C Primer Plus 第七章 課後答案
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-12
目錄
複習題
1.判斷下列表達式是true還是false
a. 100 > 3 && 'a'>'c'
b. 100 > 3 || 'a'>'c'
c. !(100>3)
a. false
b. true
c. false
2.根據下列描述的條件,分別構造一個表示式:
a number等於或大於90,但是小於100
b ch不是字元q或k
c number在1~9之間(包括1和9),但不是5
d number不在1~9之間
a. 90 <= number && number < 100
b. ch != 'q' && ch != 'k'
c. number >= 1 && number <= 9 && number != 5
d. number < 1 && number > 9
3.下面的程式關係表示式過於複雜,而且還有些錯誤,請簡化並改正
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) /* 1 */ { /* 2 */ int weight, height; /* weight以磅為單位,height以英寸為單位 *//* 4 */ scanf("%d , weight, height); /* 5 */ if (weight < 100 && height > 64) /* 6 */ if (height >= 72) /* 7 */ printf("You are very tall for your weight.\n"); else if (height < 72 &&> 64) /* 9 */ printf("You are tall for your weight.\n");/* 10 */ else if (weight > 300 && !(weight <= 300) /* 11 */ && height < 48) /* 12 */ if (!(height >= 48)) /* 13 */ printf(" You are quite short for your weight.\n"); else /* 15 */ printf("Your weight is ideal.\n"); /* 16 */ /* 17 */ return 0; }
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int weight, height; /* weight以磅為單位,height以英寸為單位 */
scanf("%d %d", &weight, &height);
if (weight < 100 && height > 64)
if (height >= 72)
printf("You are very tall for your weight.\n");
else /* 9 */
printf("You are tall for your weight.\n");
else if (weight > 300 && height < 48)
printf(" You are quite short for your weight.\n");
else
printf("Your weight is ideal.\n");
return 0;
}4.下列個表示式的值是多少
a.5 > 2
b.3 + 4 > 2 && 3 < 2
c.x >= y || y > x
d.d = 5 + ( 6 > 2 )
e.'X' > 'T' ? 10 : 5
f.x > y ? y > x : x > y
a. 1 b. 0 c. 1 d. 6 e. 10 f. 0
5.下面的程式將列印什麼
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int num;
for (num = 1; num <= 11; num++)
{
if (num % 3 == 0)
putchar('$');
else
putchar('*');
putchar('#');
putchar('%');
}
putchar('\n');
return 0;
}*#%*#%$#%*#%*#%$#%*#%*#%$#%*#%*#%
6.下面的程式將列印什麼
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < 3)
{
switch (i++)
{
case 0:
printf("fat ");
case 1:
printf("hat ");
case 2:
printf("cat ");
default:
printf("Oh no!");
}
putchar('\n');
}
return 0;
}fat hat cat Oh no!
hat cat Oh no!
cat Oh no!
7.下面的程式有哪些錯誤
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int lc = 0; // 統計小寫字母
int uc = 0; // 統計大寫字母
int oc = 0; // 統計其他字母
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if ('a' <= ch >= 'z')
lc++;
else if (!(ch < 'A') || !(ch > 'Z')
uc++;
oc++;
}
printf(%d lowercase, %d uppercase, %d other, lc, uc, oc);
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int lc = 0; // 統計小寫字母
int uc = 0; // 統計大寫字母
int oc = 0; // 統計其他字母
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if ('a' <= ch && ch <= 'z')
lc++;
else if (!(ch < 'A') && !(ch > 'Z')
uc++;
else:
oc++;
}
printf("%d lowercase, %d uppercase, %d other", lc, uc, oc);
return 0;
}8.下面的程式將列印什麼
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int age = 20;
while (age++ <= 65)
{
if ((age % 20) == 0) /* age是否能被20整除? */
printf("You are %d.Here is a raise.\n", age);
if (age = 65)
printf("You are %d.Here is your gold watch.\n", age);
}
return 0;
}先列印一次You are 20.Here is your gold watch.
再重複列印You are 65.Here is your gold watch.
