Locust壓力測試使用總結
上次做介面壓力測試前一直研究使用jmeter,本以為可以拿來使用了,但是真正進行併發介面時,發現jmeter在單機下併發1000個時,臺式電腦單機資源早就被使用完,整個jmeter卡得死死的,結果那晚使用jmeter併發失敗,幸好之前也準備了另外一個壓測小公舉Apache ab。最後使用ab勉強完成任務。估計jmeter壓測介面研究得遠遠不夠。後續繼續研究吧。事後發現基於Python開發的Locust單機併發能力很理想,於是乎在測試環境拿來壓測那次的介面。好像真的可以實現幾千的併發。記錄下方便自己下次使用:
Locust壓測介面效能2
Locust是完全基於Python,http請求完全是基於requests庫。Locust支援http、https協議,還支援測試其他協議,websocket等,只要採用Python呼叫對應的庫就可以了。
http/https採用requests;
websocket採用websocket ;
等等。
Locust和jmeter、lr優點對比3
效能測試很難在單機上獲得很高的併發量,lr、jmeter這類工具採用程序和執行緒來壓測,單機併發量不高。(一般都要用幾臺電腦做壓力發射機)
Locust併發機制擯棄了程序和執行緒,採用協程(gevent)機制。協程避免了系統級資源排程,可以大大提高單機併發能力。
Locust安裝使用3
centos6.7使用Locust
Python安裝Locust,從GitHub克隆下來,進入輸入Python setup.py install 進行安裝;
GitHub地址:https://github.com/locustio/locust
在安裝之前最好先安裝下面依賴包:
install_requires=["gevent>=1.2.2", "flask>=0.10.1", "requests>=2.9.1", "msgpack-python>=0.4.2", "six>=1.10.0", "pyzmq==15.2.0"]
- 1.gevent:在Python中實現協程的第三方庫。協程又叫微執行緒Corouine。使用gevent可以獲取極高的併發能力;
- 2.flask:Python的一個web開發框架,和django相當;
- 3.requests:支援http/https訪問的庫;
- 4.msgpack-python:一種快速、緊湊的二進位制序列化格式,使用與類似json的資料;
- 5.six:提供了一些簡單的工具封裝Python2和Python3 之間的差異;
- 6.pyzmq:安裝這個第三方庫,可以把Locust執行在多個程序或多個機器(分散式執行測試任務)
在centos 6.7安裝這些庫(注意版本):使用pip安裝就可以了;
最後在命令列中輸入Python setup.py install ,首先會檢查以上的三方庫有沒有合法安裝,最後安裝成功;
驗證安裝:
命令航輸入 locust --help
[[email protected] locust]# locust --help
Usage: locust [options] [LocustClass [LocustClass2 ... ]]
Options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-H HOST, --host=HOST Host to load test in the following format:
http://10.21.32.33 #設定執行的測試地址(被測試系統的域名或IP)
--web-host=WEB_HOST Host to bind the web interface to. Defaults to '' (all
interfaces)
-P PORT, --port=PORT, --web-port=PORT
Port on which to run web host
-f LOCUSTFILE, --locustfile=LOCUSTFILE #指定效能測試指令碼檔案
Python module file to import, e.g. '../other.py'.
Default: locustfile
--csv=CSVFILEBASE, --csv-base-name=CSVFILEBASE
Store current request stats to files in CSV format.
--master Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as master
--slave Set locust to run in distributed mode with this
process as slave
--master-host=MASTER_HOST
Host or IP address of locust master for distributed
load testing. Only used when running with --slave.
Defaults to 127.0.0.1.
--master-port=MASTER_PORT
The port to connect to that is used by the locust
master for distributed load testing. Only used when
running with --slave. Defaults to 5557. Note that
slaves will also connect to the master node on this
port + 1.
--master-bind-host=MASTER_BIND_HOST
Interfaces (hostname, ip) that locust master should
bind to. Only used when running with --master.
Defaults to * (all available interfaces).
--master-bind-port=MASTER_BIND_PORT
Port that locust master should bind to. Only used when
running with --master. Defaults to 5557. Note that
Locust will also use this port + 1, so by default the
master node will bind to 5557 and 5558.
--expect-slaves=EXPECT_SLAVES
How many slaves master should expect to connect before
starting the test (only when --no-web used).
