Django之Form元件與驗證規則
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-06
1、python2和python3中的區別
對於python2內建的字串型別有str和unicode
比如:"abc"是字串,u"你好"是unicode
字串(utf-8/gbk編碼之後值) unicode
對於python3內建的字串型別有bytes和unicode
bytes(utf-8/gbk編碼之後值) 字串(unicode)
python3 中的bytes,就是python2中的字串
python2 中的字串,就是python3中的unicode
2、資料來源無法時時更新,有兩種方法
方式一:重構構造方法(推薦)
方法一:重構構造方法(推薦)
class ClassesForm(Form):
name = fields.CharField(
required=True, # 必填欄位
error_messages={"required": "姓名不能為空!!"}, # 顯示中文錯誤提示
widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={"placeholder": "姓名", "class": "form-control"}), # 自動生成input框
)
# 如果直接定義成classteacher_id,,_id 的形式,這樣你新增資料的時候不會時時更新,所以在下面定義一個重寫的方法
方式二:
方法二:ModelChoiceField(不推薦),queryset
from django.forms.models import ModelChoiceField #先匯入
class ClassForm(Form):
caption = fields.CharField(error_messages={'required':'班級名稱不能為空'})
# headmaster = fields.ChoiceField(choices=[(1,'娜娜',)])
headmaster_id = ModelChoiceField(queryset=models.UserInfo.objects.filter(ut_id=2))
3、Form基本使用
類
欄位
is_valid()
cleaned_data
errors
欄位引數:
max_length
min_length
validators = [RegexValidators("xxx")]
鉤子函式
clean_欄位名
注意:
必須有返回值
只能拿自己當前欄位值
raise ValidationError("xxx")
下拉框資料來源時時更新
1、重寫init方法
先執行父類構造方法
self.fields["xx"].choices = xxxxx
2、ModelChoiceField
4、使用者登入
- form的欄位可以定義正則表示式
password = fields.CharField(
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=18,
error_messages={
'required': '密碼不能為空',
'min_length': '密碼長度不能小於3',
'max_length': '密碼長度不能大於18',
'invalid': '密碼格式錯誤',
},
validators=[RegexValidator('\d+','只能是數字') ]
)
注意:error_messages的優先順序比validators高
需要匯入的模組
from django.forms import Form
from django.forms import fields
from django.forms import widgets
from django.conf import settings
from django.core.validators import ValidationError
from django.core.validators import RegexValidator
class LoginForm(Form):
username = fields.CharField(
required=True, #必填欄位
min_length=3,
max_length=16,
error_messages={
"required":"使用者名稱不能為空",
"min_length":"長度不能小於3",
"max_length":"長度不能大於16"
},
widget=widgets.TextInput({"placeholder":"username","class":"form-control"})
