springboot與快取—使用、原理、整合redis
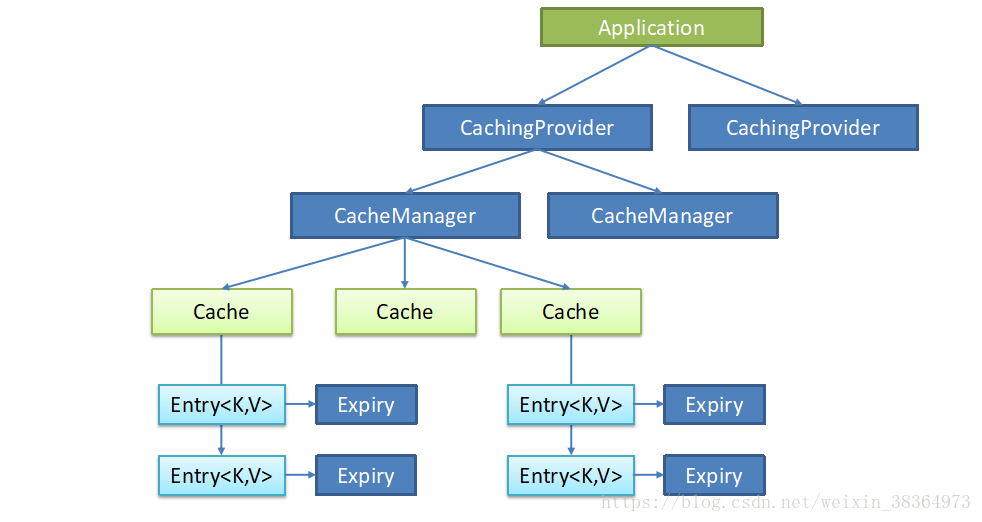
Java快取介面標準JSR-107:Java Caching定義了5個核心介面,分別是CachingProvider(快取提供者), CacheManager(快取管理器), Cache(快取元件), Entry (key-value對)和Expiry(條目有效期),他們的關係如下圖所示。但是該快取規範,整合難度較大。Spring從3.1開始定義了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager介面來統一不同的快取技術;
1、介面、快取註解、key/value生成策略
| Cache | 快取介面,定義快取操作。實現:RedisCache、EhCache等(根據快取技術不同來實現Cache介面) |
| CacheManager | 快取介面,快取管理器,管理各種快取(Cache)元件 |
| @Cacheable | 可快取的,標註方法,能夠根據方法的請求引數對其結果進行快取 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空快取 |
| @CachePut | 更新快取 |
| @EnableCaching | 開啟基於註解的快取 |
| keyGenerator | 快取資料時key生成策略 |
| serialize | 快取資料時value序列化策略 |
2、使用cache快取步驟(不使用快取時,每次訪問都會連線資料庫)
a、引入依賴
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId> </dependency>
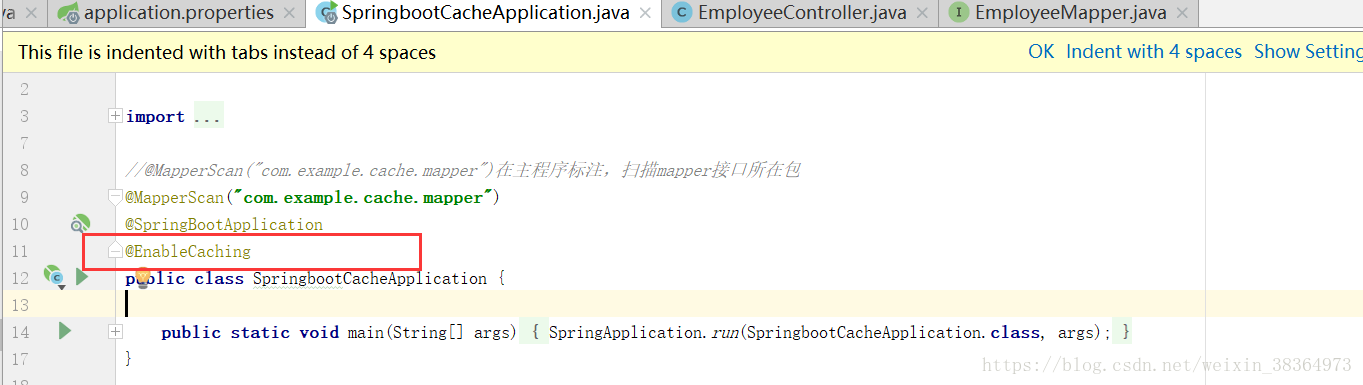
b、開啟基於註解的快取 @EnableCaching
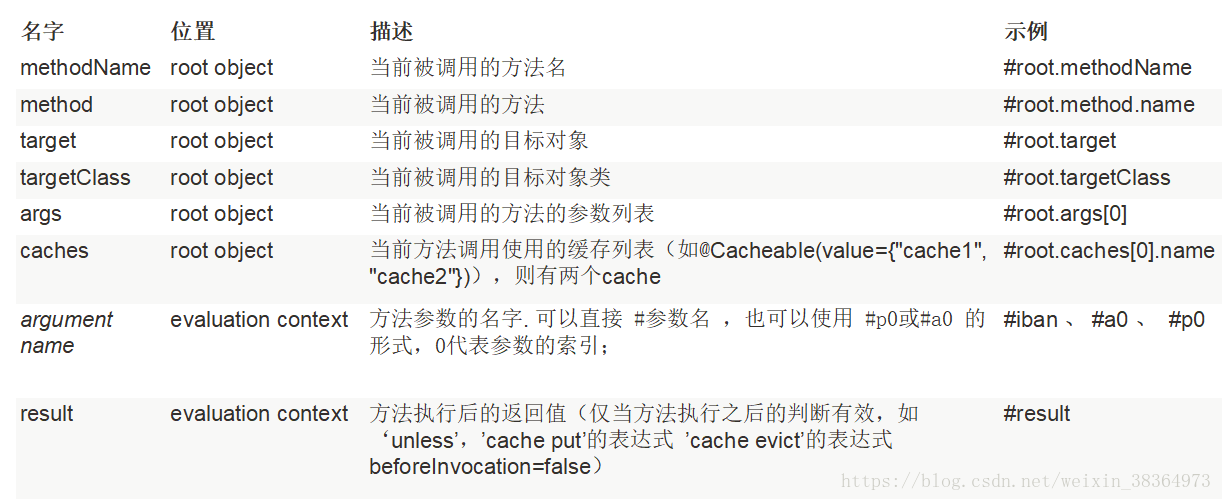
package com.example.cache.service; import com.example.cache.bean.Employee; import com.example.cache.mapper.EmployeeMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; //@Service:將service載入到容器中 //CacheConfig:公共的快取配置;cacheNames = "emp":之後的value="emp"就可以不用寫 @CacheConfig(cacheNames = "emp") @Service public class EmployeeService { @Autowired EmployeeMapper employeeMapper; /** * @Cacheable:將方法的執行結果進行儲存,以後再要相同的資料,直接從快取中獲取,不用呼叫方法 * CacheManager管理多個Cache元件,對快取的真正CRUD操作在Cache元件中,每個快取元件有自己唯一的名字 * 屬性:(快取資料時使用key-value的形式) * cacheNames/value:指定快取元件的名字;將方法的返回結果放在哪個快取中,是陣列的方式,可以指定多個快取 * key:快取資料使用的key;可以用她來指定。