--no-web Disable the web interface, and instead start running
the test immediately. Requires -c and -r to be
specified. #表示不使用web介面執行測試,介面壓力測試一般使用該些引數
-c NUM_CLIENTS, --clients=NUM_CLIENTS
Number of concurrent clients. Only used together with
--no-web #設定虛擬使用者數
-r HATCH_RATE, --hatch-rate=HATCH_RATE #設定每秒啟動的虛擬使用者數
The rate per second in which clients are spawned. Only
used together with --no-web
-n NUM_REQUESTS, --num-request=NUM_REQUESTS #設定請求個數
Number of requests to perform. Only used together with
--no-web
-L LOGLEVEL, --loglevel=LOGLEVEL
Choose between DEBUG/INFO/WARNING/ERROR/CRITICAL.
Default is INFO.
--logfile=LOGFILE Path to log file. If not set, log will go to
stdout/stderr
--print-stats Print stats in the console
--only-summary Only print the summary stats
--no-reset-stats Do not reset statistics once hatching has been
completed
-l, --list Show list of possible locust classes and exit
--show-task-ratio print table of the locust classes' task execution
ratio
--show-task-ratio-json
print json data of the locust classes' task execution
ratio
-V, --version show program's version number and exitLocust指令碼使用說明3
注意:增加開啟檔案限制的最大數量:
在每一個HTTP連線的機器上開啟一個新檔案(技術檔案描述符)。作業系統可以設定一個可以開啟的檔案的最大數量的下限。如果限制小於模擬使用者的數量,在測試時,會發生故障。增加作業系統的預設最大數量的檔案限制到一個數字高於模擬使用者數的數量,才能達到你想要的測試,在centos中在命令列中執行ulimit 655336,更改檔案描述符最大就行不會報open too many file 的錯誤。
併發單個url的例子:
from locust import HttpLocust,TaskSet,task
# 定義使用者行為,繼承TaskSet類,用於描述使用者行為
# (這個類下面放各種請求,請求是基於requests的,每個方法請求和requests差不多,請求引數、方法、響應物件和requests一樣的使用,url這裡寫的是路徑)
# client.get===>requests.get
# client.post===>requests.post
class test_126(TaskSet):
# task裝飾該方法為一個事務方法的引數用於指定該行為的執行權重。引數越大,每次被虛擬使用者執行概率越高,不設定預設是1,
@task()
def test_baidu(self):
# 定義requests的請求頭
header = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 "