)
password = fields.CharField(
required=True,
min_length=3,
max_length=16,
error_messages={
"required": "密碼不能為空",
"min_length": "密碼長度不能小於3",
"max_length": "密碼長度不能大於16",
# "invalid":"密碼格式錯誤"
# error_messages的優先順序高,如果寫上"invalid":"密碼格式錯誤"這個就會優先顯示這個錯誤
},
widget=widgets.PasswordInput({"placeholder":"password","class":"form-control"}),
validators=[RegexValidator("\d+","密碼只能是數字")] #可以進行正則匹配提示錯誤
)
def clean_username(self):
user = self.cleaned_data["username"]
is_exits = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count()
if not is_exits:
raise ValidationError("使用者名稱和密碼錯誤")
return user #必須有return
views.py ---------login
def login(request):
if request.method == "GET":
form = LoginForm()
return render(request, "login.html", {"form": form})
else:
form = LoginForm(data=request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
print(form.cleaned_data)
# username = form.cleaned_data["username"]
# password = form.cleaned_data["password"]
# user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=username, password=password).first()
user = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(**form.cleaned_data).first()
if user: #這次是和資料庫裡的資料進行比較
#驗證成功
print(user.username)
request.session[settings.GDP] = {"id":user.id,"username":user.username} #設定session
return redirect("/teacherindex/")
else:
#驗證失敗,就給增加一個錯
form.add_error("password","使用者名稱或密碼不正確")
return render(request, "login.html", {"form": form})
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"form": form})
- 主動向form中新增錯誤資訊
# form.add_error('password','使用者名稱或密碼錯誤')
form.add_error('password',ValidationError('使用者名稱或密碼錯誤'))
這兩個都可以,建議用第二個
5、Form擴充套件(鉤子函式)
如果對username做擴充套件
#先做正則表示式判斷
#然後自定義方法驗證:也就是clean_xx,稱為鉤子函式
def clean_username(self):
#可以寫自己的驗證提示
不像validators只寫正則表示式。在這裡可以隨意寫
user=self.clean_data["username"]
is_esits = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(username=user).count()
if not is_esits:
raise validationError("使用者名稱不存在")
return user #必須有返回值
如果 def clean_username(self): 只能取password欄位的值
如果 def clean_username(self): 只能取username欄位的值
注意:在自己寫鉤子函式的時候,只能拿自己的欄位不能拿別人的
每一種欄位就可以用 正則+自定義正則+自定義鉤子函式
6、中介軟體
1、中介軟體是什麼?
中介軟體顧名思義,是介於request與response處理之間的一道處理過程,相對比較輕量級,並且在全域性上改變django的輸入與輸出。因為改變的是全域性,所以需要謹慎實用,用不好會影響到效能。
2、做過什麼?
使用者登入
日誌記錄
crsf:對所有的post請求做了一個驗證
session
許可權管理
3、
注意:
對於所有請求的批量做處理的時候用中介軟體
單獨對某幾個函式做處理的時候用裝飾器
4、使用步驟:
步驟:
1、、先建一個資料夾,裡面寫一個py檔案
2、、然後開始寫類
1.中介軟體就是一個類,類裡面寫幾個方法
class M1(MiddlewareMixin): 必須繼承
def process_request(self,request): request:請求裡面的所有的東西
print("m1.request_request")
這個方法裡面別輕易返回值,要是有返回值就不再繼續執行後面的了,執行自己的process_response和上邊的response
一般是無返回值的:繼續執行後續的中介軟體和檢視函式
def process_response(self,request,response):
return response
2.在settings中的MIDDLEWARE加上路徑
資料夾名稱.py檔名稱.類名
3.找到繼承的那個類,吧那個類拿過來
一般不要用匯入的方法,不然有時候更新了就沒有這個類了,你就把它繼承的那個類拿過來,
圖示分析過程:
process_reques有返回值:
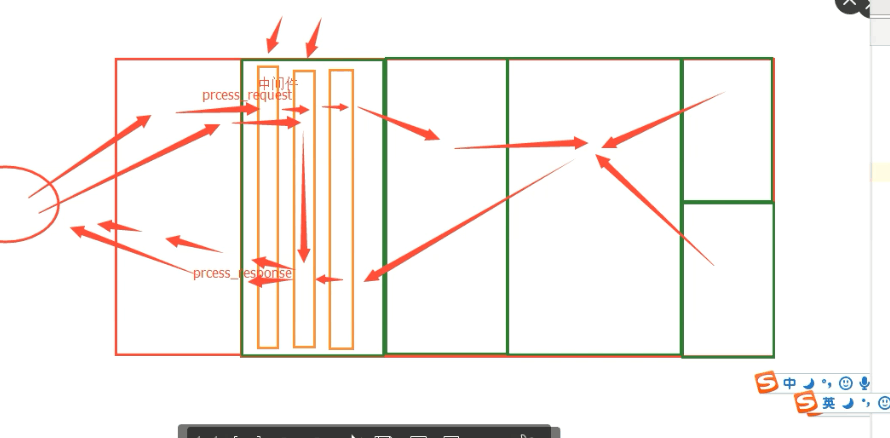
process_reques無返回值:
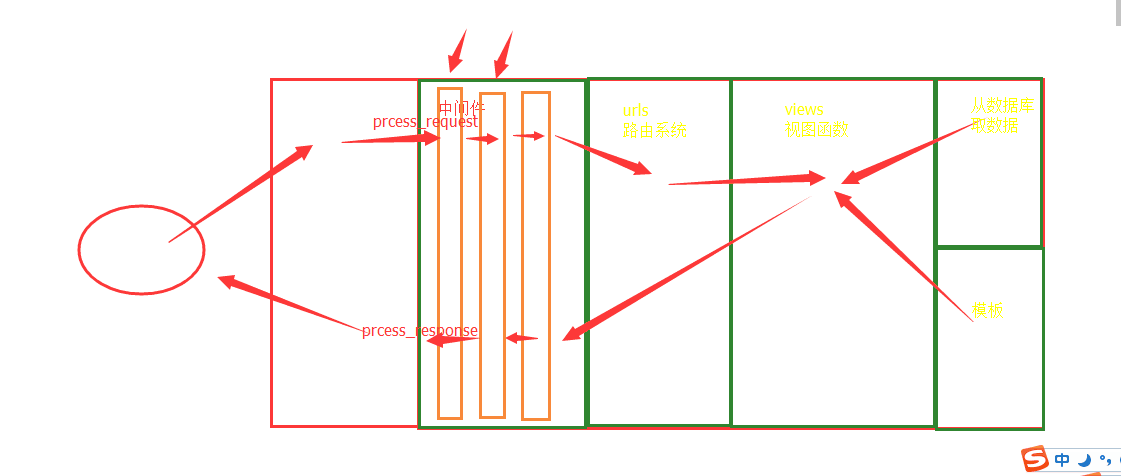
在中介軟體中設定:
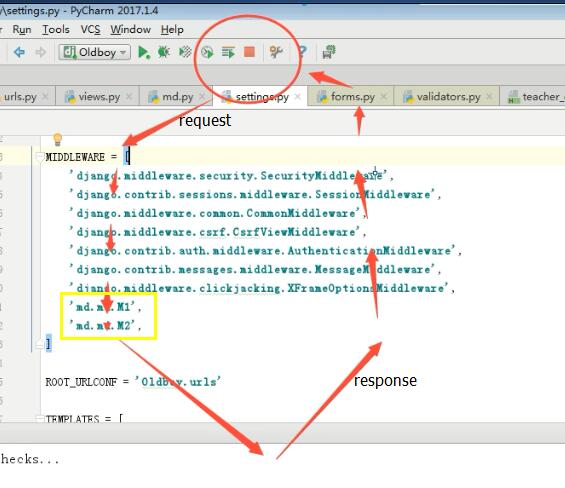
示例:
class MiddlewareMixin(object):
def __init__(self, get_response=None):
self.get_response = get_response
super(MiddlewareMixin, self).__init__()
def __call__(self, request):
response = None
if hasattr(self, 'process_request'):
response = self.process_request(request)
if not response:
response = self.get_response(request)
if hasattr(self, 'process_response'):
response = self.process_response(request, response)
return response
# 至少要有兩個類
class Md1(MiddlewareMixin): #必須繼承
def process_request(self,request):
print("md1===process_request")
l = ["/login/"]
#request.path_info:當前的路徑
if request.path_info in l: #因為login不做驗證,就直接返回none就行了
return None
if not request.session.get(settings.GDP):
return redirect("/login/")
#
# 如果無返回值,就繼續執行後續中介軟體和檢視函式
# 如果有返回值,就執行自己的process_response和上面的response
def process_response(self,request,response):
print("md1====process_response1")
return response #必須有返回值
class Md2(MiddlewareMixin):
def process_request(self,request):
print("md2====process_request2")
def process_response(self,request,response):
print("md2====process_response2")
return response
測試:
def testMD(request):
print("view.test")
return HttpResponse("...")
返回結果:

