樹(一):基本知識
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-14
概念:
n(n>=0) 個節點構成的有限集合
- 空樹
- n = 0
- 非空樹
- 有一個根節點
- 其餘節點分為m(m>0)個互不相交的有限集,每個集合本身也是樹
非樹:
特點:
- 子樹不相交
- 除了根節點外,每個節點有且僅有一個父節點
- n個節點的樹有n-1條邊
基本術語:
- 節點的度(Degree):一個節點的子節點的個數
- 樹的度:樹中,最大的節點的度
- 葉節點(Leaf):度為0的節點
- 父節點(Parent):有子樹的節點,且是子樹的的根節點
- 子節點(Child):A是B的父節點,則B是A的子節點
- 兄弟節點(Sibling):具有同一父節點的各節點彼此是兄弟節點
- 路徑:從節點n到nk的路徑為一個節點序列
- 路徑長度:路徑中所包含邊的個數為路徑長度
- 祖先節點(Ancestor):沿樹根到某個節點上的所有節點都是這個節點的祖先節點
- 子孫節點(Descendant):某一節點的子樹中所有節點是這個節點的子孫
- 節點的層次(Level):規定根節點在1層,其他任意節點是其分節點的層數+1
- 樹的深度(Depth):樹中所有節點中的最大層次是這顆樹的深度
表示:
- 陣列: 通常的樹很難用陣列表示(二叉樹)
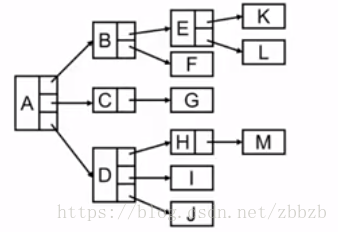
- 連結串列:
這種方式構建連結串列,發現連結串列中的指標數量是根據整個樹的度來決定的,當前樹的度是3,也就是每個節點都有3個指標,如果一個節點中沒有子節點,那麼他會浪費會浪費很多空間
優化:兒子-兄弟表示法(類似於二叉樹)
也就是左邊放置子節點,右邊放置兄弟節點
簡單的實現:
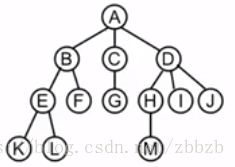
根據給的節點 { (‘A’, ‘B’),(‘A’, ‘C’),(‘A’, ‘D’) (‘B’, ‘E’),(‘B’, ‘F’) (‘C’, ‘G’) (‘D’, ‘H’),(‘D’, ‘I’),(‘D’, ‘J’) (‘E’, ‘K’),(‘E’, ‘L’) (‘H’, ‘M’) } 注:下面實現不包括值相同的節點,即B->B,這種操作不行,需要新增標誌,註明節點的順序
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> using namespace std; // 節點結構 struct TreeNode { char value; TreeNode* child; TreeNode* nextBrother; TreeNode(char val):value(val), child(NULL), nextBrother(NULL) {} }; // 樹 class Tree { public: TreeNode* root; Tree() {} ~Tree(); void CreateTree(std::map<int, std::map<char, char>> data); // 建立樹 void DestroyNode(TreeNode* node); // 銷燬樹 TreeNode* GetNodeByVal(TreeNode* node, char val); // 根據值獲取節點 }; void Tree::CreateTree(map<int, map<char, char>> data) { TreeNode* node = NULL; for (int i = 0;i < data.size();i++) { map<char, char>::iterator iter = data[i].begin(); node = GetNodeByVal(node, iter->first); if ( node == NULL) { node = new TreeNode(iter->first); if (i == 0) { root = node; } } if (node->child == NULL) { node->child = new TreeNode(iter->second); } else { TreeNode** next = &(node->child->nextBrother); while (*next != NULL) { next = &((*next)->nextBrother); } *next = new TreeNode(iter->second); } } } TreeNode* Tree::GetNodeByVal(TreeNode* node, char val) { if (node == NULL || (node!=NULL && node->value == val)) { return node; } TreeNode* cNode = GetNodeByVal(node->child, val); if (cNode != NULL) { return cNode; } else { TreeNode* bNode = GetNodeByVal(node->nextBrother, val); return bNode; } } Tree::~Tree() { DestroyNode(root); } void Tree::DestroyNode(TreeNode* node) { TreeNode* child = NULL; TreeNode * brother = NULL; if (node == NULL) { return; } child = node->child; brother = node->nextBrother; delete node; node = NULL; DestroyNode(child); DestroyNode(brother); } int main() { map<int, map<char, char>> data; data[0].insert(pair<char, char>('A', 'B')); data[1].insert(pair<char, char>('A', 'C')); data[2].insert(pair<char, char>('A', 'D')); data[3].insert(pair<char, char>('B', 'E')); data[4].insert(pair<char, char>('B', 'F')); data[5].insert(pair<char, char>('C', 'G')); data[6].insert(pair<char, char>('D', 'H')); data[7].insert(pair<char, char>('D', 'I')); data[8].insert(pair<char, char>('D', 'J')); data[9].insert(pair<char, char>('E', 'K')); data[10].insert(pair<char, char>('E', 'L')); data[11].insert(pair<char, char>('H', 'M')); Tree t; t.CreateTree(data); // t.DestroyNode(t.root); 測試是否刪除 system("pause"); return 0; }