利用Magpie開源庫給一段中文的文字內容進行分類打標籤
當下人工智慧是真心的火熱呀,各種原來傳統的業務也都在嘗試用人工智慧技術來處理,以此來節省人工成本,提高生產效率。既然人工智慧那麼火,那麼我們就先來簡單認識下什麼是人工智慧吧,人工智慧是指利用語音識別、語義理解、影象識別、視覺處理、機器學習、大資料分析等技術實現機器智慧自動化做出響應的一種模擬人行為的手段。而我們這裡介紹的Magpie則屬於人工智慧領域裡語義理解、機器學習中的一個具體的實現技術。
前述
近期因為工作原因,需要從來自於客戶聊天對話的文字中進行使用者行為判斷,並對其打上相應的標籤。而我需要解決的就是利用文字內容進行機器自動分類打標籤,但在業務中一段文字會存有不同的多個標籤,那麼如何來實現呢?通過github,找到了Magpie,發現其與我的需求非常吻合。一番折騰後,就有了本文章。
Magpie
Magpie是一個開源的文字分類庫,基於一個高層神經網路Keras技術編寫,後端預設由Tensorflow來處理。Magpie是由Python語言開發的,且預設只支援英文文字分類,我因為業務需要便在其基礎上做了中文文字的支援。如下是Magpie相關的網址:
實現
通過上面的介紹,我們清楚了需要實現的業務與目的,以及採用的技術手段。那麼,就讓我們一起來看看藉助Magpie會有什麼神祕的事情發生吧。
1、從Magpie下載原始碼包到本地,通過PyCharm IDE開發工具開啟專案後發現有“data”、“magpie”、“save”等目錄。其中“data”目錄用於存放訓練的源資料,“magpie”目錄用於存放原始碼,“save”目錄用於存放訓練後的模型檔案,具體結如下圖:
2、在專案引用相應的第三方類庫,如下:
1 'nltk~=3.2', 2 'numpy~=1.12', 3 'scipy~=0.18', 4 'gensim~=0.13', 5 'scikit-learn~=0.18', 6 'keras~=2.0', 7 'h5py~=2.6', 8 'jieba~=0.39',
3、對專案有了一定認識後,現在我們來準備源資料。我們這裡假定有三種標籤,分別為“軍事“、”旅遊“'、”政治”,每個標籤各準備一定數量的源資料(訓練資料理論上是越多越好,這裡我偷懶就準備了10條),其中拿出90%做為訓練資料,10%做為測試資料,根據Magpie規則將訓練源資料放到“data”目錄內。
4、資料準備好後,我們需要改動原始碼,使其能支援中文。中文面臨一個問題就是分詞,而我們這裡使用jieba分詞庫。依次開啟”magpie\base“目下的”Document“類中,並在該類內加入相應的分詞程式碼,具體程式碼如下:
1 from __future__ import print_function, unicode_literals 2 3 import re 4 import io 5 import os 6 import nltk 7 import string 8 import jieba 9 10 from nltk.tokenize import WordPunctTokenizer, sent_tokenize, word_tokenize 11 12 nltk.download('punkt', quiet=True) # make sure it's downloaded before using 13 14 class Document(object): 15 16 """ Class representing a document that the keywords are extracted from """ 17 def __init__(self, doc_id, filepath, text=None): 18 self.doc_id = doc_id 19 20 if text: 21 text = self.clean_text(text) 22 text = self.seg_text(text) 23 self.text = text 24 self.filename = None 25 self.filepath = None 26 else: # is a path to a file 27 if not os.path.exists(filepath): 28 raise ValueError("The file " + filepath + " doesn't exist") 29 30 self.filepath = filepath 31 self.filename = os.path.basename(filepath) 32 with io.open(filepath, 'r', encoding='gbk') as f: 33 text_context = f.read() 34 text_context = self.clean_text(text_context) 35 self.text = self.seg_text(text_context) 36 print(self.text) 37 self.wordset = self.compute_wordset() 38 39 40 41 # 利用jieba包進行分詞,並並且去掉停詞,返回分詞後的文字 42 def seg_text(self,text): 43 stop = [line.strip() for line in open('data/stopwords.txt', encoding='utf8').readlines()] 44 text_seged = jieba.cut(text.strip()) 45 outstr = '' 46 for word in text_seged: 47 if word not in stop: 48 outstr += word 49 outstr += "" 50 return outstr.strip() 51 52 # 清洗文字,去除標點符號數字以及特殊符號 53 def clean_text(self,content): 54 text = re.sub(r'[+——!,;/·。?