"(Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 "
"(KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.101 Safari/537.36"}
# r是包含所有響應內容的一個物件
r = self.client.get("/",timeout=30,headers=header)
# 這裡可以使用assert斷言請求是否正確,也可以使用if判斷
assert r.status_code == 200
# 這個類類似設定效能測試,繼承HttpLocust
class websitUser(HttpLocust):
# 指向一個上面定義的使用者行為類
task_set = test_126
#執行事物之間使用者等待時間的下界,單位毫秒,相當於lr中的think time
min_wait = 3000
max_wait = 6000啟動測試:
[root @ localhost locust_baidu] # locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://www.126.com
[2017 - 06 - 08 12: 33:42, 662] localhost.localdomain / INFO / locust.main: Starting web monitor at *: 8089
[2017 - 06 - 08 12: 33:42, 663] localhost.localdomain / INFO / locust.main: Starting Locust 0.8 a31.-f 指定效能測試檔案;
2.--host 指定被測試url的主機地址(IP地址) 通過瀏覽器訪問:http://192.168.0.107:8089/(預設埠是8089)
點選start swarming進行測試:
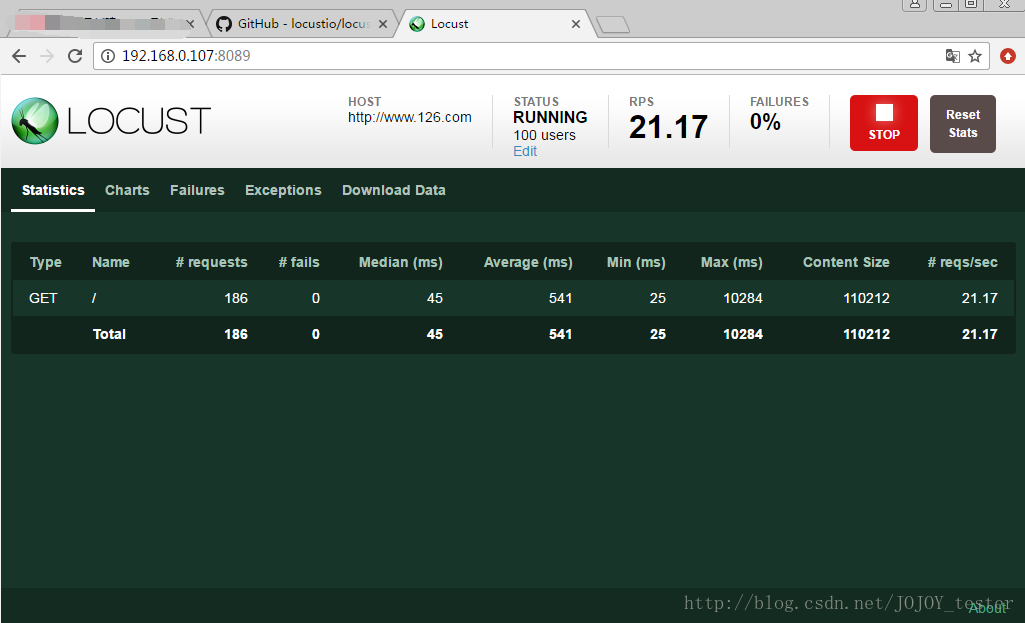
- 1.Type:請求型別;
- 2.Name:請求路徑;
- 3.requests:當前請求的數量;
- 4.fails:當前請求失敗的數量;
- 5.Median:中間值,單位毫秒,一般伺服器響應時間低於該值,而另一半高於該值;
- 6.Average:所有請求的平均響應時間,毫秒;
- 7.Min:請求的最小的伺服器響應時間,毫秒;
- 8.Max:請求的最大伺服器響應時間,毫秒;
- 9.Content Size:單個請求的大小,單位位元組;
- 10.reqs/sec:每秒鐘請求的個數。
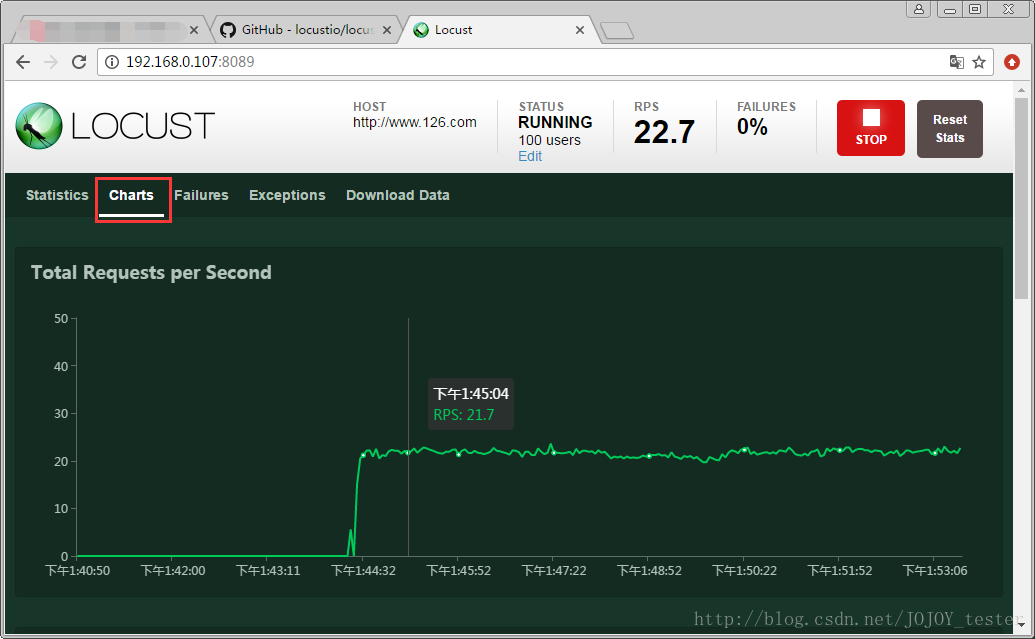
圖表顯示:
從上到下:
- 1.吞吐量/每秒響應事務數(rps)實時統計
- 2.平均響應時間/平均事務數實時統計
- 3.虛擬使用者數執行
另外,還有其他統計表格:失敗請求、異常請求(斷言失敗結果顯示在這裡)、下載測試結果。
這個是通過瀏覽器測試的形式,可以通過測試場景設計的時間長度執行,壓力測試時間(一般都是5分鐘以上吧)足夠後,需要手動點選stop按鈕,結束壓力測試。
如果希望請求數量維持在一定的情況,可以使用--no-web形式:
在shell中直接輸入:
[[email protected] locust_baidu]# locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://www.126.com --no-web -c 10 -r 10 -n 30
[2017-06-08 13:13:31,385] localhost.localdomain/INFO/locust.main: Starting Locust 0.8a3
[2017-06-08 13:13:31,385] localhost.localdomain/INFO/locust.runners: Hatching and swarming 10 clients at the rate 10 clients/s...