【每一次賦值都會重置age為65】
9.給定下面的輸入時,以下程式將列印什麼
q
c
h
b
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if (ch == '\n')
continue;
printf("Step 1\n");
if (ch == 'c')
continue;
else if (ch == 'b')
break;
else if (ch == 'h')
goto laststep;
printf("Step 2\n");
laststep:
printf("Step 3\n");
}
printf("Done\n");
return 0;
}Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 1
Step 1
Step 3
Step 1
Done
10.重寫複習題9,但這次不能使用continue和goto語句
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if (ch == '\n')
else
{
printf("Step 1\n");
if (ch == 'c')
else
{
if (ch == 'b')
break;
else if (ch == 'h')
else
printf("Step 2\n");
printf("Step 3\n");
}
}
}
printf("Done\n");
return 0;
}程式設計練習
1.編寫一個程式讀取輸入,讀到#字元停止,然後報告讀取的空格數、換行符數和所有其他字元的數量
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int kg = 0, hh = 0, qt = 0;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
switch(ch)
{
case ' ':
kg++;
break;
case '\n':
hh++;
break;
default:
qt++;
}
}
printf("%-5d %-5d %-5d\n", kg, hh, qt);
return 0;
}
2.編寫一個程式讀取輸入,讀到#字元停止。程式要列印每個輸入的字元以及對應的ASCII碼(十進位制)。一行列印8個字元。建議:使用字元計數和求模運算子(%)在每8個迴圈週期時列印一個換行符
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int t = 1;
while ((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
putchar(ch);
printf("%d ", ch);
if(!(t++ % 8))
{
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
3.編寫一個程式,讀取整數直到使用者輸入 0。輸入結束後,程式應報告使用者輸入的偶數(不包括 0)個數、這些偶數的平均值、輸入的奇數個數及其奇數的平均值
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int os = 0, js = 0, oss = 0, jss = 0;
double osa = 0.0, jsa = 0.0;
int a;
while(scanf("%d", &a) && a)
{
if(a % 2)
{
js++;
jss += a;
}
else
{
os++;
oss += a;
}
}
if(os)
{
osa = double(oss) / double(os);
}
if(js)
{
jsa = double(jss) / double(js);
}
printf("%d %.2lf %d %.2lf\n", os, osa, js, jsa);
return 0;
}
4.使用if else語句編寫一個程式讀取輸入,讀到#停止。用感嘆號替換句號,用兩個感嘆號替換原來的感嘆號,最後報告進行了多少次替換
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int n = 0;
while((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
if(ch == '.')
{
putchar('!');
n++;
}
else if(ch == '!')
{
putchar('!');
putchar('!');
n++;
}
else
{
putchar(ch);
}
}
printf("\n%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
5.使用switch重寫練習4
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int n = 0;
while((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
switch(ch)
{
case '.':
putchar('!');
n++;
break;
case '!':
putchar('!');
putchar('!');
n++;
break;
default:
putchar(ch);
}
}
printf("\n%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
6.編寫程式讀取輸入,讀到#停止,報告ei出現的次數
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
char ch;
int n = 0, f = 0;
while((ch = getchar()) != '#')
{
switch(ch)
{
case 'e':
f = 1;
break;
case 'i':
if(f)
{
n++;
f = 0;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
printf("\n%d\n", n);
return 0;
}
7.編寫一個程式,提示使用者輸入一週工作的小時數,然後列印工資總額、稅金和淨收入。做如下假設:
a.基本工資 = 10美元/小時
b.加班(超過40小時) = 1.5倍的時間
c.稅率: 前300美元為15% 續150美元為20% 餘下的為25%
用#define定義符號常量。不用在意是否符合當前的稅法
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXT 40.0
#define GH 10.0
#define FR 300.0
#define SR 450.0
#define FTR 0.15
#define STR 0.20
#define TTR 0.25
int main(void)
{
float t, sum, tax, gain;
scanf("%f", &t);
if(t > MAXT)
{
t = MAXT + (t - MAXT) * 1.5;
}
sum = GH * t;
if(sum <= FR)
{
tax = sum * FTR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
else if(sum > FR && sum < SR)
{
tax = FR * FTR + (sum - FR) * STR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
else if(sum > SR)
{
tax = FR * FTR + (SR - FR) * STR + (sum - SR) * TTR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
printf("%-10.2f%-10.2f%-10.2f%-10.2f\n", t, sum, gain, tax);
return 0;
}
8.修改練習7的假設a,讓程式可以給出一個供選擇的工資等級選單。使用switch完成工資等級選擇。執行程式後,顯示的選單應該類似這樣: *****************************************************************
Enter the number corresponding to the desired pay rate or action:
1) $8.75/hr 2) $9.33/hr
3) $10.00/hr 4) $11.20/hr
5) quit
*****************************************************************
如果選擇 1~4 其中的一個數字,程式應該詢問使用者工作的小時數。程式要通過迴圈執行,除非使用者輸入 5。如果輸入 1~5 以外的數字,程式應提醒使用者輸入正確的選項,然後再重複顯示選單提示使用者輸入。使用#define建立符號常量表示各工資等級和稅率
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAXT 40.0
#define GH 10.0
#define FR 300.0
#define SR 450.0
#define FTR 0.15
#define STR 0.20
#define TTR 0.25
int main(void)
{
float t, sum, tax, gain;
scanf("%f", &t);
if(t > MAXT)
{
t = MAXT + (t - MAXT) * 1.5;
}
float gh;
int num, f = 0, x = 1;
printf("***************************************************************** \n");
printf("Enter the number corresponding to the desired pay rate or action: \n");
printf("1) $8.75/hr 2) $9.33/hr\n3) $10.00/hr 4) $11.20/hr\n5) quit \n");
printf("***************************************************************** \n");
scanf("%d", &num);
while(x)
{
switch(num)
{
case 1:
gh = 8.75;
x = 0;
break;
case 2:
gh = 9.33;
x = 0;
break;
case 3:
gh = 10.00;
x = 0;
break;
case 4:
gh = 11.20;
x = 0;
break;
case 5:
return 0;
break;
default:
printf("input from 1 to 5:");
scanf("%d", &num);
}
}
sum = gh * t;
if(sum <= FR)
{
tax = sum * FTR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
else if(sum > FR && sum < SR)
{
tax = FR * FTR + (sum - FR) * STR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
else if(sum > SR)
{
tax = FR * FTR + (SR - FR) * STR + (sum - SR) * TTR;
gain = sum - tax;
}
printf("%-10.2f%-10.2f%-10.2f%-10.2f\n", t, sum, gain, tax);
return 0;
}
9.編寫一個程式,只接受正整數輸入,然後顯示所有小於或等於該數的素數
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
long long num;
int x = 1;
while(x)
{
if(scanf("%d", &num) == 1)
{
if(num < 1)
{
continue;
}
else
{
x = 0;
const int len = num;
int a[len + 1];
memset(a, 0, sizeof(int) * (len + 1));
