HashMap工作原理和擴容機制
1. HashMap工作原理
HashMap作為優秀的Java集合框架中的一個重要的成員,在很多程式設計場景下為我們所用。HashMap作為資料結構散列表的一種實現,就其工作原理來講單獨列出一篇部落格來講都是不過分的。由於本文主要是簡單總結其擴容機制,因此對於HashMap的實現原理僅做簡單的概述。
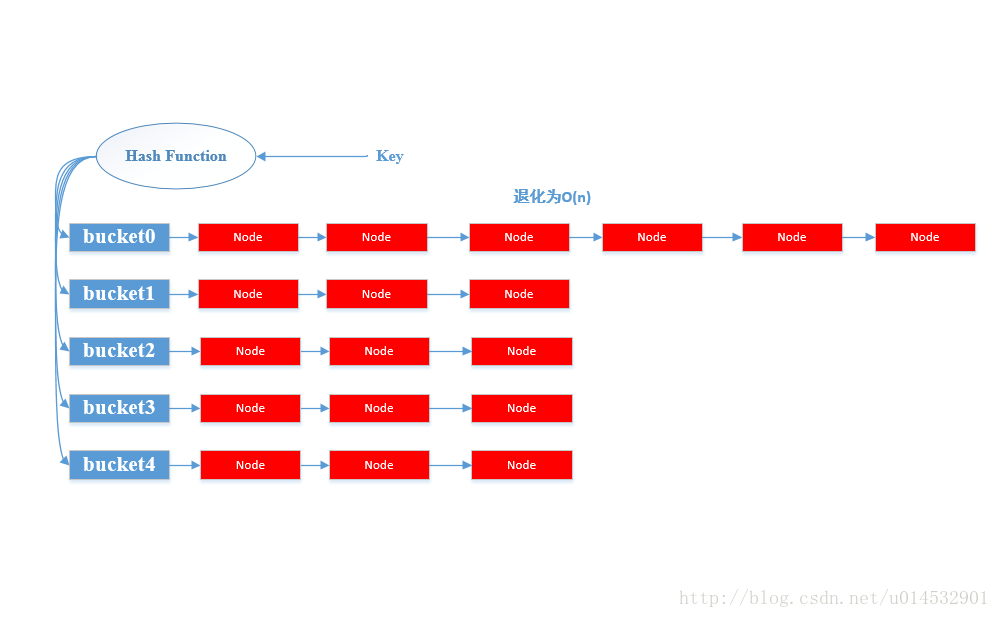
HashMap內部實現是一個桶陣列,每個桶中存放著一個單鏈表的頭結點。其中每個結點儲存的是一個鍵值對整體(Entry),HashMap採用拉鍊法解決雜湊衝突(關於雜湊衝突後面會介紹)。
由於Java8對HashMap的某些地方進行了優化,以下的總結和原始碼分析都是基於Java7。
示意圖如下:
HashMap提供兩個重要的基本操作,put(K, V)和get(K)。
- 當呼叫
put操作時,HashMap計算鍵值K的雜湊值,然後將其對應到HashMap的某一個桶(bucket)上;此時找到以這個桶為頭結點的一個單鏈表,然後順序遍歷該單鏈表找到某個節點的Entry中的Key是等於給定的引數K;若找到,則將其的old V替換為引數指定的V;否則直接在連結串列尾部插入一個新的Entry節點。 - 對於
get(K)操作類似於put操作,HashMap通過計算鍵的雜湊值,先找到對應的桶,然後遍歷桶存放的單鏈表通過比照Entry的鍵來找到對應的值。
以上就是HashMap的基本工作原理,但是問題總是比我們看到的要複雜。由於雜湊是一種壓縮對映,換句話說就是每一個Entry
Entry共用一個桶,拉成一條連結串列的情況,這種情況叫做雜湊衝突。當雜湊衝突產生嚴重的情況,某一個桶後面掛著的連結串列就會特別長,我們知道查詢最怕看見的就是順序查詢,那幾乎就是無腦查詢。
雜湊衝突無法完全避免,因此為了提高HashMap的效能,HashMap不得儘量緩解雜湊衝突以縮短每個桶的外掛連結串列長度。
頻繁產生雜湊衝突最重要的原因就像是要儲存的Entry太多,而桶不夠,這和供不應求的矛盾類似。因此,當HashMap中的儲存的Entry較多的時候,我們就要考慮增加桶的數量,這樣對於後續要儲存的Entry來講,就會大大緩解雜湊衝突。
因此就涉及到HashMap的擴容,上面算是回答了為什麼擴容,那麼什麼時候擴容?擴容多少?怎麼擴容?便是第二部分要總結的了。
2. HashMap擴容
2.1 HashMap的擴容時機
在使用HashMap的過程中,我們經常會遇到這樣一個帶引數的構造方法。
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) ;- 1
- 第一個引數:初始容量,指明初始的桶的個數;相當於桶陣列的大小。
- 第二個引數:裝載因子,是一個0-1之間的係數,根據它來確定需要擴容的閾值,預設值是0.75。
現在開始通過原始碼來尋找擴容的時機:
put(K, V)操作
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);//計算鍵的hash值
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);//通過hash值對應到桶位置
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {//順序遍歷桶外掛的單鏈表
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {//注意這裡的鍵的比較方式== 或者 equals()
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);//遍歷單鏈表完畢,沒有找到與鍵相對的Entry,需要新建一個Entry換句話說就是桶i是一個空桶;
return null;
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
既然找到一個空桶,那麼新建的Entry必然會是這個桶外掛單鏈表的第一個結點。通過addEntry,找到了擴容的時機。
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {//當size大於等於某一個閾值thresholdde時候且該桶並不是一個空桶;
/*這個這樣說明比較好理解:因為size 已經大於等於閾值了,說明Entry數量較多,雜湊衝突嚴重,那麼若該Entry對應的桶不是一個空桶,這個Entry的加入必然會把原來的連結串列拉得更長,因此需要擴容;若對應的桶是一個空桶,那麼此時沒有必要擴容。*/
resize(2 * table.length);//將容量擴容為原來的2倍
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);//擴容後的,該hash值對應的新的桶位置
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);//在指定的桶位置上,建立一個新的Entry
}
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);//連結串列的頭插法插入新建的Entry
size++;//更新size
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
上面有幾個重要成員變數:
- size
- threshold
/**
* The number of key-value mappings contained in this map.
*/
transient int size;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize (capacity * load factor).
* @serial
*/
int threshold;
/**
* The load factor for the hash table.
*
* @serial
*/
final float loadFactor;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
由註釋可以知道:
-
size記錄的是map中包含的Entry的數量
-
而threshold記錄的是需要resize的閾值 且
threshold = loadFactor * capacity -
capacity 其實就是桶的長度
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);- 1
因此現在總結出擴容的時機:
當map中包含的Entry的數量大於等於threshold = loadFactor * capacity的時候,且新建的Entry剛好落在一個非空的桶上,此刻觸發擴容機制,將其容量擴大為2倍。(為什麼2倍,而不是1.5倍,3倍,10倍;解釋見最後的補充)
當size大於等於threshold的時候,並不一定會觸發擴容機制,但是會很可能就觸發擴容機制,只要有一個新建的Entry出現雜湊衝突,則立刻resize。
直到這裡我們回答了什麼時候擴容和擴容多少的問題,那麼下面回答如何擴容的問題。
2.2 HashMap的擴容過程
上面有一個很重要的方法,包含了幾乎屬於的擴容過程,這就是resize()
/**
* Rehashes the contents of this map into a new array with a
* larger capacity. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in this map reaches its threshold.
*
* If current capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY, this method does not
* resize the map, but sets threshold to Integer.MAX_VALUE.
* This has the effect of preventing future calls.
*
* @param newCapacity the new capacity, MUST be a power of two;
* must be greater than current capacity unless current
* capacity is MAXIMUM_CAPACITY (in which case value
* is irrelevant).
*/
void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//最大容量為 1 << 30
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];//新建一個新表
boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing;
useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing;//是否再hash
transfer(newTable, rehash);//完成舊錶到新表的轉移
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
}
/**
* Transfers all entries from current table to newTable.
*/
void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) {
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (Entry<K,V> e : table) {//遍歷同桶陣列中的每一個桶
while(null != e) {//順序遍歷某個桶的外掛連結串列
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;//引用next
if (rehash) {
e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key);
}
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);//找到新表的桶位置;原桶陣列中的某個桶上的同一連結串列中的Entry此刻可能被分散到不同的桶中去了,有效的緩解了雜湊衝突。
e.next = newTable[i];//頭插法插入新表中
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
}
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
對於resize的過程,相對來講是比較簡單清晰易於理解的。舊桶陣列中的某個桶的外掛單鏈表是通過頭插法插入新桶陣列中的,並且原連結串列中的Entry結點並不一定仍然在新桶陣列的同一連結串列。
示意圖如下:

這裡很容易就想到多執行緒情況下,隱約感覺這個transfer方法在多執行緒環境下會亂套。事實上也是這樣的,由於缺乏同步機制,當多個執行緒同時resize的時候,某個執行緒t所持有的引用next(參考上面程式碼next指向原桶陣列中某個桶外掛單鏈表的下一個需要轉移的Entry),可能已經被轉移到了新桶陣列中,那麼最後該執行緒t實際上在對新的桶陣列進行transfer操作。
如果有更多的執行緒出現這種情況,那很可能出現大量執行緒都在對新桶陣列進行transfer,那麼就會出現多個執行緒對同一連結串列無限進行連結串列反轉的操作,極易造成死迴圈,資料丟失等等,因此HashMap不是執行緒安全的,考慮在多執行緒環境下使用併發工具包下的ConcurrentHashMap。
3. 補充
3.1 容量必須是2的冪
在resize(),為什麼容量需要時2倍這樣擴張,而不是1.5倍,3倍,10倍,另外在HashMap中有如下的程式碼:
/**
* The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two.
*/
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity 找到一個大於等於初始容量的且是2的冪的數作為實際容量
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity];
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
通過以上我們知道HashMap的容量必須是2的冪,那麼為什麼要這麼設計呢?答案當然是為了效能。在HashMap通過鍵的雜湊值進行定位桶位置的時候,呼叫了一個indexFor(hash, table.length);方法。
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
可以看到這裡是將雜湊值h與桶陣列的length-1(實際上也是map的容量-1)進行了一個與操作得出了對應的桶的位置,h & (length-1)。
但是為什麼不採用h % length這種計算方式呢?
通過限制length是一個2的冪數,h & (length-1)和h % length結果是一致的。這就是為什麼要限制容量必須是一個2的冪的原因。
舉個簡單的例子說明這兩個操作的結果一致性:
假設有個hashcode是311,對應的二進位制是(1 0011 0111)
length為16,對應的二進位制位(1 0000)
-
%操作:311 = 16*19 + 7;所以結果為7,二進位制位(0111); -
&操作:(1 0011 0111) & (0111) = 0111 = 7, 二進位制位(0111)1 0011 0111 = (1 0011 0000) + (0111) = (1*2^4 + 1* 2^5 + 0*2^6 + 0*2^7 + 1*2^8 ) + 7 = 2^4*(1 + 2 + 0 + 0 + 16) + 7 = 16 * 19 + 7; 和
%操作一致。如果
length是一個2的冪的數,那麼length-1就會變成一個mask, 它會將hashcode低位取出來,hashcode的低位實際就是餘數,和取餘操作相比,與操作會將效能提升很多。
3.2 rehash
通過上面的分析可以看出,不同的鍵的的hashcode僅僅只能通過低位來區分。高位的資訊沒有被充分利用,舉個例子:
假設容量為為16, 二進位制位(10000)。
key1的hashcode為11111 10101,另一個key2的hashcode為00000 10101,很明顯這兩個hashcode不是一樣的,甚至連相似性(例如海明距離)也是很遠的。但是直接進行&操作得出的桶位置是同一個桶,這直接就產生了雜湊衝突。
由於鍵的hashCode是HashMap的使用者來設計的,主要也就是我們這群程式設計師,由於設計一個良好的hashcode分佈,是比較困難的,因此會容易出現分佈質量差的hashcode分佈,極端情況就是:所有的hashCode低位全相等,而高位不相等,這大大加大了雜湊衝突,降低了HashMap的效能。
為了防止這種情況的出現,HashMap它使用一個supplemental hash function對鍵的hashCode再進行了一個supplemental hash ,將最終的hash值作為鍵的hash值來進行桶的位置對映(也就是說JDK團隊在為我們這群程式設計師加效能保險Orz)。這個過程叫做再雜湊(rehash)。
經過一個supplemental hash過程後,能保證海明距離為常數的不同的hashcode有一個雜湊衝突次數上界(裝載因子為0.75的時候,大約是8次)。
參見下段程式碼:
/**
* Retrieve object hash code and applies a supplemental hash function to the
* result hash, which defends against poor quality hash functions. This is
* critical because HashMap uses power-of-two length hash tables, that
* otherwise encounter collisions for hashCodes that do not differ
* in lower bits. Note: Null keys always map to hash 0, thus index 0.
*/
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24