System對IO支援----System.out/System.in
這篇部落格裡介紹了列印流PrintSream類,PrintSream類的方法print()和println(),可以聯想到系統輸出System.out.println(),也及時說系統輸出利用了IO流的模式完成。在System類中定義了3個操作的常量。
- 標準輸出(顯示器):public final static PrintStream out;
System.out - 錯誤輸出:public final static PrintStream err;
System.err - 標準輸入(鍵盤):public final static InputStream in;
System.in
系統輸出
out和err都是PrintStream物件,而PrintStream是OutputStream子類,所以可以直接用System.out為OutputStream的例項化,這時OutputStream輸出的終端變為顯示器。
//System對IO的支援
public class Out {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
OutputStream out=System.out; //System.out是PrintStream物件
String str= out和err都是輸出,只是err是錯誤輸出:
////out和err區別
public class Out {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OutputStream out=System.out; //System.out是PrintStream物件
File file =new File("Text.txt");
try {
InputStream in= 
有沒有發現兩者的區別只是顏色不同呢~是的,out輸出的是黑色,err輸出的是紅色。
系統輸入
在System類中另一個常量是public final static InputStream in;
System.out是InputStream物件,指的是使用者通過鍵盤進行輸入(使用者輸入)。但是Java本身沒有提供直接的使用者輸入,如果要輸入,需要藉助java.io來完成完成:
package CODE.JavaIo;
////System對輸入的支援:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream in=System.in;
System.out.println("請輸入...");
byte[] data=new byte[1024];
int len=in.read(data);
System.out.println(new String(data,0,len));
in.close();
}
}
如果輸入長度超過了1024,那麼只會讀取到1924位元組,其餘位元組資料將會丟棄。那麼就需要引入記憶體操作流,將資料儲存在記憶體流中一次取出。
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
System.out.println("請輸入...");
InputStream in=System.in; //標準輸入
ByteArrayOutputStream out =new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //記憶體位元組輸出流
byte data[]=new byte[10];
int len=0;
while((len=in.read(data))!=-1)
{
out.write(data,0,len); //將data裡數寫入記憶體儲存
//需要判斷使用者輸入完畢
if (len < data.length)
break ;
}
System.out.println(new String(out.toByteArray()));
in.close();
out.close();
}
}
可以看出這種輸入方式十分複雜,如果在IO中需要進行中文處理,最好的做法是將所有輸入的資料儲存在一起再處理,這樣才可以保證不出現亂碼。
2種輸入流
1.BufferedReader類:
BufferedReader是一個字元緩衝輸入流。當然還有位元組緩衝流(BufferedInputStream)。BufferedReader有一個優點可以 讀取一行資料:
//以回車為換行符
String readLine() throws IOException;
這種輸入流在JDK1.5被java.util.Scanner取代。
2.java.util.Scanner類:
列印流解決的是OutputStream類的缺陷,BufferedReader解決的是InputStream類的缺陷。而Scanner解決的是
BufferedReader類的缺陷(替換了BufferedReader類)
在Scanner類有以下方法
- 判斷是否有指定型別資料:public boolean hasNextXxx();
- . 取得指定型別的資料: public 資料型別 nextXxx();
- 定義分隔符:public Scanner useDelimiter(Pattern pattern)
- 構造方法:public Scanner(InputStream source)
////Scanner類的輸入
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); //標準輸入
System.out.println("請輸入...");
if(scanner.hasNext()) //輸入內容不為空
{
System.out.println("輸入內容:"+scanner.next());
}
scanner.close();
}
}
使用Scanner還可以接收各種資料型別,並且幫助使用者減少轉型處理:
////Scanner類接受指定型別
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); //標準輸入
System.out.println("請輸入...");
if(scanner.hasNextDouble()) //有輸入,並且輸入的資料是double
{
System.out.println("輸入double型資料:"+scanner.nextDouble());
}
scanner.close();
}
}
Scanner可以對接收的資料型別使用正則表示式判斷:
////正則表示式
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in); //標準輸入
System.out.println("請輸入...");
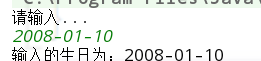
if(scanner.hasNext("\\d{4}-\\d{2}-\\d{2}")) //有輸入,並且輸入的資料是double
{
String birthday=scanner.next();
System.out.println("輸入的生日為:"+birthday);
}
else
{
System.out.println("輸入生日格式錯誤");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
由於Scanner類的構造方法:public Scanner(InputStream source),接受的是InputStream物件,也及時可以接收任意輸入流,如:檔案輸入流。
//Scanner接受檔案輸入流
public class In {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file=new File("C:"+File.separator+"Users"+File.separator+
"lenovo"+File.separator+"Desktop"+
File.separator+"Test.txt");
InputStream in=new FileInputStream(file);
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(file); //接受檔案輸入流
scanner.useDelimiter("\n");//按照"\n"分隔
while(scanner.hasNext())
{
System.out.println(scanner.next());
}
in.close();
scanner.close();
}
}
總結:輸出用列印流,輸入用Scanner。