、[email protected]#¥%……&*“”《》:()[]【】〔〕]+', '', content) 55 text = re.sub(r'[▲!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>\\[email protected][\\]^_`{|}~]+', '', text) 56 text = re.sub('\d+', '', text) 57 text = re.sub('\s+', '', text) 58 return text 59 60 def __str__(self): 61 return self.text 62 63 def compute_wordset(self): 64 tokens = WordPunctTokenizer().tokenize(self.text) 65 lowercase = [t.lower() for t in tokens] 66 return set(lowercase) - {',', '.', '!', ';', ':', '-', '', None} 67 68 def get_all_words(self): 69 """ Return all words tokenized, in lowercase and without punctuation """ 70 return [w.lower() for w in word_tokenize(self.text) 71 if w not in string.punctuation] 72 73 def read_sentences(self): 74 lines = self.text.split('\n') 75 raw = [sentence for inner_list in lines 76 for sentence in sent_tokenize(inner_list)] 77 return [[w.lower() for w in word_tokenize(s) if w not in string.punctuation] 78 for s in raw] 79
5、通這上述的改造,我們的分類程式可以較好的支援中文了,接下來就可以進行資料訓練了。專案是通過執行”train.py“類來進行訓練操作,但在執行之前我們需要對該類做下改動,具體程式碼如下:
1 from magpie import Magpie 2 3 magpie = Magpie() 4 magpie.train_word2vec('data/hep-categories', vec_dim=3) #訓練一個word2vec 5 magpie.fit_scaler('data/hep-categories') #生成scaler 6 magpie.init_word_vectors('data/hep-categories', vec_dim=3) #初始化詞向量 7 labels = ['軍事','旅遊','政治'] #定義所有類別 8 magpie.train('data/hep-categories', labels, test_ratio=0.2, epochs=20) #訓練,20%資料作為測試資料,5輪 9 10 #儲存訓練後的模型檔案 11 magpie.save_word2vec_model('save/embeddings/here', overwrite=True) 12 magpie.save_scaler('save/scaler/here', overwrite=True) 13 magpie.save_model('save/model/here.h5')
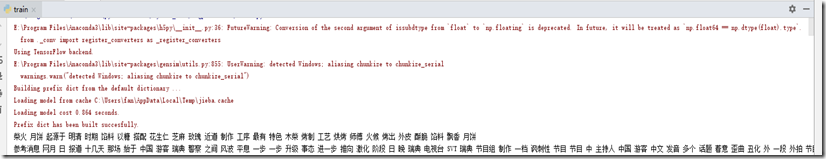
6、執行”train.py“類來進行訓練資料,截圖如下:
7、模型訓練成功後,接下來就可以進行模擬測試了。專案是通過執行”test.py“類來進行測試操作,但在執行之前我們需要對該類做下改動,具體程式碼如下:
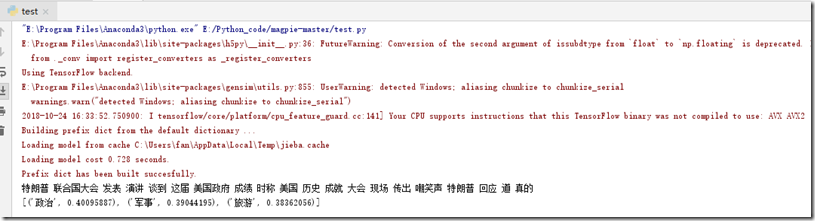
1 from magpie import Magpie 2 3 magpie = Magpie( 4 keras_model='save/model/here.h5', 5 word2vec_model='save/embeddings/here', 6 scaler='save/scaler/here', 7 labels=['旅遊', '軍事', '政治'] 8 ) 9 10 #單條模擬測試資料 11 text = '特朗普在聯合國大會發表演講談到這屆美國政府成績時,稱他已經取得了美國曆史上幾乎最大的成就。隨後大會現場傳出了嘲笑聲,特朗普立即迴應道:“這是真的。”' 12 mag1 = magpie.predict_from_text(text) 13 print(mag1) 14 15 ''' 16 #也可以通過從txt檔案中讀取測試資料進行批量測試 17 mag2 = magpie.predict_from_file('data/hep-categories/1002413.txt') 18 print(mag2) 19 '''
8、執行”test.py“類來進行測試資料,截圖如下:
總結
1、文字分類在很多場景中都能應用,比如垃圾郵件分類、使用者行為分析、文章分類等,通過本文簡單的演示後聰明的你是不是有了一個更大的發現呢!
2、本文使用了Magpie開源庫實現模型訓練與測試,後臺用Tensorflow來運算,並結合jieba分詞進行中文切詞處理。
3、本文測試分值跟訓練資料的數量有一定關係,訓練資料理論上是越多越好。
4、分享一句話:人工智慧要有多少的智慧,就必需要有多少的人工。
宣告
本文為作者原創,轉載請備註出處與保留原文地址,謝謝。如文章能給您帶來幫助,請點下推薦或關注,感謝您的支援!