Android自定義Scrollview
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-08
效果:

主要的幾個知識點有 Scroller 、VelocityTracker
主要操作View裡面的幾個方法有 onMeasure、onTouchEvent 、computeScroll 、scrollTo() 、scrollBy()
Scroller
是一個專門用於處理滾動效果的工具類,直接呼叫ScrollTo()或者ScrollBy()的方式來移動的話是瞬間完成,使用者體驗感覺不是很好,然後使用Scroller就可以有個一個種平滑的效果
使用的時候也可傳入自定義的插值器,常用的插值器有
AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator 在動畫開始與介紹的地方速率改變比較慢,在中間的時候加速 AccelerateInterpolator 在動畫開始的地方速率改變比較慢,然後開始加速 AnticipateInterpolator 開始的時候向後然後向前甩 AnticipateOvershootInterpolator 開始的時候向後然後向前甩一定值後返回最後的值 BounceInterpolator 動畫結束的時候彈起 CycleInterpolator 動畫迴圈播放特定的次數,速率改變沿著正弦曲線 DecelerateInterpolator 在動畫開始的地方快然後慢 LinearInterpolator 以常量速率改變 OvershootInterpolator 向前甩一定值後再回到原來位置(快速完成動畫,超出再回到結束樣式)
系統預設是 ViscousFluidInterpolator
用法:
Scroller mScroller = new Scroller(context, new OvershootInterpolator());相應方法解釋: mScroller.getCurrX() //獲取mScroller當前水平滾動的位置 mScroller.getCurrY() //獲取mScroller當前豎直滾動的位置 mScroller.forceFinished(true); //停止一切滑動 mScroller.computeScrollOffset()//判斷是否還在滑動中, true滑動中 ,false滑動完成 mScroller.startScroll //設定滑動 ,執行這個方法,之後執行invalidate()才會觸發View裡面的computeScroll方法的回撥的
/** *開始滾動只要提供一個開始位置和結束位置,滾動將使用預設值為250毫秒的持續時間。 * * @param startX Starting horizontal scroll offset in pixels. Positive * numbers will scroll the content to the left. * @param startY Starting vertical scroll offset in pixels. Positive numbers * will scroll the content up. * @param dx Horizontal distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the * content to the left. * @param dy Vertical distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the * content up. */ public void startScroll(int startX, int startY, int dx, int dy) { }
感覺有點不好理解,要先知道,滑動的開始都是左上角(0,0),最開始時的狀態也就是剛剛說的(0,0),向下滑動getScrollY()的值是負數,向上滑動是正數
mScroller.fling() //慣性滑動的,需要配合VelocityTracker.getYVelocity();來獲取初速度
/**
* fling 方法引數註解
*
* startX 滾動起始點X座標
* startY 滾動起始點Y座標
* velocityX 當滑動螢幕時X方向初速度,以每秒畫素數計算
* velocityY 當滑動螢幕時Y方向初速度,以每秒畫素數計算
* minX X方向的最小值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* maxX X方向的最大值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* minY Y方向的最小值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* maxY Y方向的最大值,scroller不會滾過此點。
*/
public void fling(int startX, int startY, int velocityX, int velocityY,
int minX, int maxX, int minY, int maxY) {
}用法:
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaxVelocity);
float yVelocity = mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(pointerId);
mScroller.fling(0, getScrollY(), 0, (int) -yVelocity * 2, 0, 0, 0, measuredHeight - height);
VelocityTracker
追蹤觸控事件速率,實現flinging和其他手勢的幫助類
- 當開始追蹤的時候,使用obtain來獲取VelocityTracker類的例項
- 把接收到的MotionEvent放入到addMovement(android.view.MotionEvent)中
- 當要確定速度時呼叫computeCurrentVelocity(int),使用getXVelocity(int)和getYVelocity(int)來檢測每個觸控點id的速率
onMeasure
主要用於測量控制元件的大小,剛開始直接用getMeasuredHeight()獲取到的高度,其實這個是當前內容可見區域高度,全部內容的滾動長度需要計算的,如下,計算好所有子控制元件的高度之後需要呼叫setMeasuredDimension更改高度
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//測量子控制元件的大小
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
measuredHeight += (childView.getMeasuredHeight() + layoutParams.bottomMargin + layoutParams.topMargin);
}
//呼叫此方法 重新更改高度
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasuredWidth(), measuredHeight);
computeScroll
用scollTo/scollBy/startScroll方法來進行滑動時,都需要執行invalidate()才會觸發其的回撥,從而才會看到效果
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
invalidate();
}
}
下面是全部程式碼
public class ScrollerViewLayout extends LinearLayout {