Name
# 測試過程的實時資料
。。。。。。
#測試結束
[2017-06-08 13:13:52,588] localhost.localdomain/INFO/locust.runners: All locusts dead
#資料統計
[2017-06-08 13:13:52,588] localhost.localdomain/INFO/locust.main: Shutting down (exit code 0), bye.
Name # reqs # fails Avg Min Max | Median req/s
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GET / 39 0(0.00%) 305 28 5155 | 40 2.00
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 39 0(0.00%) 2.00
Percentage of the requests completed within given times
Name # reqs 50% 66% 75% 80% 90% 95% 98% 99% 100%
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GET / 39 40 41 44 47 52 5100 5200 5200 5155
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------啟動引數說明:
- 1.--no-web:表示不使用web介面執行測試;
- 2.-c:設定虛擬使用者總數;
- 3.-r:設定每秒啟動虛擬使用者數;
- 4.-n:設定請求總個數;
測試環境壓測介面指令碼:
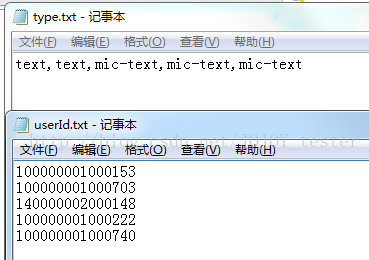
引數化資料:
readData.py
# 思路:在userId.txt、type.txt檔案中填寫資料來源,兩個檔案資料是一一對應的,通過readlines()讀取,儲存為一個列表,
# 通過list的索引讀取資料,索引使用隨機數
import random
class Readdata():
# 隨機數放在init方法中,保證只獲取一次隨機數,因為類只例項化一次
def __init__(self):
with open("./userId.txt") as f:
userId = f.readlines()
# 隨機數範圍0--(陣列長度-1)為了和list下標一樣,從0開始
self.ran = random.randint(0,len(userId)-1)
def readUserid(self):
with open("./userId.txt") as f:
userId = f.readlines()
userIds = []
# readlines獲取每一行資料儲存為list,每一行資料是一個元素,字串形式,
# 這裡要遍歷轉為int可以去掉換行符號再append一個新陣列。
for i in userId:
data = int(i)
userIds.append(data)
# 隨機獲取一個數
userId = userIds[self.ran]
return userId
def readType(self):
with open("./type.txt") as f1:
type_ = f1.readlines()
# 去掉list中的換行符號\n
type1 = ''.join(type_).strip('\n')
# 分割字串,儲存為list,
type2 = type1.split(',')
type3 = type2[self.ran]
# print(type(type2))
return type3
if __name__ == "__main__":
rd = Readdata()
print(rd.readType())
print(rd.readUserid())請求公參:
common.py
import sys,time,random,hashlib
sys.path.append('../db_set')
# from db_set.mysql_db import DB
def setUp_():
tim = time.time()
tim = tim*1000
tim = str(tim)
# ts時間戳
ts = tim.split('.')[0]
ran = random.randint(100,999)
ran = str(ran)
# reqId時間戳拼接隨機數
reqId =ts + ran
# 密匙
secret = 'xxxxxxxxxxx'
#請求頭
header = {"User-Agent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.101 Safari/537.36"}
#資料庫
# db = DB()
#測試userId
userId = "100000001000153"
#測試liveId
liveId = "140000002000038"
#測試地址
host = "http://ixxxxxxxhat.com/"
return (ts,reqId,secret,header,userId,liveId,host)
def md5(reqSign_):
md5 = hashlib.md5()
str_bytes_utf8 = reqSign_.encode(encoding="utf-8")
md5.update(str_bytes_utf8)
sign = md5.hexdigest()
return sign
locust檔案:
from locust import HttpLocust,TaskSet,task
from common import setUp_,md5
from readData import Readdata # 匯入引數化的類
# 定義使用者行為
class SpeakAdd(TaskSet):
# 定義類的例項變數
ts = setUp_()[0]
reqId = setUp_()[1]
secret = setUp_()[2]
header = setUp_()[3]
# db = setUp_()[4]
# userId = setUp_()[4]
# liveId = setUp_()[5]
# 獲取引數化資料
rd = Readdata()
# 發言型別type,因為不同使用者這個是不同的
type = rd.readType()
# 獲取發言人id,這裡和發言型別對應,上面做了處理
userId = rd.readUserid()
#加密
reqSign = reqId + ':' + secret + ':' + ts
sign = md5(reqSign)
# 請求引數
data = { "id": reqId,
"timestamp": ts,
"sign": sign,
"data": { "commentId":"",
"topicId": "100000046000082",
"type": type,
"liveId": "140000002000038",
"content": "我正在發言," + ts,
"isReplay": "N",
"page": {"size": "20", "page": "1"},
"userId": userId}}
@task(1)
def testSpeakadd(self):
# 和requests請求一樣寫
r = self.client.post("/h5/speak/add",json=self.data,headers=self.header,timeout=30)
result = r.json()# 返回字典
# 斷言
assert r.status_code == 200
assert result['state']['code'] == 0
# 設定效能測試
class WebsiteUser(HttpLocust):
task_set = SpeakAdd
# 介面測試think time 設定為0
min_wait = 0
max_wait = 0
# 下面可以通過直接執行Python locustfile1.py c r n 進行測試,這種方式適合 --no-web執行
if __name__ == "__main__":
import os,sys
# sys.argv是一個list,元素是使用者自定義的,原來是str型別,需要轉換為int
c = int(sys.argv[1])
r = int(sys.argv[2])
t = int(sys.argv[3])
for i in range(2):
# os.system(命令),可以執行shell、Windows命令
os.system("locust -f locustfile1.py --host=http://xxxxxt2.qlchat.com --no-web -c %d -r %d -n %d" %(c,r,t))測試方案一:
啟動介面壓力測試:
locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://inner.test2.qlchat.com
瀏覽器開啟: http://192.168.0.107:8089/
根據場景進行壓力測試:
場景1:執行5分鐘,使用者數1000,每秒啟動100,記錄測試結果資料,伺服器效能指標;
場景2:執行5分鐘,使用者數1000,每秒啟動200,記錄測試結果資料,伺服器效能指標;
場景3:執行5分鐘,使用者數1000,每秒啟動500,記錄測試結果資料,伺服器效能指標;
伺服器指標:CPU、記憶體等
效能測試分析:
。。。。。。
測試方案二:
使用另外一種測試方式,--no-web、-c、-r、-n:
命令列中執行測試:每種場景記錄測試結果資料,伺服器效能指標;
場景一:locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://inner.test2.qlchat.com --no-web -c 1000 -r 100 -n 30000
場景二:locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://inner.test2.qlchat.com --no-web -c 1000 -r 500 -n 30000
場景三:locust -f locustfile.py --host=http://inner.test2.qlchat.com --no-web -c 1000 -r 1000 -n 30000
總結:
不足之處:發言人id需要不不是同一個,也準備不同的發言人,引數化。使場景更加接近使用者使用場景。但是併發時還是同一個使用者 ==,傷心。。。有高手看到麻煩指導下。。。
多個url壓力測試也就是業務效能測試3:
。。。。
。。。
。。
。
思路:
在一個完整的業務場景中(從使用者登入到退出系統),點選開啟的一個頁面到另一個頁面,每個頁面都是由url定義的,可以先寫請求登入的方法,在寫另一個頁面的請求方法,最後把所有請求方法連線起來,就是一個完整的業務場景了。然後做登入關聯、使用者引數化。設定虛擬使用者、每秒啟動虛擬使用者個數,設計場景去併發。