C++中一個類包含另一個類
一個類裡面包含另外一個類,建構函式呼叫的先後關係。
1)A類的物件是B類的私有成員: #include <iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: int mInt; A() { cout<< "in A Default Constructor:mInt = " << mInt<< endl; mInt = 0; } void setIntVal(int mSet) { cout<< "in setIntVal:mInt = " << mInt<<"mSet="<< mSet<< endl; if (mInt< mSet) { mInt= mSet; } } };
class B{ private: int b; A aObj; //A類的物件 public: B() { cout<< "in B Default Constructor"<< endl; b = 10; aObj.setIntVal(20); } };
int main() { B * pB = new B(); delete pB; return 0; }
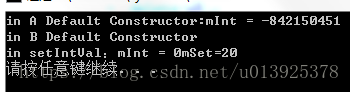
執行結果:
在主函式中new B的時候,先呼叫A的建構函式,再呼叫B的建構函式。
2)指向A類物件的指標是B類的私有成員:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: int mInt; A() { cout<< "in A Default Constructor:mInt = " << mInt<< endl; mInt = 0; } void setIntVal(int mSet) { cout<< "in setIntVal:mInt = " << mInt<<"mSet="<< mSet<< endl; if (mInt< mSet) { mInt= mSet; } } };
class B{ private: int b; A *pA; //指向A類物件的指標 public: B() { cout<< "in B Default Constructor"<< endl; b = 10; pA = new A(); pA->setIntVal(15);
} };
int main() { B * pB = new B(); delete pB; return 0; }
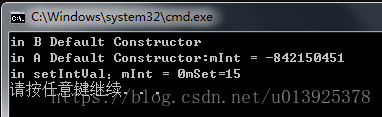
執行結果:
在主函式中new B的時候,先呼叫B的建構函式,B的建構函式中有new A的操作,則呼叫A的建構函式。