mybatis原始碼-解析配置檔案(三)之配置檔案Configuration解析(超詳細, 值得收藏)
1. 簡介
1.1 系列內容
本系列文章講解的是mybatis解析配置檔案內部的邏輯, 即
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
其背後的邏輯。
1.2 適合物件
1.3 本文內容
Configuration類的講解;parser.parse()將配置解析到Configuration中的過程;
2. 配置檔案
mybatis使用到了配置檔案, 本文中, 不講解 mapper.xml
2.1 mysql.properties
這是儲存資料庫資訊的對應檔案。
mysql.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
mysql.username=root
mysql.password=jim666
2.2 mybatis-config.xml
核心配置檔案, 管理 mybatis 的執行行為。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 配置全域性屬性 --> <properties resource="mysql.properties"> </properties> <settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/> </settings> <typeAliases> <package name="com.homejim.mybatis.entity"/> </typeAliases> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"> <property name="" value=""/> </transactionManager> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${mysql.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${mysql.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${mysql.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${mysql.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <package name="com.homejim.mybatis.mapper"/> </mappers> </configuration>
3. Configuration 類及其解析
Configuration類對應的就是我們的 mybatis-config.xml 配置檔案, 我們配置的資訊經過解析後就會儲存到Configuration的成員變數中。
3.1 解析入口
解析的入口是以下的函式:
public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; }
首先通過parser.evalNode("/configuration")函式解析解析出 configuration節點, 在使用parseConfiguration函式解析獲得旗下各個節點的資訊。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
<!--解析 properties 節點-->
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
<!--解析 settings 節點-->
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
<!--解析 typeAliases 節點-->
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
<!--解析 plugins 節點-->
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
<!--解析 objectFactory 節點-->
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
<!--解析 objectWrapperFactory 節點-->
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
<!--解析 reflectorFactory 節點-->
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
<!--解析 environments 節點, 需要在 objectFactory 和 objectWrapperFactory才能讀取-->
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
<!--解析 databaseIdProvider 節點-->
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
<!--解析 typeHandlers 節點-->
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
<!--解析 mappers 節點-->
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
3.2 常用函式
3.2.1 獲取節點
其實就是使用 DOM 結合 Xpath 的方法獲得各個節點。
public XNode evalNode(String expression) {
return evalNode(document, expression);
}
而後返回相應的 XNode 類物件。
public XNode evalNode(Object root, String expression) {
Node node = (Node) evaluate(expression, root, XPathConstants.NODE);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
return new XNode(this, node, variables);
}
最終呼叫的是xpath.evaluate(expression, root, returnType), 不理解這個過程的可參考之前的文章。
private Object evaluate(String expression, Object root, QName returnType) {
try {
return xpath.evaluate(expression, root, returnType);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error evaluating XPath. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
3.2.2 獲取子節點
public List<XNode> getChildren() {
List<XNode> children = new ArrayList<XNode>();
NodeList nodeList = node.getChildNodes();
if (nodeList != null) {
for (int i = 0, n = nodeList.getLength(); i < n; i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
children.add(new XNode(xpathParser, node, variables));
}
}
}
return children;
}
實際上是呼叫了 DOM 中的 Node 類的 getChildNodes 函式, 並將返回的節點轉換為 XNode , 新增到對應的 List 中返回。
3.2.3 獲取子節點並存到 Properties 物件中
public Properties getChildrenAsProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
for (XNode child : getChildren()) {
String name = child.getStringAttribute("name");
String value = child.getStringAttribute("value");
if (name != null && value != null) {
