python configparser配置檔案解析器使用詳解
configparser簡介
python2下該模組名為ConfigParser,到3才改為configparser,可以看官方ConfigParser模組的說明
ConfigParse 官方文件
python3中configparser模組的使用,configparser模組是用來解析ini配置檔案的解析器,關於ini配置檔案的結構可以看python官方文件中的介紹:
ini檔案結構
ini檔案結構需要注意一下幾點:
- 鍵值對可用=或者:進行分隔
- section的名字是區分大小寫的,而key的名字是不區分大小寫的
- 鍵值對中頭部和尾部的空白符會被去掉
- 值可以為多行
- 配置檔案可以包含註釋,註釋以#或者;為字首
注意:configparser有default_section的概念,預設為[DEFAULT]節,也就是之後的所有的section都有該預設section中的鍵值對,詳情參見configparser原始碼的__init__()方法
基本使用
為了建立如下ini檔案:
configparser模組主要使用ConfigParser類來解析ini檔案
[DEFAULT]
ServerAliveInterval = 45
Compression = yes
CompressionLevel = 9
ForwardX11 = yes
[bitbucket.org]
User = hg
[topsecret. 我們可以使用如下程式碼:
>>> import configparser
>>> config = configparser.ConfigParser()
>>> config['DEFAULT'] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '45',
... 'Compression': 'yes',
... 'CompressionLevel': '9'}
>> 然後我們再讀取該ini檔案:
>>> import configparser
>>> config = configparser.ConfigParser()
>>> config.sections()
[]
>>> config.read('example.ini')
['example.ini']
>>> config.sections()
['bitbucket.org', 'topsecret.server.com']
>>> 'bitbucket.org' in config
True
>>> 'bytebong.com' in config
False
>>> config['bitbucket.org']['User']
'hg'
>>> config['DEFAULT']['Compression']
'yes'
>>> topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com']
>>> topsecret['ForwardX11']
'no'
>>> topsecret['Port']
'50022'
>>> for key in config['bitbucket.org']: print(key)
...
user
compressionlevel
serveraliveinterval
compression
forwardx11
>>> config['bitbucket.org']['ForwardX11']
'yes'
除了可以使用列表的方式獲取值,也可以通過section級別的get()方法獲取,同時該函式可以指定預設值
>>> topsecret.get('Port')
'50022'
>>> topsecret.get('CompressionLevel')
'9'
>>> topsecret.get('Cipher', '3des-cbc')
'3des-cbc'
而解析器級別的get()函式的預設值是通過fallback引數指定的:
>>> config.get('bitbucket.org', 'monster',
... fallback='No such things as monsters')
'No such things as monsters'
需要注意的是,無論是通過列表方式獲取值,還是通過get()方法獲取值,獲取到的資料都字串型別,如果想要獲取指定型別的資料,可以使用如下的幾個方法:
- getint()
- getfloat()
- getboolean()
同時需要注意getboolean()方法能判斷True/False的值有: ‘yes’/‘no’, ‘on’/‘off’, ‘true’/‘false’ 和 ‘1’/‘0’
Interpolation
建立ConfigParser()類的時候可以指定interpolation引數,如果將interpolation設定為BasicInterpolation(),則配置檔案中的%(key)s結構會被解析,如,比如example.ini檔案內容如下:
[Paths]
home_dir: /Users
my_dir: %(home_dir)s/lumberjack
my_pictures: %(my_dir)s/Pictures
>>> import configparser
>>> config = configparser.ConfigParser(interpolation=configparser.BasicInterpolation())
>>> config.read(r'F:\coding\python\example.ini')
['F:\\coding\\python\\example.ini']
>>> config['Paths']['my_dir']
'/Users/lumberjack'
可以看到%(home_dir)s被解析成了/Users,說白了,相當於配置檔案中的變數
建立ConfigParser()類的時候如果沒有指定interpolation引數,則不會解析%(key)s,只會返回字串而已
>>> config['Paths']['my_dir']
'%(home_dir)s/lumberjack'
當然Interpolation還有更高階的使用方法,建立ConfigParser()類的時候指定interpolation引數為ExtendedInterpolation(),那麼解析器會解析${section:key}結構,那麼上面的ini檔案應該寫成如下的格式:
[Paths]
home_dir: /Users
my_dir: ${home_dir}/lumberjack
my_pictures: ${my_dir}/Pictures
並且ExtendedInterpolation()也能解析更復雜的,像下面這樣的ini檔案:
[Common]
home_dir: /Users
library_dir: /Library
system_dir: /System
macports_dir: /opt/local
[Frameworks]
Python: 3.2
path: ${Common:system_dir}/Library/Frameworks/
[Arthur]
nickname: Two Sheds
last_name: Jackson
my_dir: ${Common:home_dir}/twosheds
my_pictures: ${my_dir}/Pictures
python_dir: ${Frameworks:path}/Python/Versions/${Frameworks:Python}
ConfigParser
ConfigParser物件的其他方法,如:
- add_section(section)
- has_section(section)
- options(section)
- has_option(section, option)