預設是使用方法引數的值 鍵值對:1-方法的返回值 * 引數id的值:#id相當於#root.args[0] * keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器元件id * ——key和keyGenerator不可同時使用 * cacheManager:指定快取管理器(從哪個快取管理器中取);cacheResolver:指定快取解析器 * condition:指定符合條件的情況下才快取;condition="#id>0":id大於0的時候才快取 * unless:否定快取;當unless指定的true,方法的返回值就不會被快取;可以獲取到結果進行判斷 * unless="#result == null":結果為空時不快取 * sync:快取是否使用非同步模式 * @param id * @return */ @Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"}) public Employee getEmp(Integer id){ System.out.println("查詢"+id+"號員工"); Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id); return emp; } /** * @CachePut:既呼叫方法,又更新快取資料; * 修改了資料庫的某個資料,同時更新快取 * 執行過程: * 1、先呼叫目標方法 * 2、將目標方法的結果快取起來 * 更新後重新查詢出的資料是更新前的資料: * ——(key預設使用方法引數的值)查詢是的快取是@Cacheable快取的值,key是1;@CachePut更新後快取的值:key是傳入的employee物件 * ——所以要統一key:key="#employee.id";key="#result.id"; */ @CachePut(value = "emp",key="#employee.id") public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){ employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee); return employee; } /** *@CacheEvict快取清除 * key:指定要清楚的資料 * allEntries=true:指定清除這個快取中的所有資料 * beforeInvocation = false;快取的清除是否在方法之前執行;false:在方法執行之後清除 */ @CacheEvict(value="emp",key="#id") public void deleteEmp(Integer id){ } /** * 指定多個快取規則 */ @Caching( cacheable = { @Cacheable(value = "emp",key = "#lastName") }, put={ @CachePut(value = "emp",key="#result.id"), @CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.email") } ) public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName) { return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName); } }
3、整合redis進行快取;開發中常使用快取中介軟體:redis、memcahed、ehcache;
引入redis啟動器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>配置redis資訊
spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1
spring.redis.password=使用redis
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootCacheApplicationTests implements Serializable {
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Autowired
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;//key-value都是操作字串
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;//key-value都是物件
//@Autowired
//RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate;
/**
* Redis常見的五大資料型別
* String(字串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(雜湊)、ZSet(有序集合)
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[操作String(字串)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[操作List(列表)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[操作Set(集合)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[操作Hash(雜湊)]
* stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[操作ZSet(有序集合)]
*/
@Test
public void test01(){
//stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().append("msg","hello");
String msg = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("msg");
System.out.println(msg);
}
//測試儲存物件(需要序列化)
@Test
public void test02(){
Employee empById = employeeMapper.getEmpById(1);
//預設如果儲存物件,使用jdk序列化機制,序列化後的資料儲存到redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp-01",empById);
//將資料以json的方式儲存:1、自己將物件轉化為json;2、redisTemplate預設的序列化規則:改變預設的序列化規則
//empRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("emp-01",empById);
}
}自定義序列化器,改變預設的序列化規則;使其儲存的資料為json格式,而不是序列化格式。
package com.example.cache.config;
import com.example.cache.bean.Employee;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
//RedisTemplate<Object, Employee>:序列化Employee
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> empRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Employee> template = new RedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
//序列化器
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee> ser = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Employee>(Employee.class);
template.setDefaultSerializer(ser);
return template;
}
}原理:預設使用快取管理器CacheManager來建立Cache快取元件,來給快取中存取資料。加入redis後,開啟了RedisCacheConfiguration。RedisCacheManager幫我們建立RedisCache來作為快取元件。
4、快取執行流程
@Cacheable:
a、方法執行之前,先去查詢Cache(快取元件),按照cacheNames指定的名字獲取;(CacheManager先獲取相應的快取),如果沒有Cache元件,第一次獲取快取會自動建立
b、去Cache中查詢快取的內容,使用一個key,預設就是方法的引數;
key是按照某種策略生成的;預設是使用keyGenerator生成的;預設使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key
SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的預設策略:
如果沒有引數:key=new SimpleKey();如果有一個引數,key=引數的值;如果有多個引數:key= new SimpleKey(params);
c、沒有查到快取就呼叫目標方法;
d、將目標方法返回的結果放到快取中
@Cacheable標註的方法執行之前來檢查快取中有沒有這個資料,預設按照引數的值作為key去查詢快取,如果沒有就執行方法,並將結果放入快取。以後再來呼叫,就可以使用快取中的資料;
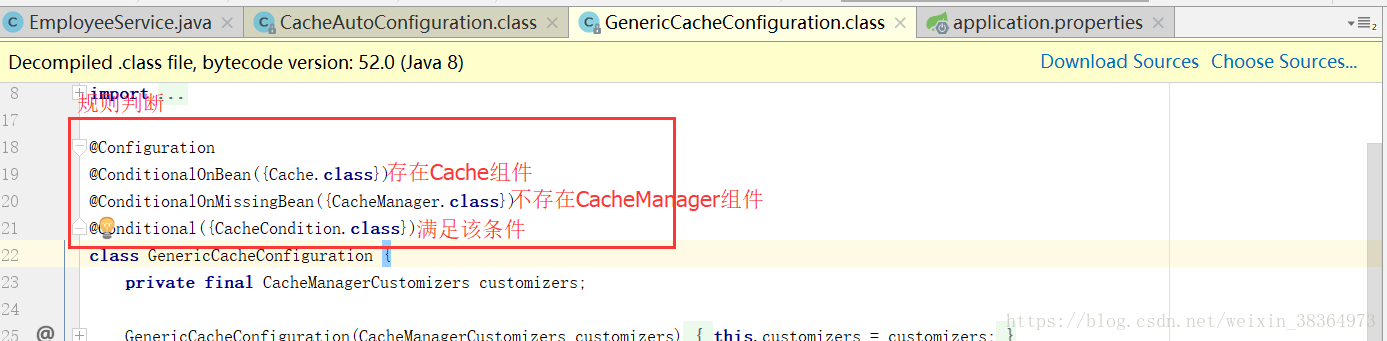
5、快取原理
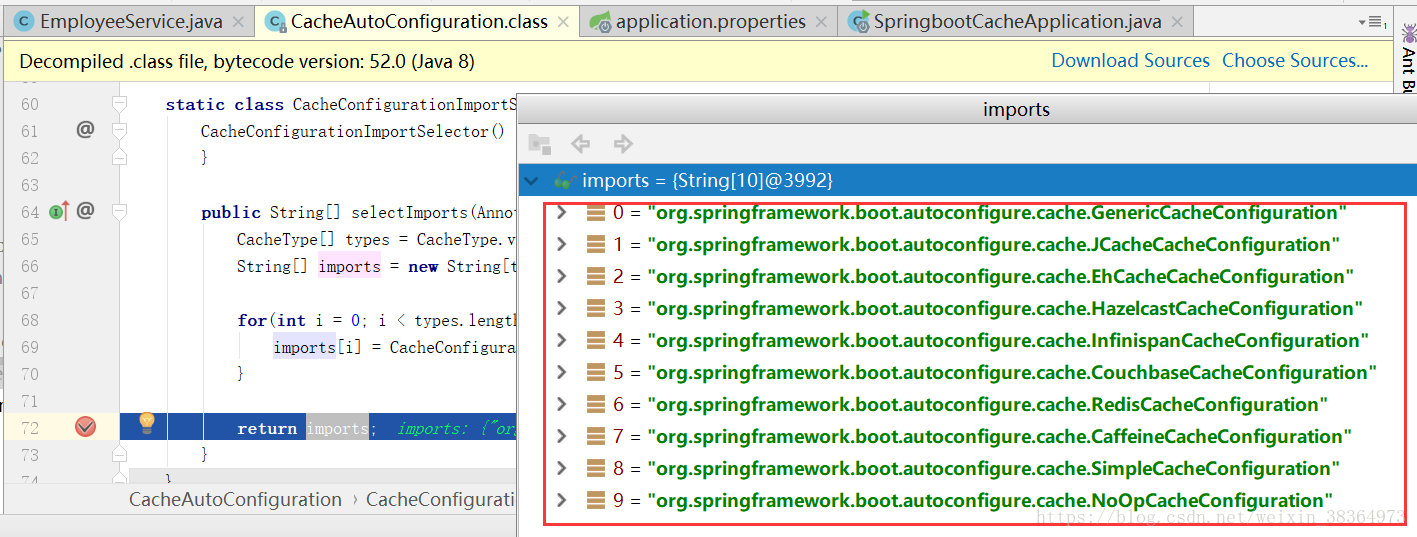
a、自動配置類CacheAutoConfiguration給容器中匯入元件
b、各快取的配置類
c、預設生效的配置類:SimpleCacheConfiguration
d、給容器中註冊了一個CacheManager:ConcurrentManager;可以獲取和建立ConcurrentMapCache型別的快取元件,他的作用是將資料儲存在ConcurrentMap中。