android系統瀏覽器下載流程
簡介
當我們用瀏覽器點開一個下載連結,然後去下載,從巨集觀上認識,有下載進度的實時更新和介面的跳轉。整個過程中,主要涉及到以下過程。瀏覽器點選下載按鈕,瀏覽器分發下去一個下載請求,跳轉介面的同時在DownloadProvider程序中去真正的下載資料以及更新資料庫,在介面上監聽資料庫的變化,去實時更新相關進度。全過程中,Browser程序負責分發下載請求,DownloadProvider程序負責真正的下載操作。
目前而言,主要有兩種結構,C-S和B-S結構。對於Browser來說,主要在於對Webview這個控制元件的認識,底層的核心實現也是非常複雜,這裡我們不做討論。對於一個瀏覽器連結,webkit底層會去解析,同時也會判斷這個連結屬於什麼型別。比如我們今天的這個下載連結,Browser就有專門的下載監聽器去回撥執行這個action,下面我們會詳細分析。
WebView控制元件簡單介紹
WebView控制元件提供了一個內嵌的瀏覽器試圖,用於顯示本地的html或網路上的網頁。 並且比較強大的是,還可以直接跟js相互呼叫。 WebView有兩個方法:setWebChromeClient和setWebClient WebChromeClient:主要處理解析,渲染網頁等瀏覽器做的事情,也是輔助WebView處理Javascript 的對話方塊,網站圖示,網站title,載入進度等 WebViewClient :就是幫助WebView處理各種通知、請求事件的。
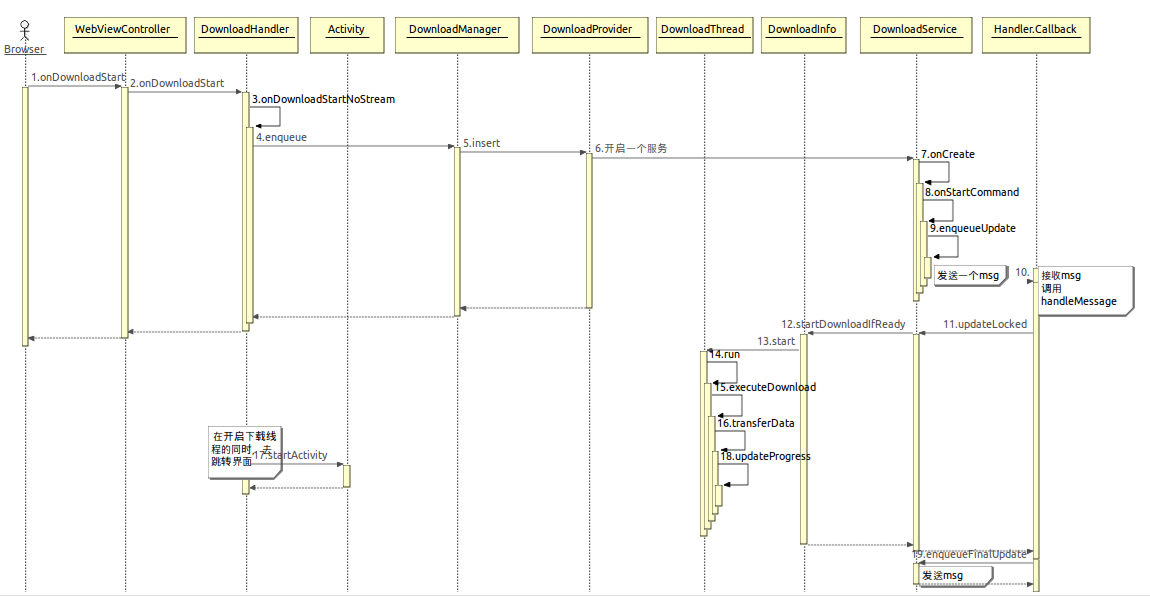
Browser下載的時序圖。
下面來詳細分析具體的程式碼實現細節,時序圖是更加細節的步驟,這裡我們著重分析下面的流程。
Step 1:Tab.setWebView
void setWebView(WebView w, boolean restore) { .... mMainView = w; // attach the WebViewClient, WebChromeClient and DownloadListener if (mMainView != null) { mMainView.setWebViewClient(mWebViewClient); mMainView.setWebChromeClient(mWebChromeClient); mMainView.setDownloadListener(mDownloadListener); .... } }
這個方法定義在packages/apps/Browser/src/com/android/browser/Tab.java 瀏覽器是用過Webview來顯示UI。這裡設定了一個WebView物件,然後setWebViewClient和setWebChromeClient主要設定了對頁面載入以及js的處理。這裡我們只分析setDownloadListener這個監聽,首先要理解一點,對於WebView上的一個下載按鈕,它的事件是怎麼處理的,瀏覽器如何判斷這個是下載?以上其實瀏覽器核心已經處理,瀏覽器核心是根據指定的url判斷該連結是否是一個下載連結,如果點選的是一個下載連結,那麼最終會回撥到該監聽器中去處理,具體底層實現比較複雜,暫不作討論。
Tab(WebViewController wvcontroller, WebView w, Bundle state) {
/// M: add for save page
....