properties.setProperty(name, value);
}
}
return properties;
}
這些子節點都含有 name 和 value 屬性, 存 name->value 的形式。
3.3 節點相關成員變數及其解析
Configuration中有很多成員變數:
可以分為以下幾種, 按配置的順序:
3.3.1 properties 屬性相關
3.3.1.1 成員變數
protected Properties variables = new Properties();
對應 Properties>類, 可以將相應的配置 .properties 的檔案資訊存放到裡面。
3.3.1.2 對應 XML 節點:<properties>
<properties resource="mysql.properties"> </properties>
3.3.1.3 作用
如 mysql.properties 檔案, 其內容如下:
mysql.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
mysql.username=root
mysql.password=jim666
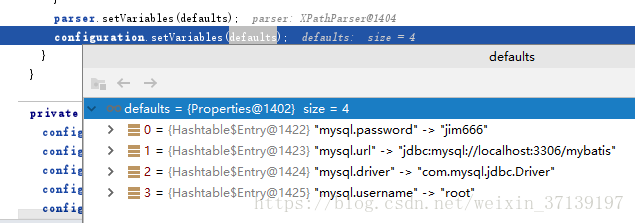
在解析後, 存放在 variables 成員變數中, 是這樣:
這樣做的目的是我們可以將這些屬性在後面的內容中複用:
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${mysql.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${mysql.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${mysql.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${mysql.password}"/>
</dataSource>
3.3.1.4 解析過程
private void propertiesElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 先解析<properties>下的各個子節點, 以name->value的形式記錄到 Properties 物件中
Properties defaults = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 解析 resource 和 url 屬性
String resource = context.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = context.getStringAttribute("url");
// resource 和 url 屬性不能同時不為空, 也就是說只能存在一個
if (resource != null && url != null) {
throw new BuilderException("The properties element cannot specify both a URL and a resource based property file reference. Please specify one or the other.");
}
// 根據 resource 或 url, 將對應的 .properties 檔案載入進來, 並將內容全部存到 Properties 物件中
if (resource != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getResourceAsProperties(resource));
} else if (url != null) {
defaults.putAll(Resources.getUrlAsProperties(url));
}
// 將Configuration 物件中原先的屬性合併進來。
Properties vars = configuration.getVariables();
if (vars != null) {
defaults.putAll(vars);
}
// 兩個含有該成員變數的類物件更新
parser.setVariables(defaults);
configuration.setVariables(defaults);
}
}
幾個要點:
- 先讀取的是 <properties> 下的 <propertie> 屬性;
- <properties> 中, 不能同時存在 resource 和 url 屬性;
- 更新時, 不單單只是更新 configuration, XPathParser 物件也需要更新, 後面用得到。
3.3.2 settings 屬性相關
3.3.2.1 成員變數
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
protected String logPrefix;
protected Class <? extends Log> logImpl;
protected Class <? extends VFS> vfsImpl;
protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION;
protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER;
protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" }));
protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout;
protected Integer defaultFetchSize;
protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE;
protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL;
protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE;
protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false;
protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory();
protected Class<?> configurationFactory;
成員變數名稱和以上配置檔案的 name 屬性一一對應。
3.3.2.2 對應 XML 節點:<settings>
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
...
</settings>
在 XML 檔案中, <settings>節點內其實有很多 <setting> 節點, 但是他們都有預設值, 因此一般情況下, 我們只需要配置一些我們需要改變的配置即可。
一個配置完整的 settings 元素的示例如下:
<settings>
<!--允許在巢狀語句中使用分頁(RowBounds)。如果允許使用則設定為false。-->
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<!--允許在巢狀語句中使用分頁(ResultHandler)。如果允許使用則設定為false。-->
<setting name="safeResultHandlerEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--是否開啟自動駝峰命名規則(camel case)對映,即從經典資料庫列名 A_COLUMN 到經典 Java 屬性名 aColumn 的類似對映。 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<!--當開啟時,任何方法的呼叫都會載入該物件的所有屬性。否則,每個屬性會按需載入(參考lazyLoadTriggerMethods). (true in ≤3.4.1) -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
<!--是否允許單一語句返回多結果集(需要相容驅動)。-->
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--允許 JDBC 支援自動生成主鍵,需要驅動相容。 如果設定為 true 則這個設定強制使用自動生成主鍵,儘管一些驅動不能相容但仍可正常工作(比如 Derby)。-->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<!--使用列標籤代替列名。不同的驅動在這方面會有不同的表現, 具體可參考相關驅動文件或通過測試這兩種不同的模式來觀察所用驅動的結果。-->
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<!--全域性地開啟或關閉配置檔案中的所有對映器已經配置的任何快取。 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!--指定當結果集中值為 null 的時候是否呼叫對映物件的 setter(map 物件時為 put)方法,這對於有 Map.keySet() 依賴或 null 值初始化的時候是有用的。注意基本型別(int、boolean等)是不能設定成 null 的。-->
<setting name="callSettersOnNulls" value="false"/>
<!--允許使用方法簽名中的名稱作為語句引數名稱。 為了使用該特性,你的工程必須採用Java 8編譯,並且加上-parameters選項。(從3.4.1開始)-->
<setting name="useActualParamName" value="true"/>
<!--當返回行的所有列都是空時,MyBatis預設返回null。 當開啟這個設定時,MyBatis會返回一個空例項。 請注意,它也適用於巢狀的結果集 (i.e. collectioin and association)。(從3.4.2開始) -->
<setting name="returnInstanceForEmptyRow" value="false"/>
<!--增加到日誌名稱的字首, 預設沒有-->
<setting name="logPrefix" value=""/>
<!--日誌的實現型別, 預設未指定, 未指定時將自動查詢-->
<setting name="logImpl" value=""/>
<!--指定VFS的實現, 預設未指定-->
<setting name="vfsImpl" value=""/>
<!--預設值為 SESSION,這種情況下會快取一個會話中執行的所有查詢。 若設定值為 STATEMENT,本地會話僅用在語句執行上,對相同 SqlSession 的不同調用將不會共享資料。 -->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<!--當沒有為引數提供特定的 JDBC 型別時,為空值指定 JDBC 型別-->
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<!-- 指定哪個物件的方法觸發一次延遲載入。-->
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
<!--設定超時時間,它決定驅動等待資料庫響應的秒數。-->
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<!--為驅動的結果集獲取數量(fetchSize)設定一個提示值。此引數只可以在查詢設定中被覆蓋。 -->
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100"/>
<!--配置預設的執行器。SIMPLE 就是普通的執行器;REUSE 執行器會重用預處理語句(prepared statements); BATCH 執行器將重用語句並執行批量更新。-->
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<!--指定 MyBatis 應如何自動對映列到欄位或屬性-->
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<!--指定發現自動對映目標未知列(或者未知屬性型別)的行為-->
<setting name="autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior" value="WARNING"/>
<!--延遲載入的全域性開關-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="false"/>
<!--指定 Mybatis 建立具有延遲載入能力的物件所用到的代理工具-->
<setting name="proxyFactory" value="JAVASSIST"/>
<!--指定一個提供Configuration例項的類-->
<setting name="configurationFactory" value=""/>
</settings>
3.3.2.3 作用
settings 是 MyBatis 中極為重要的設定,它們會改變 MyBatis 的執行時行為。
3.3.1.4 解析過程
private Properties settingsAsProperties(XNode context) {
if (context == null) {
return new Properties();
}
// 解析所有的子節點, 並存到 Properties 物件中。
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// Check that all settings are known to the configuration class
// 建立對應的 MetaClass 物件
MetaClass metaConfig = MetaClass.forClass(Configuration.class, localReflectorFactory);
// 檢測 Configuraion 物件中是否定義了相應的 setter 方法, 不定義代表不存在該屬性, 直接拋異常
for (Object key : props.keySet()) {
if (!metaConfig.hasSetter(String.valueOf(key))) {
throw new BuilderException("The setting " + key + " is not known. Make sure you spelled it correctly (case sensitive).");
}
}
return props;
}
3.3.3 typeAliases 相關屬性
3.3.3.1 成員變數
protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry = new TypeAliasRegistry();
3.3.3.2 對應 XML 節點:<typeAliases>
typeAliases, 即類型別名。類型別名是為 Java 型別設定一個短的名字。它只和 XML 配置有關,存在的意義僅在於用來減少類完全限定名的冗餘。
3.3.3.3 作用
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Author" type="domain.blog.Author"/>
</typeAliases>
類似以上配置, 當需要使用domain.blog.Author時, 我們可以用Author來進行代替。
當開啟包掃描之後, 在沒有註解的情況下,會使用 Bean 的首字母小寫的非限定類名來作為它的別名。
3.3.3.4 解析過程
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
// 處理全部的子類
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 處理 <package> 子節點
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
// 獲取配置處的屬性 name , 其對應著包名
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
// 處理 <typeAlias>節點
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
Class<?> clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
// 如果alias沒有配置,則按照約定的方式註冊類
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
// alias 配置了, 則將類註冊到alias
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
3.3.4 plugins 相關屬性
3.3.4.1 成員變數
protected final InterceptorChain interceptorChain = new InterceptorChain();
