一種Android上基於畫素對比做基本圖案識別的簡單粗暴辦法
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-16
使用者希望通過書寫不規則的圖形之後,能夠識別出這個圖案是什麼,並輸出同等大小的規則圖形。第一步當然就是識別圖案了,我用的方法原理大致分如下幾步:
1、將使用者輸入的圖片長寬壓縮為目標大小,如100*100畫素
2、和圖案庫中預留的幾張預定大小(例如100*100畫素)的基礎圖案的畫素都進行一次對比,並分別得出使用者輸入的圖案影象和基礎圖案圖片的畫素相似量
3、輸出畫素相似量最大的基礎圖片的名字作為結果
實現方法:
1、首先製作預定圖案圖片,並插入到Drawable資原始檔夾:
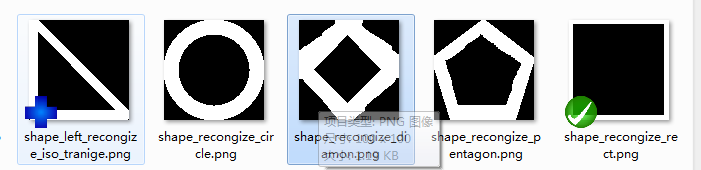

2、編寫識別程式碼:
public class ShapeRecognize { public static enum Shapes{ TRANIGLE, LEFT_ISO_TRANIGLE, RIGHT_ISO_TRANIGLE, TOP_LEFT_ISO_TRANIGLE, TOP_RIGHT_ISO_TRANIGLE, RECTANGLE, CIRCLE, DIAMON, PENTAGON } /**一定要ARGB8888編碼**/ private static class SimilarityInfo{ public float totalSimilarity; //雷同畫素量 public Shapes kind; //型別 } public static Shapes recogine(Context context, Bitmap srcBmp){ List<SimilarityInfo> similarityInfoList = new LinkedList<>(); Log.i(ShapeRecognize.class.getName(), "開始識別"); int resIdArray[] = new int[]{ R.drawable.shape_recongize_tranige, R.drawable.shape_left_recongize_iso_tranige, R.drawable.shape_right_recongize_iso_tranige, R.drawable.shape_top_left_recongize_iso_tranige, R.drawable.shape_top_right_recongize_iso_tranige, R.drawable.shape_recongize_rect, R.drawable.shape_recongize_circle, R.drawable.shape_recongize_diamon, R.drawable.shape_recongize_pentagon }; for(int ri = 0; ri < resIdArray.length; ri++){ int resId = resIdArray[ri]; //和等腰三角形匹配的概率 Bitmap comapreBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(context.getResources(), resId); int trianglePixels[] = new int[comapreBitmap.getWidth() * comapreBitmap.getHeight()]; comapreBitmap.copyPixelsToBuffer(IntBuffer.wrap(trianglePixels)); Log.i(ShapeRecognize.class.getName(), "畫素大小:" + trianglePixels.length); Bitmap srcBmpScaled = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(srcBmp, comapreBitmap.getWidth(), comapreBitmap.getHeight(), false); int srcBmpScaledPixels[] = new int[srcBmpScaled.getWidth() * srcBmpScaled.getHeight()]; srcBmpScaled.copyPixelsToBuffer(IntBuffer.wrap(srcBmpScaledPixels)); int count = 0; float totalSimilarity = 0; for(int i = 0; i < trianglePixels.length; i ++ ){ if(trianglePixels[i] != 0){ int compareR = trianglePixels[i] >> 16 & 0xFF; int compareG = trianglePixels[i] >> 8 & 0xFF; int compareB = trianglePixels[i] & 0xFF; int srcBmpR = srcBmpScaledPixels[i] >> 16 & 0xFF; int srcBmpG = srcBmpScaledPixels[i] >> 8 & 0xFF; int srcBmpB = srcBmpScaledPixels[i] & 0xFF; float similarity = 0; if(compareR > 0){ similarity += ( srcBmpR / compareR); } if(compareG > 0){ similarity += ( srcBmpG / compareG); } if(compareB > 0){ similarity += ( srcBmpB / compareB); } similarity /= 3; totalSimilarity += similarity; count ++; } } //Log.i("雷同顏色量", totalSimilarity + ""); SimilarityInfo similarityInfo = new SimilarityInfo(); similarityInfo.totalSimilarity = totalSimilarity; similarityInfo.kind = Shapes.values()[ri]; similarityInfoList.add(similarityInfo); } Shapes resultKind = Shapes.TRANIGLE; float resultSim = 0f; for(SimilarityInfo similarityInfo : similarityInfoList){ if(similarityInfo.totalSimilarity > resultSim){ resultKind = similarityInfo.kind; resultSim = similarityInfo.totalSimilarity; } } Log.i("識別結果", resultKind.name()); return resultKind; } }
3、根據結果的體驗手動微調目標識別圖片的邊框粗細提高識別率
實驗結果:
輸入:
輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
輸入:

輸出:
![]()
總結:
該方法識別時間耗時短,在模擬器上大概識別一個圖案只需要不到15ms,準確度尚可。但是目標圖片的大小比較影響精度,目標圖片的線條扭曲程度也會影響精度,實際上精度和對複雜圖案的識別能力上是完全比不過基於神經網路等的實現的。這種方法僅適用於目標圖案簡單而且對速度有一定要求的場合,對時間不敏感的話建議還是使用神經網路。