mDownloadListener = new BrowserDownloadListener() {
public void onDownloadStart(String url, String userAgent,
String contentDisposition, String mimetype, String referer,
long contentLength) {
/// M: add for fix download page url
mCurrentState.mIsDownload = true;
mWebViewController.onDownloadStart(Tab.this, url, userAgent, contentDisposition,
mimetype, referer, contentLength);
}
};
....
setWebView(w);
....
}這個方法定義在packages/apps/Browser/src/com/android/browser/Tab.java 分析Tab的構造方法,這裡主要看BrowserDownloadListener這個物件。當點選了下載按鈕,則會去回撥BrowserDownloadListener的onDownloadStart方法,這個最終是委託給了mWebViewController去處理。
Step 2:WebViewController.onDownloadStart
@Override
public void onDownloadStart(Tab tab, String url, String userAgent,
String contentDisposition, String mimetype, String referer,
long contentLength) {
....
DownloadHandler.onDownloadStart(mActivity, url, userAgent,
contentDisposition, mimetype, referer, false, contentLength);
...
}這個方法定義在packages/apps/Browser/src/com/android/browser/Controller.java WebViewController是一個介面,Controller是它的具體實現,在onDownloadStart方法中,實現比較簡單,直接是將引數委託給DownloadHandler的靜態方法onDownloadStart去進一步處理。 在這裡,引數: url下載的網址連結 userAgent瀏覽器userAgent資訊 mimetype下載內容的type型別 contentLength下載內容大小
Step 3:DownloadHandler.onDownloadStart
這個方法定義在packages/apps/Browser/src/com/android/browser/DownloadHandler.java 實現很簡單,直接將引數繼續傳遞到onDownloadStartNoStream方法。
Step 4:DownloadHandler.onDownloadStartNoStream
/*package */
public static void onDownloadStartNoStream(Activity activity,
String url, String userAgent, String contentDisposition,
String mimetype, String referer, boolean privateBrowsing, long contentLength) {
....
// java.net.URI is a lot stricter than KURL so we have to encode some
// extra characters. Fix for b 2538060 and b 1634719
WebAddress webAddress;
try {
webAddress = new WebAddress(url);
webAddress.setPath(encodePath(webAddress.getPath()));
} catch (Exception e) {
// This only happens for very bad urls, we want to chatch the
// exception here
Log.e(LOGTAG, "Exception trying to parse url:" + url);
return;
}
String addressString = webAddress.toString();
Uri uri = Uri.parse(addressString);
final DownloadManager.Request request = new DownloadManager.Request(uri);
request.setMimeType(mimetype);
// let this downloaded file be scanned by MediaScanner - so that it can
// show up in Gallery app, for example.
request.allowScanningByMediaScanner();
request.setDescription(webAddress.getHost());
// XXX: Have to use the old url since the cookies were stored using the
// old percent-encoded url.
