Java-併發-佇列-PriorityBlockingQueue
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-09
Java-併發-佇列-PriorityBlockingQueue
0x01 摘要
PriorityBlockingQueue是優先順序阻塞佇列,本文簡要分析下。
0x02 簡介
PriorityBlockingQueue特點如下:
- 支援優先順序
- 無界阻塞佇列
PriorityBlockingQueue 是無界佇列,不會“隊滿”。實際當到達佇列最大值後(Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8,減8的原因是:陣列作為一個物件,需要一定的記憶體儲存物件頭資訊,物件頭資訊最大佔用記憶體不可超過8位元組。),就拋OOM異常了,因此這點在使用優先佇列的時候需要注意。 - 放入佇列的元素必須實現
Comparable介面的public int compareTo(T o)方法 - 預設情況下
comparator為null。此時會根據元素的compareTo方法來來排序,比如String型別就是按其實現的挨個比較內部char陣列的Ascii碼來排序。採取從小到大順序升序排列,也可以自定義類實現compareTo()方法來指定元素排序規則,需要注意的是不能保證同優先順序元素的順序。 - 執行緒安全
通過一個可重入鎖ReentrantLock來控制入隊和出隊操作 - 入隊出隊不可併發
- 通過二叉堆來實現
預設情況下,父元素的值永遠比任何子元素的值還小。也就是說,最小的值是queue[0] - 不可放入null元素
- 動態擴容策略
0x03 原始碼分析
3.1 類定義和繼承關係
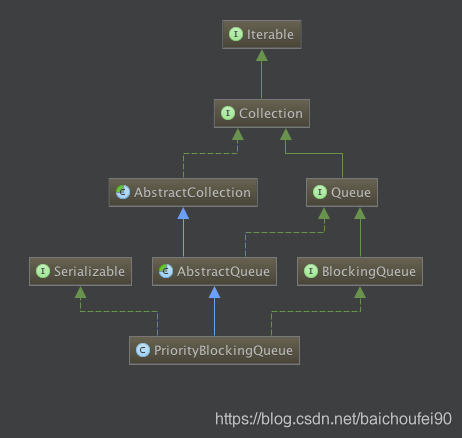
可以看到該類就是阻塞佇列家族的一員。
public class PriorityBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable
3.2 重要成員屬性
// 序列化值
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5595510919245408276L;
// 預設容量是11 3.3 初始化
3.3.1
static {
try {
UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe();
// 獲取PriorityBlockingQueue的class物件例項
Class<?> k = PriorityBlockingQueue.class;
// 獲取allocationSpinLock屬性在記憶體中的偏移量
allocationSpinLockOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset
(k.getDeclaredField("allocationSpinLock"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new Error(e);
}
}
3.3 構造方法
// 預設構造方法, comparator為null
public PriorityBlockingQueue() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, null);
}
// 指定佇列初始容量, comparator為null
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, null);
}
public PriorityBlockingQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 初始化一個全域性可重入鎖
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
this.comparator = comparator;
// 初始化一個指定容量的Object陣列
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
// 用指定容器來構建一個 PriorityBlockingQueue
// 如果目標容器是SortedSet或PriorityQueue,那就會按相同排序來排序
// 否則按元素的compareTo方法排序
public PriorityBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this.lock = new ReentrantLock();
this.notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
boolean heapify = true; // true if not known to be in heap order
boolean screen = true; // true if must screen for nulls
if (c instanceof SortedSet<?>) {
SortedSet<? extends E> ss = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) ss.comparator();
heapify = false;
}
else if (c instanceof PriorityBlockingQueue<?>) {
PriorityBlockingQueue<? extends E> pq =
(PriorityBlockingQueue<? extends E>) c;
this.comparator = (Comparator<? super E>) pq.comparator();
screen = false;
if (pq.getClass() == PriorityBlockingQueue.class) // exact match
heapify = false;
}
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int n = a.length;
// If c.toArray incorrectly doesn't return Object[], copy it.