3.3.4.2 對應 XML 節點:<plugins>
在之前的專案中, 沒有配置相應的plugins, 但可以參考使用 Mybatis-PageHelper 的配置
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<!-- config params as the following -->
<property name="param1" value="value1"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
3.3.4.3 作用
外掛是 MyBatis 提供的擴充套件機制之一,使用者可以通過新增自定義外掛在 SQL 語句執行過程中的某一點進行攔截。
更具體的後面會專門開一章進行講解。
3.3.4.4 解析過程
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 遍歷 <pluagins> 下的所有 <plugin> 節點
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 獲取對應的 <plugin> 中的 interceptor 屬性
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
// 獲取 <plugin> 下的所有 <property> 節點, 並以 name->value 的形式存入 Properties 物件中
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 通過反射生成物件
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
// 設定攔截器的屬性
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
// 將攔截器新增到 Configuration 物件中
configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
3.3.5 objectFactory 相關屬性
3.3.5.1 成員變數
protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory();
3.3.5.2 對應 XML 節點:<objectFactory>
<objectFactory type="org.mybatis.example.ExampleObjectFactory">
<property name="someProperty" value="100"/>
</objectFactory>
3.3.5.3 作用
MyBatis 每次建立結果物件的新例項時,它都會使用一個物件工廠(ObjectFactory)例項來完成。 預設的物件工廠需要做的僅僅是例項化目標類,要麼通過預設構造方法,要麼在引數對映存在的時候通過引數構造方法來例項化。 如果想覆蓋物件工廠的預設行為,則可以通過建立自己的物件工廠來實現。
3.3.5.4 解析過程
private void objectFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 獲取 <objectFactory> 的type屬性
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 獲取 <plugin> 下的所有 <property> 節點, 並以 name->value 的形式存入 Properties 物件中
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 通過反射生成物件
ObjectFactory factory = (ObjectFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
// 設定屬性
factory.setProperties(properties);
// 將 ObjectFactory 物件設定到 Configuration 物件中
configuration.setObjectFactory(factory);
}
}
3.3.6 objectWrapperFactory 相關屬性
3.3.6.1 成員變數
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
3.3.6.2 對應 XML 節點:<objectWrapperFactory>
<objectWrapperFactory type=""/>
3.3.6.3 作用
啟用之後, 可以自己實現駝峰效果。
3.3.6.4 解析過程
private void objectWrapperFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 獲取 <objectWrapperFactory> 的type屬性
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 通過反射生成 ObjectWrapperFactory 物件
ObjectWrapperFactory factory = (ObjectWrapperFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
// 將 ObjectWrapperFactory 物件設定到 Configuration 物件中
configuration.setObjectWrapperFactory(factory);
}
}
3.3.7 reflectorFactory 相關屬性
3.3.7.1 成員變數
protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory();
3.3.7.2 對應 XML 節點:<reflectorFactory>
<reflectorFactory type=""/>
3.3.7.3 作用
可以自己定義反射類
3.3.7.4 解析過程
private void reflectorFactoryElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 獲取 <objectWrapperFactory> 的type屬性
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// 通過反射生成 ReflectorFactory 物件
ReflectorFactory factory = (ReflectorFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
// 將 ReflectorFactory 物件設定到 Configuration 物件中
configuration.setReflectorFactory(factory);
}
}
3.3.8 environments 相關屬性
3.3.8.1 成員變數
protected Environment environment;
Enviroment 中, 含有id, 事務, 資料來源:
public final class Environment {
private final String id;
private final TransactionFactory transactionFactory;
private final DataSource dataSource;
...
}
3.3.8.2 對應 XML 節點:<environments>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC">
<property name="" value=""/>
</transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${mysql.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${mysql.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${mysql.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${mysql.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
Environment主要用於配置資料來源和事務資訊。Mybatis支援多環境設定,可以為開發,測試,生產使用不同的配置。
3.3.8.3 作用
就是設定資料庫連線的環境, 需要配置事務管理器和資料來源來構造相應的物件。
既然environments可以配置多個environment, 那麼為什麼成員變數的型別不是List?
