - 4)));
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
return true;
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(context.getString(R.string.oem_key_code_action))) {
if (len > 10 && !input.startsWith("*#*#")
&& input.startsWith("*#") && input.endsWith("#")) {
Intent intent = new Intent(context.getString(R.string.oem_key_code_action));
intent.putExtra(context.getString(R.string.oem_code), input);
context.sendBroadcast(intent);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
工程碼是“*#*#5567#*#*”或者“*#44565#”的形式。都是通過傳送廣播的形式,將不同的action傳送出去。第一種傳送的Intent是:
new Intent("android.provider.Telephony.SECRET_CODE", Uri.parse("android_secret_code://5567"));注意,這個Uri裡面解析出來,scheme是“android_secret_code”,host就是5567了。這個對應到一個BroadcastReceiver的data元素的內容。具體請搜尋瞭解Intent-filter匹配規則。
第二種傳送的Intent是:
//oem_key_code_action在xml中定義,在qualcomm中是為空的。oem_code也是為空的。所以如果各位需要自定義oem相關的內容,最好在給這兩個賦值,並且在響應的activity中新增對應的內容。
new Intent("oem_key_code_action").putExtra("oem_code", input);
針對第一種情況,在Packages/apps/下面搜尋這個action,會發現在Email模組裡面的AndroidManifest.xml中有對這個action和data的響應:
<receiver
android:name=".service.EmailBroadcastReceiver"
android:enabled="true" android:permission="com.android.email.permission.ACCESS_PROVIDER">
<!-- To handle secret code to activate the debug screen. -->
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.provider.Telephony.SECRET_CODE" />
<data android:scheme="android_secret_code" android:host="36245" />
</intent-filter>
</receiver>注意,這個對應上了action,以及對應的data。檢視一下這個Receiver:
//EmailBroadcastReceiver.java
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
EmailBroadcastProcessorService.processBroadcastIntent(context, intent)
}
當然你也可以在這個onReceiver裡面啟動一個activity,取決於你的實際需求。通過實際在撥號介面”*#*#36245#*#*”確實彈出了Email模組的設定介面。
整體UML圖如下
圖一 工程碼響應流程
應用
如果是自己需要在專案中使用,只需要在對應模組的AndroidManifest中宣告一個BroadcastReceiver,來響應指定action(注意,針對第一種情況和第二種情況的action不一樣。對於第二種情況,需要自己宣告對應的”oem_key_code_action”和”oem_code”)和Data。具體參考Email模組的AndroidManifest檔案。然後在這個BroadcastReceiver裡面的onReceive函式裡面startActivity,啟動你想要啟動的介面即可。