Day 9——java多執行緒2及字元編碼集合
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-16
java.lang.Runnable
- 介面
- Runnable中有Public void run();方法
- 供現有Runnable物件建立執行緒
- 使用Runnable物件建立執行緒
New Thread(Runnable r).start(); - 靜態同步方法是使用class作為鎖
- 非靜態方法是使用this(當前物件)作為鎖
樣例
Class car implements Runnable{ … Static synchronized void xxx(){ //靜態同步方法 } } New Thread(Runnable r).start(); s.start();
同步(synchronized),格式
synchronized(物件){
需要同步的程式碼;
}
同步可以解決安全問題的根本原因就在那個物件上,該物件如同鎖的功能。
同步的前提條件:
1.同步需要兩個或者兩個以上的執行緒。
2.多個執行緒使用的是同一個鎖。
未滿足這兩個條件不能稱為同步。
同步的弊端:
當執行緒相當多時,因為每個執行緒都會去判斷同步上的鎖,這是很耗資源的,無形中會降低程式的執行效率。
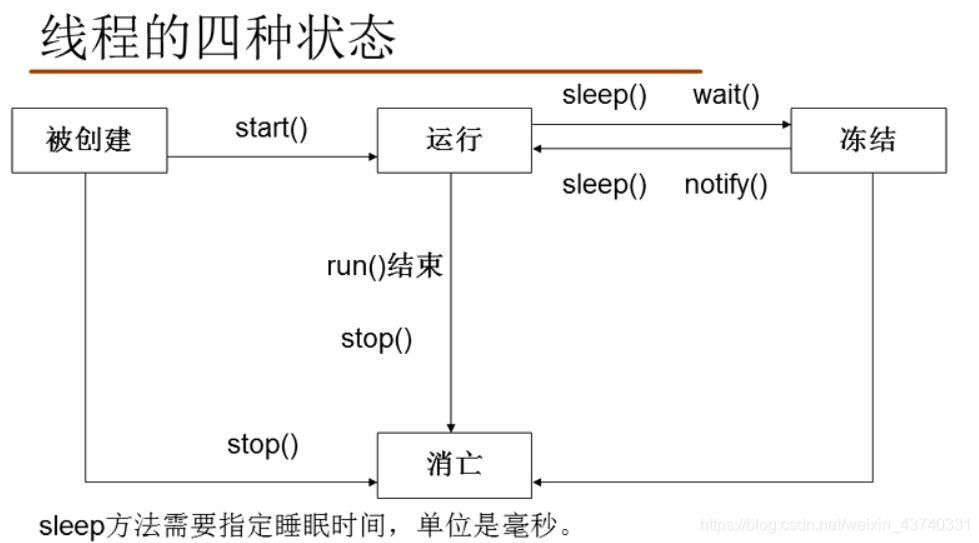
停止執行緒
- 利用迴圈結束執行緒
- 使用interrupt(中斷)方法
該方法是結束執行緒的凍結狀態,使執行緒回到執行狀態中來。
注:stop方法已經過時,不再使用。
執行緒類的其他方法
優先順序
setPriority(int num) 1<=num<=10
使用方法
xx.setPriority(num);
優先順序數越大,則優先執行
setDaemon(boolean b)
join()
自定義執行緒名稱
toString()
執行緒安全性
synchronized(Object){
…
}
public synchronized void xxx(){
…
}
public static syzchronized void xxx(){
…
}
優先順序函式例子
public class t93 {
public static void main(String[] args){
mythread a=new mythread("a");
//使得a的優先順序為1
a.setPriority(1);
mythread b=new mythread("b");
//b的優先順序為10,列印結果先列印b,後列印a
b.setPriority(10);
a.start();
b.start();
}
}
class mythread extends Thread{
private String name;
public mythread(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public void run(){
System.out.println(name);
}
}
String類
//字串池中的量
String str=”abc”;
//new String 分配記憶體空間(堆區)
String str1=new String(“abc”);
字符集編碼
//字串長度,字元的個數
str.length();
//提取指定位置上的字元0<=x<=str.length();
str.charAt(x);
//複製String中的[],產生新的陣列,但不會影響原來的陣列
char[] arr=str.toCharArray();
//返回子串在母串中的位置(索引值,以0為基址)
int pos =str.indexOf(“world”);
//判斷是否以指定的字元開頭或者結尾,返回true/false
startsWith(“xxx”);
endsWith(“xxx”);
//切割字串,形成字串陣列
str.split("xxx");
//除錯 debug(抄自ifeng)
F9 resume programe 恢復程式
Alt+F10 show execution point 顯示執行斷點
F8 Step Over 相當於eclipse的f6 跳到下一步
F7 Step Into 相當於eclipse的f5就是 進入到程式碼
Alt+shift+F7 Force Step Into 這個是強制進入程式碼
Shift+F8 Step Out 相當於eclipse的f8跳到下一個斷點,也相當於eclipse的f7跳出函式
Atl+F9 Run To Cursor 執行到游標處
ctrl+shift+F9 debug執行java類
ctrl+shift+F10 正常執行java類
alt+F8 debug時選中檢視值
樣例程式碼
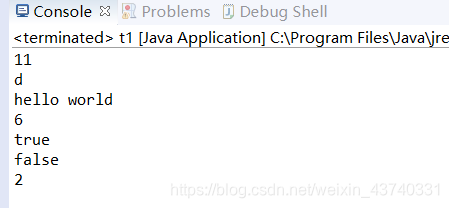
public class t1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="hello world";
//串長度,字元的個數
System.out.println(str.length());
//提取指定位置上的字元
System.out.println(str.charAt(10));
//複製String中的[ ],產生新的陣列,不會影響原來的陣列
char[] arr=str.toCharArray();
System.out.println(arr);
//返回子串在母串中的位置
int pos=str.indexOf("world");
System.out.println(pos);
//判斷是否以指定的字元開頭或結尾
String s1="syzniubi6";
String s2="ccyniubi7";
String s3="lzxniubi8";
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("6"));
System.out.println(s2.startsWith("lzx"));
//切割字串,形成字串組
str="hello world";
String[] strArr=str.split(" ");
System.out.println(strArr.length);
}
}
列印結果