for(int i = 2; i <= num; i++)
{
if(!a[i])
{
for(int j = i + i; j <= num; j += i)
{
a[j] = 1;
}
}
}
for(int i = 2; i <= num; i++)
{
if(!a[i])
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
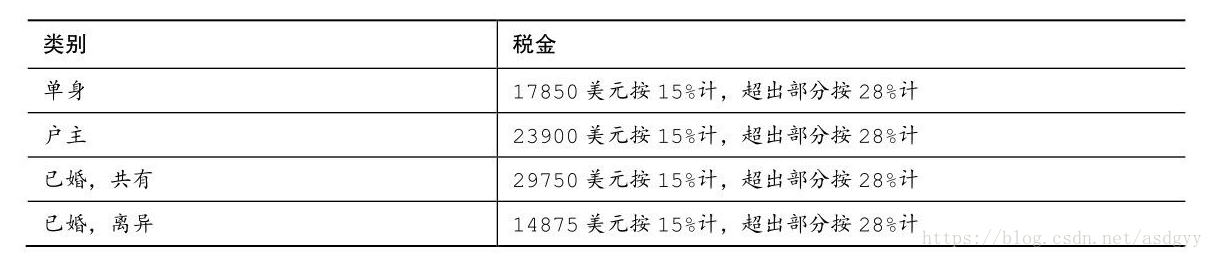
10.1988年的美國聯邦稅收計劃是近代最簡單的稅收方案。它分為4個類別,每個類別有兩個等級。 下面是該稅收計劃的摘要(美元數為應徵稅的收入):
例如,一位工資為20000美元的單身納稅人,應繳納稅0.15×17850+0.28×(20000−17850)美元。編寫一個程式,讓使用者指定繳納稅金的種類和應納稅收入,然後計算稅金。程式應通過迴圈讓使用者可以多次輸入
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
float income, tax_r, tax;
int type;
printf("*******************************************************\n");
printf("1)單身 2)戶主\n3)已婚,共有 4)已婚,離異\n5)退出\n");
printf("*******************************************************\n");
printf("input type:");
while(scanf("%d", &type) == 1)
{
int x = 1;
while(x)
{
switch(type)
{
case 1:
tax_r = 17850.0;
x = 0;
break;
case 2:
tax_r = 23900.0;
x = 0;
break;
case 3:
tax_r = 29750.0;
x = 0;
break;
case 4:
tax_r = 14875.0;
x = 0;
break;
case 5:
return 0;
default:
printf("input from 1 to 5:");
scanf("%d", &type);
}
}
printf("input income:");
scanf("%f", &income);
if(income > tax_r)
{
tax = tax_r * 0.15 + (income - tax_r) * 0.28;
}
else
{
tax = income * 0.15;
}
printf("tax is %.2f\n", tax);
printf("input from 1 to 4 to continue or input 5 to exit:");
}
return 0;
}
11.ABC 郵購雜貨店出售的
洋薊售價為 2.05 美元/磅,
甜菜售價為 1.15 美元/磅,
胡蘿蔔售價為 1.09美元/磅。
在新增運費之前,100美元的訂單有5%的打折優惠。
少於或等於5磅的訂單收取6.5美元的運費和包裝費,
5磅~20磅的訂單收取14美元的運費和包裝費,
超過20磅的訂單在14美元的基礎上每續重1磅增加0.5美元。
編寫一個程式,在迴圈中用switch語句實現使用者輸入不同的字母時有不同的響應,即輸入a的響應是讓使用者輸入洋薊的磅數,b是甜菜的磅數,c是胡蘿蔔的磅數,q 是退出訂購。程式要記錄累計的重量。即,如果使用者輸入 4 磅的甜菜,然後輸入 5磅的甜菜,程式應報告9磅的甜菜。然後,該程式要計算貨物總價、折扣(如果有的話)、運費和包裝費。隨後,程式應顯示所有的購買資訊:物品售價、訂購的重量(單位:磅)、訂購的蔬菜費用、訂單的總費用、折扣(如果有的話)、運費和包裝費,以及所有的費用總額
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
const float ap = 2.05;
const float bp = 1.15;
const float cp = 1.09;
int main(void)
{
char ch;
float sum, discount, df;
int an = 0, bn = 0, cn = 0, sn = 0, n;
while((ch = getchar()) != 'q')
{
switch(ch)
{
case 'a':
printf("\ninput n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
an += n;
sn += n;
sum += ap * n;
break;
case 'b':
printf("\ninput n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
bn += n;
sn += n;
sum += bp * n;
break;
case 'c':
printf("\ninput n:");
scanf("%d", &n);
cn += n;
sn += n;
sum += cp * n;
break;
default:
printf("input a or b or c or q:");
}
getchar();
}
if(sum > 100)
{
discount = 0.05 * sum;
}
else
{
discount = 0.0;
}
if(sn <= 5)
{
df = 6.5;
}
else if(sn < 20)
{
df = 14.0;
}
else
{
df = 14.0 + (sn - 20) * 0.5;
}
printf("ap = %.2f, bp = %.2f, cp = %.2f\n", ap, bp, cp);
printf("an = %d, bn = %d, cn = %d\n", an, bn, cn);
printf("a is %.2f, b is %.2f, c is %.2f\n", ap * an, bp * bn, cp * cn);
printf("sum is %.2f, discount is %.2f, df is %.2f\n", sum, discount, df);
return 0;
}