if (a.getClass() != Object[].class)
a = Arrays.copyOf(a, n, Object[].class);
if (screen && (n == 1 || this.comparator != null)) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (a[i] == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.queue = a;
this.size = n;
if (heapify)
heapify();
}
3.4 放入元素
放入元素主要有offer,add,put三個方法。由於PriorityBlockingQueue是無界佇列,所以add 和 put直接呼叫的 offer 方法。
3.2.1 offer
/**
* 插入元素到佇列
* 該元素無界,所以不會返回false
*
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws ClassCastException if the specified element cannot be compared
* with elements currently in the priority queue according to the
* priority queue's ordering
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 嘗試獲取鎖
lock.lock();
int n, cap;
Object[] array;
// n存當前元素個數,cap存物件陣列長度
while ((n = size) >= (cap = (array = queue).length))
// 當元素個數大於等於物件陣列長度就進行擴容
tryGrow(array, cap);
try {
Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null)
// Comparator為空時採用元素實現的compareTo方法排序後,插入元素
siftUpComparable(n, e, array);
else
// 否則採用指定的Comparator的compareTo方法排序後,插入元素
siftUpUsingComparator(n, e, array, cmp);
// 插入成功後元素個數加1
size = n + 1;
// 將wait在notEmpty condition上的執行緒喚醒(就是那些嘗試獲取元素但無元素可用的執行緒)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
// 最後釋放鎖
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
3.5 獲取元素
3.5.1 dequeue-出隊
/**
* 主要的思想就是將根元素即優先順序數值最小,優先順序最高的那個根元素返回,
* 把尾節點放到原來根節點的位置,然後根據堆規則來調整堆即可
*/
private E dequeue() {
int n = size - 1;
if (n < 0)
// 元素個數已經為0 不能出隊
return null;
else {
Object[] array = queue;
// 最小的根元素
E result = (E) array[0];
// 尾元素
E x = (E) array[n];
array[n] = null;
Comparator<? super E> cmp = comparator;
if (cmp == null)
siftDownComparable(0, x, array, n);
else
siftDownUsingComparator(0, x, array, n, cmp);
// 此時元素出隊,size--
size = n;
return result;
}
}
3.5.2 poll
/**
* 搜尋、返回、刪除佇列中的頭結點
* 當佇列為空時,返回null
*
*/
public E poll() {
// 該方法很簡單,就是先鎖定,然後呼叫dequeue返回頭節點,最後調整堆
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
再看看帶超時時間的poll方法:
/**
* 搜尋、返回、刪除佇列中的頭結點
* 如果佇列為空,就按指定的timeout進行等待可用的元素
*
* @param timeout how long to wait before giving up, in units of
* {@code unit}
* @param unit a {@code TimeUnit} determining how to interpret the
* {@code timeout} parameter
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
*/
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// 將等待時間按單位轉換為納秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 以獨佔可中斷模式獲取鎖
lock.lockInterruptibly();
E result;
try {
// 持續呼叫dequeue元素直到拿到元素或者已經達到指定的超時時間
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null && nanos > 0)
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
} finally {
// 釋放鎖
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
3.5.3 take
/**
* 搜尋、返回、刪除佇列中的頭結點
* 如果無元素可用時就等待
*
* @return 佇列中頭結點
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting
*/
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
E result;
try {
while ( (result = dequeue()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return result;
}
3.5.4 peek
/**
* 搜尋、返回佇列中的頭結點,但不刪除他
* 當佇列為空時,返回null
*
*/
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (size == 0) ? null : (E) queue[0];
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
3.6 擴容
/**
* Tries to grow array to accommodate at least one more element
* (but normally expand by about 50%), giving up (allowing retry)
* on contention (which we expect to be rare). Call only while
* holding lock.
*
* @param array 元素陣列
* @param oldCap 陣列長度
*/
private void tryGrow(Object[] array, int oldCap) {
// 先釋放鎖再擴容完成後再獲取鎖
lock.unlock();
Object[] newArray = null;
// 如果需要自旋,且成功以CAS的方式將allocationSpinLock設為了1
// 這裡需要這麼操作的原因是有可能多個執行緒在進行tryGrow
if (allocationSpinLock == 0 &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, allocationSpinLockOffset,
0, 1)) {
try {
// 擴容演算法為:
// 元素個數小於64就僅擴容為: oldCap + oldCap + 2 = 2*oldCap + 2
// 大於等於64時:oldCap + oldCap/2 = 3/2*oldCap
// 也就是說小於64時擴容更迅速
int newCap = oldCap + ((oldCap < 64) ?
