神經網路實踐-全連線網路實踐
輸入手寫數字輸出識別結果
本節目標:
輸入手寫數字圖片輸出識別結果&製作資料集
1、實現斷點續訓
2、輸入真實圖片,輸出預測結果
3、製作資料集,實現特定應用
輸入手寫數字圖片輸出識別結果
一、斷點續訓
關鍵處理:加入ckpt操作:
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt andckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess,ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)1、註解:
1)tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(checkpoint_dir,latest_filename=None)
該函式表示如果斷點資料夾中包含有效斷點狀態檔案,則返回該檔案。
引數說明:checkpoint_dir:表示儲存斷點檔案的目錄
latest_filename=None:斷點檔案的可選名稱,預設為“checkpoint”
2)saver.restore(sess,ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
該函式表示恢復當前會話,將ckpt中的值賦給w和b。
引數說明:sess:表示當前會話,之前儲存的結果將被載入入這個會話
ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:表示模型儲存的位置,不需要提供模型的名字,它會去檢視checkpoint檔案,看看最新的是誰,叫做什麼。
二、輸入真實圖片,輸出預測結果
網路輸入:一維陣列(784個畫素點)
畫素點:0-1之間的浮點數(接近0越黑,接近1越白)
畫素為0 畫素為1
網路輸出:一維陣列(十個可能性概率),陣列中最大的那個元素所對應的索引號就是預測的結果。
關鍵處理:
def application(): testNum =input("input the number of test pictures:") for i in range(testNum): testPic =raw_input("the path of test picture:") testPicArr = pre_pic(testPic) preValue = restore_model(testPicArr) print "Theprediction number is:",preValue
註解: 任務分成兩個函式完成
1)testPicArr =pre_pic(testPic)對手寫數字圖片做預處理
2)preValue =restore_model(testPicArr) 將符合神經網路輸入要求的圖片餵給復現的神經網路模型,輸出預測值
程式碼正規化:
#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import mnist_backward
import mnist_forward
def restore_model(testPicArr):
#利用tf.Graph()復現之前定義的計算圖
with tf.Graph().as_default() as tg:
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_forward.INPUT_NODE])
#呼叫mnist_forward檔案中的前向傳播過程forword()函式
y = mnist_forward.forward(x, None)
#得到概率最大的預測值
preValue = tf.argmax(y, 1)
#例項化具有滑動平均的saver物件
variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(mnist_backward.MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY)
variables_to_restore = variable_averages.variables_to_restore()
saver = tf.train.Saver(variables_to_restore)
with tf.Session() as sess:
#通過ckpt獲取最新儲存的模型
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(mnist_backward.MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
preValue = sess.run(preValue, feed_dict={x:testPicArr})
return preValue
else:
print("No checkpoint file found")
return -1
#預處理,包括resize,轉變灰度圖,二值化
def pre_pic(picName):
img = Image.open(picName)
reIm = img.resize((28,28), Image.ANTIALIAS)
im_arr = np.array(reIm.convert('L'))
#對圖片做二值化處理(這樣以濾掉噪聲,另外除錯中可適當調節閾值)
threshold = 50
#模型的要求是黑底白字,但輸入的圖是白底黑字,所以需要對每個畫素點的值改為255減去原值以得到互補的反色。
for i in range(28):
for j in range(28):
im_arr[i][j] = 255 - im_arr[i][j]
if (im_arr[i][j] < threshold):
im_arr[i][j] = 0
else: im_arr[i][j] = 255
#把圖片形狀拉成1行784列,並把值變為浮點型(因為要求畫素點是0-1 之間的浮點數)
nm_arr = im_arr.reshape([1, 784])
nm_arr = nm_arr.astype(np.float32)
#接著讓現有的RGB圖從0-255之間的數變為0-1之間的浮點數
img_ready = np.multiply(nm_arr, 1.0/255.0)
return img_ready
def application():
#輸入要識別的幾張圖片
testNum = input("input the number of test pictures:")
for i in range(testNum):
#給出待識別圖片的路徑和名稱
testPic = raw_input("the path of test picture:")
#圖片預處理
testPicArr = pre_pic(testPic)
#獲取預測結果
preValue = restore_model(testPicArr)
print "The prediction number is:", preValue
def main():
application()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
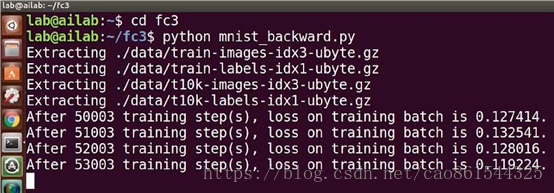
實踐程式碼驗證
1)執行mnist_backward.py
2)執行 mnist_test.py來監測模型的準確率
3) 執行mnist_app.py輸入10(表示迴圈驗證十張圖片)
製作資料集,實現特定應用
1、資料集生成讀取檔案(mnist_generateds.py)
tfrecords檔案
1)tfrecords:是一種二進位制檔案,可先將圖片和標籤製作成該格式的檔案。使用tfrecords進行資料讀取,會提高記憶體利用率。
2)tf.train.Example: 用來儲存訓練資料。訓練資料的特徵用鍵值對的形式表示。
如:‘ img_raw ’ : 值
‘label ’ : 值
值是 Byteslist/FloatList/Int64List
3)SerializeToString():把資料序列化成字串儲存。
生成tfrecords檔案,程式碼正規化:
#生成tfrecords檔案
def write_tfRecord(tfRecordName, image_path, label_path):
#新建一個writer
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfRecordName)
num_pic = 0
f = open(label_path, 'r')
contents = f.readlines()
f.close()
#迴圈遍歷每張圖和標籤
for content in contents:
value = content.split()
img_path = image_path + value[0]
img = Image.open(img_path)
img_raw = img.tobytes()
labels = [0] * 10
labels[int(value[1])] = 1
#把每張圖片和標籤封裝到example中
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'img_raw': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw])),
'label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=labels))
}))
#把example進行序列化
writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
num_pic += 1
print ("the number of picture:", num_pic)
#關閉writer
writer.close()
print("write tfrecord successful")
def generate_tfRecord():
isExists = os.path.exists(data_path)
if not isExists:
os.makedirs(data_path)
print 'The directory was created successfully'
else:
print 'directory already exists'
write_tfRecord(tfRecord_train, image_train_path, label_train_path)
write_tfRecord(tfRecord_test, image_test_path, label_test_path)
解析tfrecords檔案
程式碼正規化:
#解析tfrecords檔案
def read_tfRecord(tfRecord_path):
#該函式會生成一個先入先出的佇列,檔案閱讀器會使用它來讀取資料
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer([tfRecord_path], shuffle=True)
#新建一個reader
reader = tf.TFRecordReader()
#把讀出的每個樣本儲存在serialized_example中進行解序列化,標籤和圖片的鍵名應該和製作tfrecords的鍵名相同,其中標籤給出幾分類。
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue)
#將tf.train.Example協議記憶體塊(protocol buffer)解析為張量
features = tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([10], tf.int64),
'img_raw': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
#將img_raw字串轉換為8位無符號整型
img = tf.decode_raw(features['img_raw'], tf.uint8)
#將形狀變為一行784列
img.set_shape([784])
img = tf.cast(img, tf.float32) * (1. / 255)
#變成0到1之間的浮點數
label = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.float32)
#返回圖片和標籤
return img, label
def get_tfrecord(num, isTrain=True):
if isTrain:
tfRecord_path = tfRecord_train
else:
tfRecord_path = tfRecord_test
img, label = read_tfRecord(tfRecord_path)
#隨機讀取一個batch的資料
img_batch, label_batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([img, label],
batch_size = num,
num_threads = 2,
capacity = 1000,
min_after_dequeue = 700)
#返回的圖片和標籤為隨機抽取的batch_size組
return img_batch, label_batch
2、反向傳播檔案修改圖片標籤獲取的介面(mnist_backward.py)
關鍵操作:利用多執行緒提高圖片和標籤的批獲取效率
方法:將批獲取的操作放到執行緒協調器開啟和關閉之間開啟執行緒協調器:
coord = tf.train.Coordinator( )
threads =tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
關閉執行緒協調器:
coord.request_stop( ) coord.join(threads)
註解:
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=None,
coord=None,
daemon=True,
start=True,
collection=tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS)這個函式將會啟動輸入佇列的執行緒,填充訓練樣本到佇列中,以便出隊操作可以從佇列中拿到樣本。這種情況下最好配合使用一個 tf.train.Coordinator,這樣可以在發生錯誤的情況下正確地關閉這些執行緒。
引數說明:sess:用於執行佇列操作的會話。 預設為預設會話。
coord:可選協調器,用於協調啟動的執行緒。
daemon: 守護程序,執行緒是否應該標記為守護程序,這意味著它們不會阻止程式退出。
start:設定為False只建立執行緒,不啟動它們。
collection:指定圖集合以獲取啟動佇列的 GraphKey。預設為
GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS。
反向傳播中示例程式碼mnist_backward.py
#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import mnist_forward
import os
import mnist_generateds#1
BATCH_SIZE = 200
LEARNING_RATE_BASE = 0.1
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY = 0.99
REGULARIZER = 0.0001
STEPS = 50000
MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY = 0.99
MODEL_SAVE_PATH="./model/"
MODEL_NAME="mnist_model"
#手動給出訓練的總樣本數6萬
train_num_examples = 60000#2
def backward():
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_forward.INPUT_NODE])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_forward.OUTPUT_NODE])
y = mnist_forward.forward(x, REGULARIZER)
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
ce = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=y, labels=tf.argmax(y_, 1))
cem = tf.reduce_mean(ce)
loss = cem + tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('losses'))
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(
LEARNING_RATE_BASE,
global_step,
train_num_examples / BATCH_SIZE,
LEARNING_RATE_DECAY,
staircase=True)
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(loss, global_step=global_step)
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY, global_step)
ema_op = ema.apply(tf.trainable_variables())
with tf.control_dependencies([train_step, ema_op]):
train_op = tf.no_op(name='train')
saver = tf.train.Saver()
#一次批獲取 batch_size張圖片和標籤
img_batch, label_batch = mnist_generateds.get_tfrecord(BATCH_SIZE, isTrain=True)#3
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
#利用多執行緒提高圖片和標籤的批獲取效率
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()#4
#啟動輸入佇列的執行緒
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)#5
for i in range(STEPS):
#執行圖片和標籤的批獲取
xs, ys = sess.run([img_batch, label_batch])#6
_, loss_value, step = sess.run([train_op, loss, global_step], feed_dict={x: xs, y_: ys})
if i % 1000 == 0:
print("After %d training step(s), loss on training batch is %g." % (step, loss_value))
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(MODEL_SAVE_PATH, MODEL_NAME), global_step=global_step)
#關閉執行緒協調器
coord.request_stop()#7
coord.join(threads)#8
def main():
backward()#9
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
3、測試檔案修改圖片標籤獲取的介面(mnist_test.py)
#coding:utf-8
import time
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import mnist_forward
import mnist_backward
import mnist_generateds
TEST_INTERVAL_SECS = 5
#手動給出測試的總樣本數1萬
TEST_NUM = 10000#1
def test():
with tf.Graph().as_default() as g:
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_forward.INPUT_NODE])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, mnist_forward.OUTPUT_NODE])
y = mnist_forward.forward(x, None)
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(mnist_backward.MOVING_AVERAGE_DECAY)
ema_restore = ema.variables_to_restore()
saver = tf.train.Saver(ema_restore)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
#用函式get_tfrecord替換讀取所有測試集1萬張圖片
img_batch, label_batch = mnist_generateds.get_tfrecord(TEST_NUM, isTrain=False)#2
while True:
with tf.Session() as sess:
ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state(mnist_backward.MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
if ckpt and ckpt.model_checkpoint_path:
saver.restore(sess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
global_step = ckpt.model_checkpoint_path.split('/')[-1].split('-')[-1]
#利用多執行緒提高圖片和標籤的批獲取效率
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()#3
#啟動輸入佇列的執行緒
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)#4
#執行圖片和標籤的批獲取
xs, ys = sess.run([img_batch, label_batch])#5
accuracy_score = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: xs, y_: ys})
print("After %s training step(s), test accuracy = %g" % (global_step, accuracy_score))
#關閉執行緒協調器
coord.request_stop()#6
coord.join(threads)#7
else:
print('No checkpoint file found')
return
time.sleep(TEST_INTERVAL_SECS)
def main():
test()#8
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
4、實踐程式碼驗證
1)執行測試程式碼mnist_test.py
2)準確率穩定在95%以上後執行應用程式mnist_app.py
部分示範程式碼和影象來自於skytoby,致謝。