String cookies = CookieManager.getInstance().getCookie(url, privateBrowsing);
request.addRequestHeader("cookie", cookies);
request.addRequestHeader("User-Agent", userAgent);
request.addRequestHeader("Referer", referer);
request.setNotificationVisibility(
DownloadManager.Request.VISIBILITY_VISIBLE_NOTIFY_COMPLETED);
request.setUserAgent(userAgent);
final DownloadManager manager = (DownloadManager)
activity.getSystemService(Context.DOWNLOAD_SERVICE);
new Thread("Browser download") {
public void run() {
manager.enqueue(request);
}
}.start();
/// M: Add to start Download activity. @{
Intent pageView = new Intent(DownloadManager.ACTION_VIEW_DOWNLOADS);
pageView.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
activity.startActivity(pageView);
/// @}
}這個方法定義在packages/apps/Browser/src/com/android/browser/DownloadHandler.java 在該方法中,主要做了三件事 1.將下載資訊url,minetype等封裝成一個Request物件,供後續使用。 2.獲取一個DownloadManager物件,將前面封裝的Request物件,安排到下載佇列 3.開始下載的同時,去跳轉UI介面,同步顯示UI資訊。 這裡我們重點分析資料流程這塊,接下來分析enqueue這個方法的具體實現。
Step 5:DownloadManager.enqueue
public long enqueue(Request request) {
ContentValues values = request.toContentValues(mPackageName);
Uri downloadUri = mResolver.insert(Downloads.Impl.CONTENT_URI, values);
if (downloadUri != null) {
long id = Long.parseLong(downloadUri.getLastPathSegment());
return id;
}
return -1;
}這個方法定義在frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/DownloadManager.java 首先toContentValues將Request的資訊要存資料庫的欄位轉化為一個ContentValues物件,以上幾步都是在Browser程序中進行的,接下來insert方法,通過uri開始最終跨程序請求去插入資料。這裡Downloads.Impl.CONTENT_URI為content://downloads/my_downloads,從pacakges/providers/DownloadProvider的清單檔案中很容易知道最終是呼叫了DownloadProvider的insert方法去插入資料。 pacakges/providers/DownloadProvider的清單檔案如下:
....
<provider android:name=".DownloadProvider"
android:authorities="downloads" android:exported="true">
....Step 6:DownloadProvider.insert
@Override
public Uri insert(final Uri uri, final ContentValues values) {
....
long rowID = db.insert(DB_TABLE, null, filteredValues);
if (rowID == -1) {
Log.d(Constants.TAG, "couldn't insert into downloads database");
return null;
}
insertRequestHeaders(db, rowID, values);
notifyContentChanged(uri, match);
// Always start service to handle notifications and/or scanning
final Context context = getContext();
context.startService(new Intent(context, DownloadService.class));
return ContentUris.withAppendedId(Downloads.Impl.CONTENT_URI, rowID);
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadProvider.java insert方法即是往DB_TABLE(downloads)表中插入了一條資料。接下來在insert方法最後啟動DownloadService,這幾步都是在DownloadProvider程序中進行的。接下來會有兩條主線。 1,在DownloadProvider程序中啟動的這個DownloadService繼續執行。 2,返回到Step 4 Browser程序的中的DownloadHandler.onDownloadStartNoStream方法中去跳轉介面。 這裡我們不討論UI介面,接下來分析DownloadService的操作。
Step 7:DownloadService.onCreate
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
....
mUpdateThread = new HandlerThread(TAG + "-UpdateThread");
mUpdateThread.start();
mUpdateHandler = new Handler(mUpdateThread.getLooper(), mUpdateCallback);
mScanner = new DownloadScanner(this);
mNotifier = new DownloadNotifier(this);
mNotifier.cancelAll();
mObserver = new DownloadManagerContentObserver();
getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(Downloads.Impl.ALL_DOWNLOADS_CONTENT_URI,
true, mObserver);
....
}
這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadService.java 第一次啟動,首次執行onCreate方法,建立一個HandlerThread工作執行緒,並註冊了一個監聽資料庫改變的一個DownloadManagerContentObserver物件,監聽的uri為”content://downloads/all_downloads”,第2個引數為true,表示可以同時匹配其派生的Uri。接下來進入onStartCommand方法,在onStartCommand方法中繼續執行enqueueUpdate方法。
public void enqueueUpdate() {
if (mUpdateHandler != null) {
mUpdateHandler.removeMessages(MSG_UPDATE);
mUpdateHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_UPDATE, mLastStartId, -1).sendToTarget();
}
}這個方法執行很簡單,首先是移除掉之前所有的MSG_UPDATE訊息,然後再重新發送一個MSG_UPDATE訊息,接下來分析Handler這個訊息的回撥實現。
private Handler.Callback mUpdateCallback = new Handler.Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message msg) {
Process.setThreadPriority(Process.THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND);
final int startId = msg.arg1;
final boolean isActive;
synchronized (mDownloads) {
isActive = updateLocked();
}
if (msg.what == MSG_FINAL_UPDATE) {
mNotifier.dumpSpeeds();
}
if (isActive) {
// Still doing useful work, keep service alive. These active
// tasks will trigger another update pass when they're finished.
// Enqueue delayed update pass to catch finished operations that
// didn't trigger an update pass; these are bugs.
enqueueFinalUpdate();
} else {
// No active tasks, and any pending update messages can be
// ignored, since any updates important enough to initiate tasks
// will always be delivered with a new startId.
if (stopSelfResult(startId)) {
if (DEBUG_LIFECYCLE) Log.v(TAG, "Nothing left; stopped");
getContentResolver().unregisterContentObserver(mObserver);
mScanner.shutdown();
mUpdateThread.quit();
}
}
return true;
}
};這個方法處理的邏輯比較多,先整體上認識這個,主要有updateLocked方法主要負責具體的下載實現,它的返回值是一個boolean型別,用以判斷當前下載是否是啟用狀態,也就是是否有下載任務。接下來如果判斷isActive為true,則會去執行enqueueFinalUpdate方法。
private void enqueueFinalUpdate() {
mUpdateHandler.removeMessages(MSG_FINAL_UPDATE);
mUpdateHandler.sendMessageDelayed(
mUpdateHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_FINAL_UPDATE, mLastStartId, -1),
5 * MINUTE_IN_MILLIS);
}從這裡我們可以看出,這個回撥其實是當有下載任務的時候,會一直的迴圈執行下去,用以保證下載的任務的連續性,如果有中斷,則會重新啟動。 下面我們來分析updateLocked的具體實現,是如何將下載任務放入執行緒中去執行的,又是怎麼知道有哪些下載任務的。
Step 8 :DownloadService.updateLocked
private boolean updateLocked() {
...
final Cursor cursor = resolver.query(Downloads.Impl.ALL_DOWNLOADS_CONTENT_URI,
null, null, null, null);
try {
final DownloadInfo.Reader reader = new DownloadInfo.Reader(resolver, cursor);
final int idColumn = cursor.getColumnIndexOrThrow(Downloads.Impl._ID);
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
final long id = cursor.getLong(idColumn);
staleIds.remove(id);
DownloadInfo info = mDownloads.get(id);
if (info != null) {
updateDownload(reader, info, now);
} else {
info = insertDownloadLocked(reader, now);
}
if (info.mDeleted) {
// Delete download if requested, but only after cleaning up
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(info.mMediaProviderUri)) {
resolver.delete(Uri.parse(info.mMediaProviderUri), null, null);
}
deleteFileIfExists(info.mFileName);
resolver.delete(info.getAllDownloadsUri(), null, null);
} else {
// Kick off download task if ready
final boolean activeDownload = info.startDownloadIfReady(mExecutor);
// Kick off media scan if completed
final boolean activeScan = info.startScanIfReady(mScanner);
isActive |= activeDownload;
isActive |= activeScan;
}
// Keep track of nearest next action
nextActionMillis = Math.min(info.nextActionMillis(now), nextActionMillis);
}
} finally {
cursor.close();
}
// Clean up stale downloads that disappeared
for (Long id : staleIds) {
deleteDownloadLocked(id);
}
...
return isActive;
}這個方法的實現分為幾步: 1.查詢downloads表中的所有記錄,接著將其封裝成一個DownloadInfo物件。 2.顯然第一次DownloadInfo的info是空值,接下來insertDownloadLocked會根據Cursor去新建一個DownloadInfo資訊。 3.DownloadInfo快取的管理,將DownloadInfo快取至mDownloads中管理。這裡有個小的判斷分支,如果info.mDeleted為true,則刪除掉這條下載記錄,並且對應的檔案也將被刪除,其實屬於邏輯控制,跟下載無太大關係,不用太糾結。 4.對於一個新的下載,info.mDeleted顯然是false,所以會進入到到else語句,呼叫DownloadInfo的startDownloadIfReady方法開始下載。 我們先分析insertDownloadLocked新建一個下載任務DownloadInfo的流程
private DownloadInfo insertDownloadLocked(DownloadInfo.Reader reader, long now) {
final DownloadInfo info = reader.newDownloadInfo(this, mSystemFacade, mNotifier);
mDownloads.put(info.mId, info);
if (Constants.LOGVV) {
Log.v(Constants.TAG, "processing inserted download " + info.mId);
}
return info;
}這個方法中,呼叫DownloadInfo.Reader去新建一個下載任務,從前面可以看出,這個reader物件是由資料庫Cursor進行封裝的,具體分析reader.newDownloadInfo方法
public DownloadInfo newDownloadInfo(
Context context, SystemFacade systemFacade, DownloadNotifier notifier)
final DownloadInfo info = new DownloadInfo(context, systemFacade, notifier);
updateFromDatabase(info);
readRequestHeaders(info);
return info;
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadInfo.java Reader是DownloadInfo的一個靜態內部類,這個方法中,首先是new了一個DownloadInfo物件,然後呼叫updateFromDatabase去更新DownloadInfo的一些屬性值。實現比較簡單,就是根據前面的Cursor物件,獲取資料庫的一些欄位值儲存在DownloadInfo中。
從這裡我們可以看出,資料庫中所有的資訊都會封裝成一個下載DownloadInfo,那麼它是通過什麼來判斷當前資料是否是需要下載的任務呢?顯然如果這個url對應的任務已經被下載完成了,那麼肯定是不需要再次下載的。接下來我們繼續往下走,進入到startDownloadIfReady這個方法。
Step 9:DownloadInfo.startDownloadIfReady
public boolean .startDownloadIfReady(ExecutorService executor) {
synchroized (this) {
final boolean isReady = isReadyToDownload();
final boolean isActive = mSubmittedTask != null && !mSubmittedTask.isDone();
if (isReady && !isActive) {
if (mStatus != Impl.STATUS_RUNNING) {
mStatus = Impl.STATUS_RUNNING;
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(Impl.COLUMN_STATUS, mStatus);
mContext.getContentResolver().update(getAllDownloadsUri(), values, null, null);
}
mTask = new DownloadThread(mContext, mSystemFacade, mNotifier, this);
mSubmittedTask = executor.submit(mTask);
}
return isReady;
}
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadInfo.java 我們先分析isReadyToDownload這個方法。
private boolean isReadyToDownload() {
....
switch (mStatus) {
case 0: // status hasn't been initialized yet, this is a new download
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_PENDING: // download is explicit marked as ready to start
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_RUNNING: // download interrupted (process killed etc) while
// running, without a chance to update the database
return true;
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_WAITING_FOR_NETWORK:
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_QUEUED_FOR_WIFI:
return checkCanUseNetwork(mTotalBytes) == NetworkState.OK;
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_WAITING_TO_RETRY:
// download was waiting for a delayed restart
final long now = mSystemFacade.currentTimeMillis();
return restartTime(now) <= now;
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_DEVICE_NOT_FOUND_ERROR:
// is the media mounted?
return Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED);
/// M: Because OMA DL spec, if insufficient memory, we
/// will show to user but not retry.
//case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_INSUFFICIENT_SPACE_ERROR:
// should check space to make sure it is worth retrying the download.
// but thats the first thing done by the thread when it retries to download
// it will fail pretty quickly if there is no space.
// so, it is not that bad to skip checking space availability here.
//return true;
/// M: Add for fix alp00406729, file already exist but user do not operation. @{
case Downloads.Impl.STATUS_FILE_ALREADY_EXISTS_ERROR:
return false;
/// @}
}
return false;
}一切都明白了,這裡就是根據mStatus這個欄位,來判斷這個任務是否需要下載,也解決了我們之前的疑問,返回值為true的才會去執行下載,我們可以回頭看看Browser裡面當時insert一條下載記錄的時候,是沒有插入mStatus這個欄位的,所以對於一個新任務這裡mStatus為預設值即0,整個返回值為true。 接下來分析isActive這個boolean值,它主要用來標識當前DownloadInfo是否線上程中去執行了,保證一個DownloadInfo只執行一次,對於新任務,顯然初始化的時候mSubmittedTask為null。
接下來進入if語句,先update資料庫中的COLUMN_STATUS欄位置為STATUS_RUNNING。然後新建一個DownloadThread,放入到ExecutorService執行緒池中去執行,這樣一個下載連結就正式開始下載了。接下來分析下載讀寫檔案以及更新資料庫的動作。
Step 10:new DownloadThread
@Override
public void run() {
....
if (DownloadInfo.queryDownloadStatus(mContext.getContentResolver(), mId)
== Downloads.Impl.STATUS_SUCCESS) {
logDebug("Already finished; skipping");
return;
}
....
executeDownload();
....
}這個方法定義在 DownloadThread是一個Runnable物件,這裡我們關注構造方法中的第4個引數,即DownloadInfo,將DownloadInfo這個物件的資訊,傳給DownloadThread的成員變數,還有DownloadInfoDelta物件,最後用於更新下載進度資料庫資訊,我們後續分析。這樣就完全得到了這條下載資訊的內容。接下來去執行DownloadThread的run方法,在新的執行緒中進行下載。在run方法的實現中,首先是再次確認這個任務是需要下載的,否則直接return,執行緒結束,然後如果需要下載則去呼叫executeDownload方法去執行。
private void executeDownload() throws StopRequestException {
.....
URL url;
try {
// TODO: migrate URL sanity checking into client side of API
url = new URL(mInfoDelta.mUri);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_BAD_REQUEST, e);
}
int redirectionCount = 0;
while (redirectionCount++ < Constants.MAX_REDIRECTS) {
// Open connection and follow any redirects until we have a useful
// response with body.
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
try {
checkConnectivity();
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setInstanceFollowRedirects(false);
conn.setConnectTimeout(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
conn.setReadTimeout(DEFAULT_TIMEOUT);
addRequestHeaders(conn, resuming);
final int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
switch (responseCode) {
case HTTP_OK:
....
/// @}
transferData(conn);
return;
.....
}
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS, "Too many redirects");
}在executeDownload方法中根據url建立一個HttpURLConnection連線。然後判斷getResponseCode網路端返回值。這裡我們分析HTTP_OK的情況。在HTTP_OK:接下來呼叫transferData(conn);傳入的引數為這個HttpURLConnection這個連線。
Step 11:DownloadThread.transferData
private void transferData(HttpURLConnection conn) throws StopRequestException {
....
DrmManagerClient drmClient = null;
ParcelFileDescriptor outPfd = null;
FileDescriptor outFd = null;
InputStream in = null;
OutputStream out = null;
try {
try {
in = conn.getInputStream();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_HTTP_DATA_ERROR, e);
}
try {
outPfd = mContext.getContentResolver()
.openFileDescriptor(mInfo.getAllDownloadsUri(), "rw");
outFd = outPfd.getFileDescriptor();
if (DownloadDrmHelper.isDrmConvertNeeded(mInfoDelta.mMimeType)) {
drmClient = new DrmManagerClient(mContext);
out = new DrmOutputStream(drmClient, outPfd, mInfoDelta.mMimeType);
} else {
out = new ParcelFileDescriptor.AutoCloseOutputStream(outPfd);
}
// Pre-flight disk space requirements, when known
if (mInfoDelta.mTotalBytes > 0) {
final long curSize = Os.fstat(outFd).st_size;
final long newBytes = mInfoDelta.mTotalBytes - curSize;
StorageUtils.ensureAvailableSpace(mContext, outFd, newBytes);
// We found enough space, so claim it for ourselves
Os.posix_fallocate(outFd, 0, mInfoDelta.mTotalBytes);
}
// Move into place to begin writing
Os.lseek(outFd, mInfoDelta.mCurrentBytes, OsConstants.SEEK_SET);
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_FILE_ERROR, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_FILE_ERROR, e);
}
// Start streaming data, periodically watch for pause/cancel
// commands and checking disk space as needed.
transferData(in, out, outFd);
....
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadThread.java 在這個方法中,獲取一個該url對應的網路輸入流物件InputStream,同時根據uri構造一個檔案描述符,進而構建一個輸出流OutputStream物件,最後到過載的transferData方法,將輸入輸出流,以及檔案描述符傳入transferData開始儲存檔案。
private void transferData(InputStream in, OutputStream out, FileDescriptor outFd)
throws StopRequestException {
final byte buffer[] = new byte[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
while (true) {
checkPausedOrCanceled();
int len = -1;
try {
len = in.read(buffer);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(
STATUS_HTTP_DATA_ERROR, "Failed reading response: " + e, e);
}
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
try {
// When streaming, ensure space before each write
if (mInfoDelta.mTotalBytes == -1) {
final long curSize = Os.fstat(outFd).st_size;
final long newBytes = (mInfoDelta.mCurrentBytes + len) - curSize;
StorageUtils.ensureAvailableSpace(mContext, outFd, newBytes);
}
out.write(buffer, 0, len);
mMadeProgress = true;
mInfoDelta.mCurrentBytes += len;
updateProgress(outFd);
} catch (ErrnoException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_FILE_ERROR, e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_FILE_ERROR, e);
}
}
.....
}真正開始下載都是在這段code中,首先checkPausedOrCanceled方法檢查是否有取消下載請求,如果有直接進入catch語句跳過,下載結束。如果沒有取消,則執行while語句,執行輸入輸出流的讀寫操作。每一次讀寫的同時都會執行updateProgress方法,顯然該方法是用來更新進度的,下面具體來分析。
Step 12:DownloadThread.updateProgress
private void updateProgress(FileDescriptor outFd) throws IOException, StopRequestException {
....
final long bytesDelta = currentBytes - mLastUpdateBytes;
final long timeDelta = now - mLastUpdateTime;
if (bytesDelta > Constants.MIN_PROGRESS_STEP && timeDelta > Constants.MIN_PROGRESS_TIME) {
// fsync() to ensure that current progress has been flushed to disk,
// so we can always resume based on latest database information.
outFd.sync();
//mInfoDelta.writeToDatabaseOrThrow();
mInfoDelta.writeToDatabaseWithoutModifyTime();
mLastUpdateBytes = currentBytes;
mLastUpdateTime = now;
}
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadThread.java 總共做了兩件事,第一,呼叫outFd.sync強制所有系統緩衝區與基礎裝置同步,第二呼叫mInfoDelta的writeToDatabaseWithoutModifyTime去更新資料庫操作,即將當前進度,下載了多少update到資料庫。
Step 13:DownloadInfoDelta.writeToDatabaseWithoutModifyTime
public void writeToDatabaseWithoutModifyTime() throws StopRequestException {
final ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_URI, mUri);
values.put(Downloads.Impl._DATA, mFileName);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_MIME_TYPE, mMimeType);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_STATUS, mStatus);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_FAILED_CONNECTIONS, mNumFailed);
values.put(Constants.RETRY_AFTER_X_REDIRECT_COUNT, mRetryAfter);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_TOTAL_BYTES, mTotalBytes);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_CURRENT_BYTES, mCurrentBytes);
values.put(Constants.ETAG, mETag);
values.put(Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_ERROR_MSG, mErrorMsg);
if (mContext.getContentResolver().update(mInfo.getAllDownloadsUri(),
values, Downloads.Impl.COLUMN_DELETED + " == '0'", null) == 0) {
throw new StopRequestException(STATUS_CANCELED, "Download deleted or missing!");
}
}
}這個方法定義在packages/providers/DownloadProvider/src/com/android/providers/downloads/DownloadThread.java DownloadInfoDelta是DownloadThread的一個內部類,主要用於更新資料庫進度操作,這個方法中此時uri為”content://downloads/all_downloads/id”,對應DownloadProvider的update方法去更新資料庫,而此時又會回撥至DowbloadService中的DownloadManagerContentObserver監聽中,因為此時對應uri資料庫內容已經改變。至此,整個updateLocked方法執行完畢。
簡單分析DownloadManagerContentObserver內容,可以看出這個目的還是保證了下載的連續性,只要每次有下載資料更新,則會迴圈檢測,以確保下載任務的連續性。
private class DownloadManagerContentObserver extends ContentObserver {
public DownloadManagerContentObserver() {
super(new Handler());
}
@Override
public void onChange(final boolean selfChange) {
enqueueUpdate();
}
}至此,整個下載過程已經結束,至於UI介面的更新情況,則只需要監聽資料庫中的資料變化,或者在有下載任務時候,間隔一段時間去資料庫查詢進度資訊,更新進度即可。
對於下載介面,自4.4之後,都是BrowserActivity->DownloadList->DocumentActivity,而且對於DocumentUI正是採用的一段時間查詢資料庫,更新的方式,這裡我們也不討論了。