private int measuredHeight;//全部item高度
private int height; //可見內容高度
private Scroller mScroller;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
private float mMaxVelocity;
public ScrollerViewLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null, 0);
}
public ScrollerViewLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public ScrollerViewLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
setOrientation(VERTICAL);
mScroller = new Scroller(context, new OvershootInterpolator());
ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(getContext());
mMaxVelocity = vc.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
measuredHeight = 0;
//得到控制元件原始顯示高度
height = getMeasuredHeight();
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
//測量子控制元件的大小
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
measuredHeight += (childView.getMeasuredHeight() + layoutParams.bottomMargin + layoutParams.topMargin);
}
//呼叫此方法 重新更改高度
setMeasuredDimension(getMeasuredWidth(), measuredHeight);
}
private float downY;
private int pointerId;
private boolean isSilde = false;
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
handlerScroll(event);
return true;
}
/**
* 處理滾動事件
* @param event
*/
private void handlerScroll(MotionEvent event) {
float y = event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
pointerId = event.getPointerId(0);
//停止一切滾動
mScroller.forceFinished(true);
mVelocityTracker.clear();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
downY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event);
int move = (int) (downY - y);
if (isSilde || move == 0) {
return;
}
//向下滑動
if (move < 0) {
scrollBy(0, move);
downY = y;
}
//向上滑動
else if (move > 0) {
scrollBy(0, move);
downY = y;
}
Log.e("kawa", ">>>>move:" + move
+ ">>>downY:" + downY
+ ">>>y:" + y
+ ">>>height:" + height
+ ">>>measuredHeight:" + measuredHeight
+ ">>>getScrollY:" + getScrollY());
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
if ((measuredHeight - height) < getScrollY() || getScrollY() < 0) {
scrollReset();
} else {
scrollFling();
}
break;
}
}
@Override //每次執行draw都會執行,獲取當前的滾動位置進行重繪製
public void computeScroll() {
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
isSilde = true;
scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(), mScroller.getCurrY());
invalidate();
} else {
isSilde = false;
}
}
/**
* 超出頂部/底部的進行復位
*/
private void scrollReset() {
int scrollY = getScrollY();
if (scrollY < 0) {
int startY = scrollY;
int endY = -scrollY;
mScroller.startScroll(0, startY, 0, endY);
invalidate();
} else {
//向上滑動超出底部界限時才進行復位
if ((measuredHeight - height) < getScrollY()) {
int startY = scrollY;
int endY = -(scrollY - (measuredHeight - height));
mScroller.startScroll(0, startY, 0, endY);
invalidate();
}
}
}
/**
* 慣性滾動
*/
private void scrollFling() {
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaxVelocity);
float yVelocity = mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(pointerId);
/**
* fling 方法引數註解
*
* startX 滾動起始點X座標
* startY 滾動起始點Y座標
* velocityX 當滑動螢幕時X方向初速度,以每秒畫素數計算
* velocityY 當滑動螢幕時Y方向初速度,以每秒畫素數計算
* minX X方向的最小值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* maxX X方向的最大值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* minY Y方向的最小值,scroller不會滾過此點。
* maxY Y方向的最大值,scroller不會滾過此點。
*/
mScroller.fling(0, getScrollY(), 0, (int) -yVelocity * 2, 0, 0, 0, measuredHeight - height);
invalidate();
}
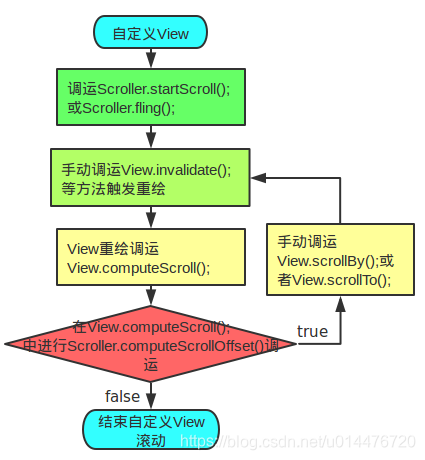
}這裡有張圖可以更好的理解使用Scroller (圖來源網路)