(oldCap + 2) : // grow faster if small
(oldCap >> 1));
// 如果擴容結果大於MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
// 此時就看看oldCap 只加 1是否超出了限制
int minCap = oldCap + 1;
// 如果超過了限制就丟擲OOM異常
// 這裡minCap<0的意思是已經從最大的服務號正數int值做加法後變為了負數
if (minCap < 0 || minCap > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 否則就只能設為MAX_ARRAY_SIZE
newCap = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
if (newCap > oldCap && queue == array)
// 擴容成功而且queue還是指向原陣列時,就建立一個新陣列
newArray = new Object[newCap];
} finally {
// 自旋鎖由1重置為0
allocationSpinLock = 0;
}
}
if (newArray == null) // back off if another thread is allocating
// newArray為Null說明其他執行緒也在做擴容操作,此時就放棄執行緒CPU許可權,重新競爭CPU
Thread.yield();
// 重新嘗試獲取鎖
lock.lock();
if (newArray != null && queue == array) {
// 此時已經拿到鎖,且newArray是本執行緒擴容的
// 就把 全域性queue引用指向新的queue
queue = newArray;
// 然後把內容也複製到新陣列中,擴容完畢
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, oldCap);
}
}
3.7 輔助方法
3.7.1 siftUpComparable
此方法是用指定的比較器,從下往上找元素應當放的位置,並調整沿途的元素位置
/**
* 插入元素 x 到位置 k ,使用的是元素自帶的比較器
* 與此同時會根據堆的規則調整堆,主要是讓孩子大於父節點的值
*
* To simplify and speed up coercions and comparisons. the
* Comparable and Comparator versions are separated into different
* methods that are otherwise identical. (Similarly for siftDown.)
* These methods are static, with heap state as arguments, to
* simplify use in light of possible comparator exceptions.
*
* @param k 插入的目標位置
* @param x 待插入的元素
* @param array the heap array
*/
private static <T> void siftUpComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array) {
// 獲取元素x實現的比較器
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>) x;
while (k > 0) {
// 得到父節點所在位置, 公式為(k-1)/2
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
// 父節點
Object e = array[parent];
// 比較是否待插入元素x的值大於父節點值,大於就說明符合堆要求
if (key.compareTo((T) e) >= 0)
break;
// 此時說明待插入元素x的值小於父節點值
// 就把父元素下放到當前位置k
array[k] = e;
// 從parent位置繼續往上查詢
k = parent;
}
// 當前元素放到正確的陣列位置即可
array[k] = key;
}
3.7.2 siftUpUsingComparator
此方法是用指定的比較器,從下往上找元素應當放的位置,並調整沿途的元素位置
// 插入元素 x 到位置 k ,使用的是指定的比較器
// 查詢方法其實和上面介紹的siftUpComparable方法相同
private static <T> void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, T x, Object[] array,
Comparator<? super T> cmp) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = array[parent];
if (cmp.compare(x, (T) e) >= 0)
break;
array[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
array[k] = x;
}
3.7.3 siftDownComparable
/**
* Inserts item x at position k, maintaining heap invariant by
* demoting x down the tree repeatedly until it is less than or
* equal to its children or is a leaf.
* 將元素x插入到位置k,並按堆的規則來調整堆
*
* @param k 插入元素的目標位置
* @param x 需要插入的元素
* @param array 堆陣列
* @param n 堆大小
*/
private static <T> void siftDownComparable(int k, T x, Object[] array,
int n) {
if (n > 0) {
Comparable<? super T> key = (Comparable<? super T>)x;
int half = n >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
// k節點的左孩子
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = array[child];
// 右孩子下標
int right = child + 1;
// 比較左右孩子較大的,讓c指向較小的孩子,child指向其下標
if (right < n &&
((Comparable<? super T>) c).compareTo((T) array[right]) > 0)
// 此時左孩子大於右孩子的值
// 就讓child指向右孩子下標,c指向右孩子物件,
c = array[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((T) c) <= 0)
// 比較插入元素的指和較小的孩子節點,
// 如果插入元素較小,就說明