- remove_option(section, option)
- remove_section(section)
都很常用,具體就不介紹了,看名字就知道是幹什麼的了
Python2.7 ConfigParser
該模組用來解析Microsoft Windows INI檔案,就是我們平常所說的ini檔案。INI檔案是一種按照特點方式排列的文字檔案。每一個INI檔案結構都非常類似,由若干段落(section)組成,在每個帶括號的標題下面,是若干個以單個單詞開頭的關鍵詞(keyword)和一個等號,等號右邊的就是關鍵字對應的值(value)。其一般形式如下:
[Section1]
KeyWord1 = Valuel
KeyWord2 = Value2
[Section2]
KeyWord3 = Value3
KeyWord4 = Value4
配置檔案由section組成,每個section裡面由name=value或者name:value組成,values中的空白符會被移除,在同一個section下的values可以包含該section下的其他values,以格式化字串的形式表現,或者該values在DEFAULT section中定義過。額外的DEFAULT section可以提供values的初始化,以#開頭的為註釋。
該模組下有三個類:
ConfigParser.RawConfigParser([defaults[, dict_type[, allow_no_value]]])
這是基本的配置類,該類不支援魔術插入。方法如下:
- RawConfigParser.defaults() 返回一個包含全部例項的字典
- RawConfigParser.sections() 返回一個包含有效section的列表,DEFAULT不包含在該列表中
- RawConfigParser.add_section(section) 增加一個section,如果section存在DuplicateSectionError會被觸發。
- RawConfigParser.has_section(section) 判斷section是否在配置檔案中存在
- RawConfigParser.options(section) 返回section中可用的options 列表
- RawConfigParser.has_option(section, option) 判斷section中是否存在options
- RawConfigParser.read(filenames) 讀入被解析的配置檔案
- RawConfigParser.readfp(fp[, filename]) 讀入並解析配置檔案
- RawConfigParser.get(section, option) 獲取section中option的值
- RawConfigParser.getint(section, option) 已整形返回option的值
- RawConfigParser.getfloat(section, option) 同理上面,返回float
- RawConfigParser.getboolean(section, option)
- RawConfigParser.items(section) 以列表(name,value)的形式返回section中的每個值
- RawConfigParser.set(section, option, value) 如果section存在,則設定該option和value,否則引起NoSectionError.
- RawConfigParser.write(fileobject) 配置寫入配置檔案中
- RawConfigParser.remove_option(section, option) 移除section中的option,如果section不存在,引起NoSectionError,移除後返回True,否則返回False
- RawConfigParser.remove_section(section) 移除section,返回True/False
- RawConfigParser.optionxform(option)
ConfigParser.ConfigParser([defaults[, dict_type[, allow_no_value]]])
該類是RawConfigParser的派生類。支援魔術插入,增加了get和items方法。
- ConfigParser.get(section, option[, raw[, vars]]) 獲取section中option的值,
- ConfigParser.items(section[, raw[, vars]]) 返回一個由(name,value)組成的列表對
ConfigParser.SafeConfigParser([defaults[, dict_type[, allow_no_value]]])
該類是ConfigParser的派生類,支援更多的魔術插入。
- SafeConfigParser.set(section, option, value) 如果section存在,則設定option的值。value必須是string。 生成ini配置檔案
#!/usr/bin/python
import ConfigParser
conf=ConfigParser.RawConfigParser()
conf.add_section('section1')
conf.add_section('section2')
conf.set('section1','name1','guol')
conf.set('section1','name2','alex')
conf.set('section2','name3','polo')
conf.set('section2','name4','mark')
conffile=open('file.ini','wb')
conf.write(conffile)
結果如下:
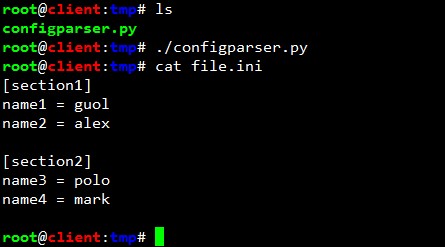
解析ini配置檔案:
import ConfigParser
conf=ConfigParser.RawConfigParser()
conf.read('file.ini')
if conf.has_section('section2'):
print 'Exist section2'
if conf.has_option('section2','name3'):
print 'section2 has opetion name3, is value' + ' ' +conf.get('section2','name3')
結果如下:

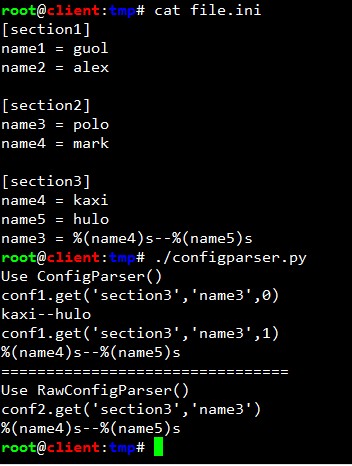
魔術插入:
import ConfigParser
conf1=ConfigParser.ConfigParser()
conf1.read('file.ini')
conf2=ConfigParser.RawConfigParser()
conf2.read('file.ini')
print 'Use ConfigParser()'
print '''conf1.get('section3','name3',0)'''
print conf1.get('section3','name3',0)
print '''conf1.get('section3','name3',1)'''
print conf1.get('section3','name3',1)
print '================================'
print 'Use RawConfigParser()'
print '''conf2.get('section3','name3')'''
print conf2.get('section3','name3')
結果如下: