特徵提取演算法提取二進位制後面的特徵資料,使用Java流實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-08
幫別人解決一個問題:在搞圖片特徵相似度檢索的東西,特徵提取演算法提取出來的二進位制特徵資料,想要讀取二進位制檔案的每一行固定位之後的資料有啥好的辦法沒?
首先讀取二進位制檔案,考慮到使用位元組流,但是不能解決如何判斷換行的問題,綜上,本人是先使用BufferedReader流讀取一行的資料,然後將拿到的tempString轉化為位元組陣列,使用System.arraycopy方法去擷取位元組陣列,得到想要的資料,然後通過FileOutputStream流將資料寫入到對應的檔案中。
先查詢一些資料:JAVA中讀取檔案內容的方法有很多,比如按位元組讀取檔案內容,按字元讀取檔案內容,按行讀取檔案內容,隨機讀取檔案內容等方法。
import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.io.Reader; public class ReadFromFile { /** * 以位元組為單位讀取檔案,常用於讀二進位制檔案,如圖片、聲音、影像等檔案。 */ public static void readFileByBytes(String fileName) { File file = new File(fileName); InputStream in = null; try { System.out.println("以位元組為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀一個位元組:"); // 一次讀一個位元組 in = new FileInputStream(file); int tempbyte; while ((tempbyte = in.read()) != -1) { System.out.write(tempbyte); } in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return; } try { System.out.println("以位元組為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀多個位元組:"); // 一次讀多個位元組 byte[] tempbytes = new byte[100]; int byteread = 0; in = new FileInputStream(fileName); ReadFromFile.showAvailableBytes(in); // 讀入多個位元組到位元組陣列中,byteread為一次讀入的位元組數 while ((byteread = in.read(tempbytes)) != -1) { System.out.write(tempbytes, 0, byteread); } } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (in != null) { try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } } /** * 以字元為單位讀取檔案,常用於讀文字,數字等型別的檔案 */ public static void readFileByChars(String fileName) { File file = new File(fileName); Reader reader = null; try { System.out.println("以字元為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀一個位元組:"); // 一次讀一個字元 reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(file)); int tempchar; while ((tempchar = reader.read()) != -1) { // 對於windows下,\r\n這兩個字元在一起時,表示一個換行。 // 但如果這兩個字元分開顯示時,會換兩次行。 // 因此,遮蔽掉\r,或者遮蔽\n。否則,將會多出很多空行。 if (((char) tempchar) != '\r') { System.out.print((char) tempchar); } } reader.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { System.out.println("以字元為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀多個位元組:"); // 一次讀多個字元 char[] tempchars = new char[30]; int charread = 0; reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(fileName)); // 讀入多個字元到字元陣列中,charread為一次讀取字元數 while ((charread = reader.read(tempchars)) != -1) { // 同樣遮蔽掉\r不顯示 if ((charread == tempchars.length) && (tempchars[tempchars.length - 1] != '\r')) { System.out.print(tempchars); } else { for (int i = 0; i < charread; i++) { if (tempchars[i] == '\r') { continue; } else { System.out.print(tempchars[i]); } } } } } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } } /** * 以行為單位讀取檔案,常用於讀面向行的格式化檔案 * @throws Exception */ public static void readFileByLines(String fileName) { File file = new File(fileName); BufferedReader reader = null; File fileout = new File("C:\\newword.txt"); FileOutputStream fos = null; try { System.out.println("以行為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀一整行:"); reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file)); fos= new FileOutputStream(fileout); String tempString = null; int line = 1; // 一次讀入一行,直到讀入null為檔案結束 while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) { // 顯示行號 byte[] bytes = tempString.getBytes(); int begin = 3; byte[] subbytes = new byte[bytes.length-1]; System.arraycopy(bytes,begin , subbytes, 0, bytes.length-begin); System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + subbytes.toString()); fos.write(subbytes); fos.flush(); // System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + tempString); line++; } reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (reader != null) { try { reader.close(); fos.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } } /** * 隨機讀取檔案內容 */ public static void readFileByRandomAccess(String fileName) { RandomAccessFile randomFile = null; try { System.out.println("隨機讀取一段檔案內容:"); // 開啟一個隨機訪問檔案流,按只讀方式 randomFile = new RandomAccessFile(fileName, "r"); // 檔案長度,位元組數 long fileLength = randomFile.length(); // 讀檔案的起始位置 int beginIndex = (fileLength > 4) ? 4 : 0; // 將讀檔案的開始位置移到beginIndex位置。 randomFile.seek(beginIndex); byte[] bytes = new byte[10]; int byteread = 0; // 一次讀10個位元組,如果檔案內容不足10個位元組,則讀剩下的位元組。 // 將一次讀取的位元組數賦給byteread while ((byteread = randomFile.read(bytes)) != -1) { System.out.write(bytes, 0, byteread); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (randomFile != null) { try { randomFile.close(); } catch (IOException e1) { } } } } /** * 顯示輸入流中還剩的位元組數 */ private static void showAvailableBytes(InputStream in) { try { System.out.println("當前位元組輸入流中的位元組數為:" + in.available()); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String fileName = "C:/word.txt"; ReadFromFile.readFileByBytes(fileName); ReadFromFile.readFileByChars(fileName); ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName); ReadFromFile.readFileByRandomAccess(fileName); } }
參考以上資料,寫出:
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileOutputStream; /** * * @ClassName IOTest * @Description * @author rk * @Date 2018年11月21日下午7:03:19 */ public class IOTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { File file = new File("C:\\word.txt"); FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file); File fileout = new File("C:\\newword.txt"); FileOutputStream fos = null; fos= new FileOutputStream(fileout); byte[] d = new byte[3]; fis.read(d, 0, 3); byte[] b = new byte[(int) (file.length()-3)]; fis.read(b); fos.write(b); fos.flush(); fis.close(); fos.close(); } }
最終版:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
*
* @ClassName ReadFileByLines
* @Description
* @author rk
* @Date 2018年11月21日下午8:20:23
*/
public class ReadFileByLines {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String fileName = "C:/word.txt";
File outFileName = new File("C:\\newword.txt");
ReadFromFile.readFileByLines(fileName);
}
public static void readFileByLines(String fileName, String outFileName) {
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
File outFile = new File(outFileName);
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
System.out.println("以行為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀一整行:");
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
fos = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
String tempString = null;
int line = 1;
// 一次讀入一行,直到讀入null為檔案結束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 顯示行號
byte[] bytes = (tempString+"\r\n").getBytes();
int begin = 3;
byte[] subbytes = new byte[bytes.length - begin];
System.arraycopy(bytes, begin, subbytes, 0, bytes.length - begin);
System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + Arrays.toString(subbytes));
fos.write(subbytes);
fos.flush();
// System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + tempString);
line++;
}
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
}
}
}
}
}
最終實現:
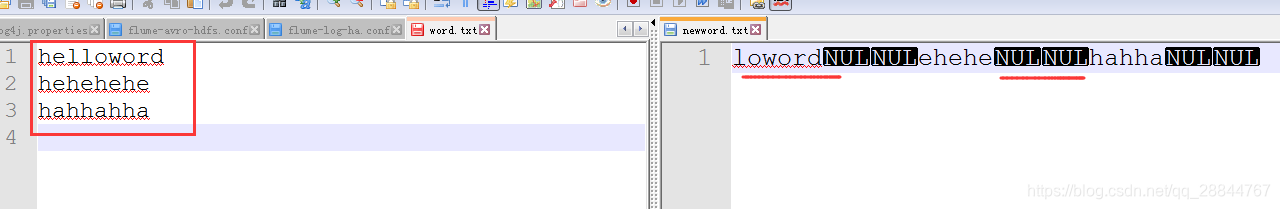
問題:生成了一個NUL的不知道的字元,換行符沒有了
解決:發現是最後讀取為一行後要加"\r\n",擷取位元組陣列的長度是總長度-開始擷取的位置長度
問題是解決了,有待優化!(在查詢資料中發現有CharArrayReader類,應該也可以實現,不過要考慮換行位置的問題 )
以上解決方法是基於Java編寫的,個人感覺有Python和C應該可以更好的實現,Python中應該有一些更方便的方法,C裡面使用指標,應該可以輕鬆實現。不過整體思路應該是一樣的。
版本一:讀取一個目錄下的所有的檔案,然後擷取每一行欄位後面的位元組,最後寫入到一個指定檔案
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 遞迴查詢一個資料夾
* @ClassName Recursion
* @Description
* @author rk
* @Date 2018年11月26日上午10:56:31
*/
public class RecursionTest {
public static FileOutputStream fos = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
fos = connection("C:\\out\\result\\result.txt");
List<File> files = recursion("C:\\out\\face_data");
for(File file : files) {
readFileByLines(file.toString(),114);
}
close(fos);
}
// 儲存指定資料夾的所有的檔案路徑
public static List<File> listFiles = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 遞迴查詢出該路徑下所有檔案的路徑
* @param strPath
* @return
*/
public static List<File> recursion(String strPath) {
File dir = new File(strPath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
if(files[i].isDirectory()) {
recursion(files[i].getAbsolutePath());
}else {
// System.out.println(files[i].toString());
listFiles.add(files[i]);
}
}
}
return listFiles;
}
/**
* 將指定的檔案先按照開始index擷取,後輸出到fos檔案中
* @param fileName 輸入檔名
* @param index 開始擷取的位置
*/
public static void readFileByLines(String fileName,int index) {
File file = new File(fileName);
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
System.out.println("以行為單位讀取檔案內容,一次讀一整行:");
reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
String tempString = null;
int line = 1;
// 一次讀入一行,直到讀入null為檔案結束
while ((tempString = reader.readLine()) != null) {
// 顯示行號
line++;
// 新增\r\n進行換行
byte[] bytes = (tempString+"\r\n").getBytes();
byte[] subbytes = null;
/**
* 判斷擷取長度是否小於位元組陣列長度,如果小於,正常處理
* 如果大於,跳出迴圈,進行下一行讀取
*/
if(bytes.length >= index) {
subbytes = new byte[bytes.length - index];
// 陣列的copy
System.arraycopy(bytes, index, subbytes, 0, bytes.length - index);
}else {
System.out.println("在"+fileName+"中的第"+line+"行,長度小於擷取的長度");
continue;
}
// 列印到控制檯測試
System.out.println("line " + line + ": " + Arrays.toString(subbytes));
// 寫入指定位置開始的檔案內容
fos.write(subbytes);
// 寫入整個檔案內容
// fos.write(bytes);
// 重新整理檔案內容
fos.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 獲取一個輸出流的連線
* @return
*/
public static FileOutputStream connection(String outFileName) {
File outFile = new File(outFileName);
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return fos;
}
/**
* 關閉一個輸出流 fos
* @param fos
*/
public static void close(FileOutputStream fos) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
版本二:檔案是二進位制檔案,沒有換行,所以要求是每616byte一條資料,擷取104byte後面的512byte資料。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 遞迴查詢一個資料夾,檔案是二進位制檔案,沒有換行,
* 所以要求是每626byte一條資料,擷取114byte後面的512byte資料。
* @ClassName Recursion
* @Description
* @author rk
* @Date 2018年11月26日上午10:56:31
*/
public class RecursionByteTest {
public static FileOutputStream fos = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
//獲取輸出流
fos = connection("C:\\out\\result\\human");
//獲取一個目錄下的所有檔案
List<File> files = recursion("C:\\out\\human_data");
for(File file : files) {
//每個檔案取每一條資料切分,寫入到fos
readFileByBuffer(file.toString(),104,616);
}
//關閉輸出流
close(fos);
}
// 儲存指定資料夾的所有的檔案路徑
public static List<File> listFiles = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* 遞迴查詢出該路徑下所有檔案的路徑
* @param strPath
* @return
*/
public static List<File> recursion(String strPath) {
File dir = new File(strPath);
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < files.length; i++) {
if(files[i].isDirectory()) {
recursion(files[i].getAbsolutePath());
}else {
// System.out.println(files[i].toString());
listFiles.add(files[i]);
}
}
}
return listFiles;
}
// 統計檔案的個數
public static int file = 1;
// 記錄資料條數
public static int line = 1;
/**
* 將指定的檔案選取size的長度為一條資料,再按照開始index擷取,最後輸出到fos檔案中
* @param fileName 輸入檔名
* @param index 開始擷取的位置
* @param size 一條資料的長度
*/
public static void readFileByBuffer(String fileName,int index,int size) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
try {
// 顯示第幾個檔案
System.out.println("第"+(file++)+"個檔案-------");
fis = new FileInputStream(fileName);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis,size);
byte[] bytes = new byte[size];
byte[] subbytes = new byte[bytes.length - index];
while(bis.read(bytes) != -1) {
// 顯示條數
System.out.println("正在寫入--第"+(line++)+"條資料");
// 判斷最後一條資料是否是完整的一條資料
if(isNull(bytes)) {
System.out.println("寫入--第"+(line-1)+"條資料不完整");
}else {
// 陣列的copy
System.arraycopy(bytes, index, subbytes, 0, bytes.length - index);
// 寫入指定位置開始的檔案內容
fos.write(subbytes);
// 重新整理檔案內容
fos.flush();
}
// 重置,更新下一條資料
bytes = new byte[size];
}
/** //直接使用流去訪問
byte[] bytes1 = new byte[size];
byte[] subbytes1 = new byte[bytes1.length - index];
while(fis.read(bytes1) != -1) {
System.arraycopy(bytes1, index, subbytes1, 0, bytes1.length - index);
fos.write(subbytes1);
fos.flush();
}*/
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
bis.close();
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 判斷最後一個位元組陣列中是否有空,即不完整的資料
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
public static boolean isNull(byte[] bytes) {
Boolean bool = null;
for(byte b : bytes) {
if(b == 0) {
bool = true;
}else {
bool = false;
}
}
return bool;
}
/**
* 獲取一個輸出流的連線
* @return
*/
public static FileOutputStream connection(String outFileName) {
File outFile = new File(outFileName);
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return fos;
}
/**
* 關閉一個輸出流 fos
* @param fos
*/
public static void close(FileOutputStream fos) {
try {
fos.close();
System.out.println("寫入完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
需要注意的是:如果檔案最後一條資料是不完整的,將不會寫入。此程式碼要求是嚴格的資料結構,有不完整的將有錯誤提示。
