STL系列之四 heap 堆
下面再介紹STL中與堆相關的4個函式——建立堆make_heap(),在堆中新增資料push_heap(),在堆中刪除資料pop_heap()和堆排序sort_heap():
標頭檔案 #include <algorithm>
下面的_First與_Last為可以隨機訪問的迭代器(指標),_Comp為比較函式(仿函式),其規則——如果函式的第一個引數小於第二個引數應返回true,否則返回false。
建立堆
make_heap(_First, _Last, _Comp)
預設是建立最大堆的。對int型別,可以在第三個引數傳入greater<int>()得到最小堆。
在堆中新增資料
push_heap (_First, _Last)
要先在容器中加入資料,再呼叫push_heap ()
在堆中刪除資料
pop_heap(_First, _Last)
要先呼叫pop_heap()再在容器中刪除資料
堆排序
sort_heap(_First, _Last)
排序之後就不再是一個合法的heap了
有關堆與堆排序的更詳細介紹請參閱——《白話經典算法系列之七 堆與堆排序》
下面給出STL中heap相關函式的使用範例:
//by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows ) 掌握其基本用法後,我們用這個堆排序和《白話經典算法系列》中的堆排序、快速排序,歸併排序來進行個性能測試(Win7 + VS2008 Release下),測試程式碼如下:
// by MoreWindows( http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows )
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//------------------------快速排序----------------------------
void quick_sort(int s[], int l, int r)
{
if (l < r)
{
int i = l, j = r, x = s[l];
while (i < j)
{
while(i < j && s[j] >= x) // 從右向左找第一個小於x的數
j--;
if(i < j)
s[i++] = s[j];
while(i < j && s[i] < x) // 從左向右找第一個大於等於x的數
i++;
if(i < j)
s[j--] = s[i];
}
s[i] = x;
quick_sort(s, l, i - 1); // 遞迴呼叫
quick_sort(s, i + 1, r);
}
}
//------------------------歸併排序----------------------------
//將有二個有序數列a[first...mid]和a[mid...last]合併。
void mergearray(int a[], int first, int mid, int last, int temp[])
{
int i = first, j = mid + 1;
int m = mid, n = last;
int k = 0;
while (i <= m && j <= n)
{
if (a[i] < a[j])
temp[k++] = a[i++];
else
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= m)
temp[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= n)
temp[k++] = a[j++];
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
a[first + i] = temp[i];
}
void mergesort(int a[], int first, int last, int temp[])
{
if (first < last)
{
int mid = (first + last) / 2;
mergesort(a, first, mid, temp); //左邊有序
mergesort(a, mid + 1, last, temp); //右邊有序
mergearray(a, first, mid, last, temp); //再將二個有序數列合併
}
}
bool MergeSort(int a[], int n)
{
int *p = new int[n];
if (p == NULL)
return false;
mergesort(a, 0, n - 1, p);
return true;
}
//------------------------堆排序---------------------------
inline void Swap(int &a, int &b)
{
int c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
}
//建立最小堆
// 從i節點開始調整,n為節點總數 從0開始計算 i節點的子節點為 2*i+1, 2*i+2
void MinHeapFixdown(int a[], int i, int n)
{
int j, temp;
temp = a[i];
j = 2 * i + 1;
while (j < n)
{
if (j + 1 < n && a[j + 1] < a[j]) //在左右孩子中找最小的
j++;
if (a[j] >= temp)
break;
a[i] = a[j]; //把較小的子結點往上移動,替換它的父結點
i = j;
j = 2 * i + 1;
}
a[i] = temp;
}
//建立最小堆
void MakeMinHeap(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
MinHeapFixdown(a, i, n);
}
void MinheapsortTodescendarray(int a[], int n)
{
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--)
{
Swap(a[i], a[0]);
MinHeapFixdown(a, 0, i);
}
}
const int MAXN = 5000000;
int a[MAXN];
int b[MAXN], c[MAXN], d[MAXN];
int main()
{
int i;
srand(time(NULL));
for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
a[i] = rand() * rand(); //注rand()產生的數在0到0x7FFF之間
for (i = 0; i < MAXN; ++i)
d[i] = c[i] = b[i] = a[i];
clock_t ibegin, iend;
printf("--當前資料量為%d--By MoreWindows(http://blog.csdn.net/MoreWindows)--\n", MAXN);
//快速排序
printf("快速排序: ");
ibegin = clock();
quick_sort(a, 0, MAXN - 1);
iend = clock();
printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
//歸併排序
printf("歸併排序: ");
ibegin = clock();
MergeSort(b, MAXN);
iend = clock();
printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
//堆排序
printf("堆排序: ");
ibegin = clock();
MakeMinHeap(c, MAXN);
MinheapsortTodescendarray(c, MAXN);
iend = clock();
printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
//STL中的堆排序
printf("STL中的堆排序: ");
ibegin = clock();
make_heap(d, d + MAXN);
sort_heap(d, d + MAXN);
iend = clock();
printf("%d毫秒\n", iend - ibegin);
return 0;
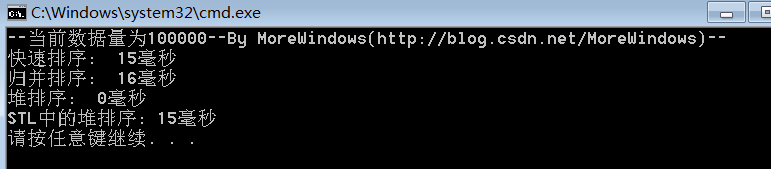
}對100000(十萬)個數據的測試結果:
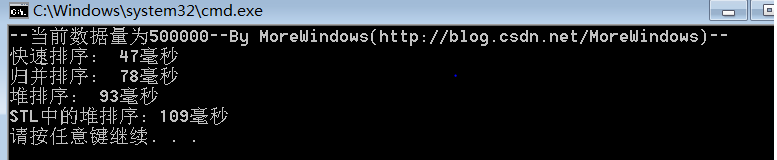
對500000(五十萬)個數據的測試結果:
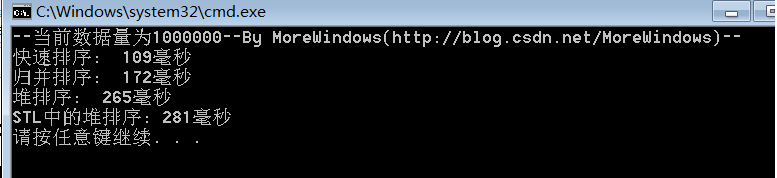
對1000000(一百萬)個數據的測試結果:
對5000000(五百萬)個數據的測試結果:
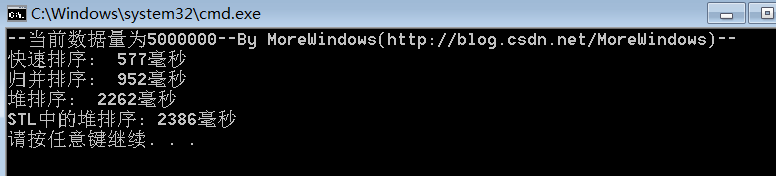
從中可以看出快速排序的效率確實要比其它同為O(N * logN)的排序演算法要高,而STL中堆操作函式的效能與《白話經典算法系列之七 堆與堆排序》一文中堆操作函式的效能是相差無幾的。
轉載請標明出處,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6967409
再分享一下我老師大神的人工智慧教程吧。零基礎!通俗易懂!風趣幽默!希望你也加入到我們人工智慧的隊伍中來!http://www.captainbed.net