答: 多個環境,每個 SqlSessionFactory 例項只能選擇其一
3.3.8.4 解析過程
private void environmentsElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
// 未指定, 則使用 default 屬性指定的 <environment>
if (environment == null) {
environment = context.getStringAttribute("default");
}
// 遍歷所有的 <environment> 子節點
for (XNode child : context.getChildren()) {
String id = child.getStringAttribute("id");
// 只有 id 與 XMLConfigBuilder 的 environment 匹配上才會進行解析裡面的內容
if (isSpecifiedEnvironment(id)) {
// 建立 TransactionFactory 物件
TransactionFactory txFactory = transactionManagerElement(child.evalNode("transactionManager"));
// 建立 DataSourceFactory 物件, 並以之建立 DataSource 物件
DataSourceFactory dsFactory = dataSourceElement(child.evalNode("dataSource"));
DataSource dataSource = dsFactory.getDataSource();
// 建立 Environment.Builder 物件, 將以上產生的物件對應設定到該物件中
Environment.Builder environmentBuilder = new Environment.Builder(id)
.transactionFactory(txFactory)
.dataSource(dataSource);
// environmentBuilder.build()建立 Environment 物件, 並設定到 Configuration 物件對應的成員變數中
configuration.setEnvironment(environmentBuilder.build());
}
}
}
}
3.3.9 databaseIdProvider 相關屬性
3.3.9.1 成員變數
protected String databaseId;
3.3.9.2 對應 XML 節點:<databaseIdProvider>
<databaseIdProvider type="DB_VENDOR" />
3.3.9.3 作用
MyBatis 可以根據不同的資料庫廠商執行不同的語句,這種多廠商的支援是基於對映語句中的 databaseId 屬性。在後續的 XXXXmapper.xml 檔案中, 可以指定 databaseId。
3.3.9.4 解析過程
private void databaseIdProviderElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
DatabaseIdProvider databaseIdProvider = null;
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
// awful patch to keep backward compatibility
// 為了相容, 更改 type 為 VENDOR 至 DB_VENDOR
if ("VENDOR".equals(type)) {
type = "DB_VENDOR";
}
// 解析對應的配置資訊
Properties properties = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
// 通過反射生成物件
databaseIdProvider = (DatabaseIdProvider) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
// 設定屬性
databaseIdProvider.setProperties(properties);
}
Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
if (environment != null && databaseIdProvider != null) {
String databaseId = databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(environment.getDataSource());
configuration.setDatabaseId(databaseId);
}
}
3.3.10 typeHandlers 相關屬性
3.3.10.1 成員變數
protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry;
3.3.10.2 對應 XML 節點:<typeHandlers>
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="org.mybatis.example.ExampleTypeHandler"/>
</typeHandlers>
3.3.10.3 作用
無論是 MyBatis 在預處理語句(PreparedStatement)中設定一個引數時,還是從結果集中取出一個值時, 都會用型別處理器將獲取的值以合適的方式轉換成 Java 型別。
3.3.10.4 解析過程
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
// 遍歷所有的子節點
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// 包(package)子節點
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else { // 非 package 子節點
// 獲取相應的屬性
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
// 根據屬性, 通過反射建立物件
Class<?> javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
Class<?> typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
// 將物件註冊到 typeHandlerRegistry 物件中
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
3.3.11 mappers 相關屬性
3.3.11.1 成員變數
//對映的語句
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
// 快取集合
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<Cache>("Caches collection");
// 結果集合
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
// 儲存過程引數集合
protected final Map<String, ParameterMap> parameterMaps = new StrictMap<ParameterMap>("Parameter Maps collection");
// 主鍵生成器合集
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<KeyGenerator>("Key Generators collection");
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>();
protected final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments = new StrictMap<XNode>("XML fragments parsed from previous mappers");
// 儲存不完整的語句
protected final Collection<XMLStatementBuilder> incompleteStatements = new LinkedList<XMLStatementBuilder>();
protected final Collection<CacheRefResolver> incompleteCacheRefs = new LinkedList<CacheRefResolver>();
protected final Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps = new LinkedList<ResultMapResolver>();
protected final Collection<MethodResolver> incompleteMethods = new LinkedList<MethodResolver>();
3.3.11.2 對應 XML 節點:<mappers>
<mappers>
<package name="com.homejim.mybatis.mapper"/>
</mappers>
3.3.11.3 作用
mybatis-config.xml 配置檔案中的<mappers>節點會告訴 MyBatis 去哪些位置查詢對映配置檔案以及使用了配置註解標識的介面。
這也是配置檔案解析的重點, 後續會開一篇文章進行講解。
3.3.11.4 解析過程
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
// <package> 子節點, 就是包下面的類
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else { // 對應 <mapper> 子節點
// resource / url / class 中 3選1
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
// 如果節點指定了 resource 或 url, 則建立 XMLMapperBuilder 物件,
// 通過該物件的 parse() 函式將 mapper 新增到 configuration 中
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
這個是後面需要更詳細的開章節進行講解的。
結語
至此, 本文章就結束了。 本來是想寫更詳細一點的, 後面發現篇幅越來越大, 因此有一些部分沒有展開。後續會挑某些部分的解析過程進行更深入的講解。
如果您覺得還可以, 給個贊吧!