【深度學習】Alexnet網路分析及程式碼實現
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-17
簡介
Alexnet是2012年ImageNet比賽的冠軍Hinton及其學生Alex Krizhevsky提出,並以其姓名命名的網路。Alexnet的提出也正式掀起了深度學習的熱潮,激發了研究者對深度學習的熱情。雖然後面出現了更為優秀的VGGNet、GooLeNet、ResNet等網路,但是Alexnet的地位是不可撼動的,因此我們有必要去花些時間瞭解一下這一深度學習史上的偉大傑作。
網路結構

上圖為論文中的網路結構圖。因為論文中使用了兩塊GPU進行訓練,所以有兩個分支。為了使網路結構看起來更加直觀,將網路結構簡化為下圖,
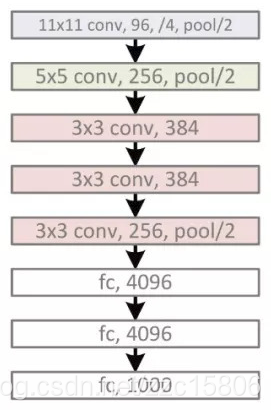
Alexnet共包含5個卷積層和3個全連線層,其中第1,2,5個卷積層後接最大池化和LRN操作。
主要貢獻
1. 使用ReLU代替Sigmoid作為啟用函式,成功解決了Sigmoid在網路較深時的梯度彌散問題;
2. 最後幾個全連線層使用Dropout,避免過擬合;
3. 使用了重疊最大池化操作,即池化步長比池化核尺寸小,提升了特徵的豐富性。此前CNN普遍採用平均池化,最大池化能夠避免平均池化的模糊化效果;
4. 提出了LRN層。LRN全稱Local Response Normalization,對區域性神經元建立競爭機制,增大響應大的單元,抑制反饋小的神經元,增強了模型的泛化能力。(VGGNet沒有使用LRN,作者表示LRN對模型沒有提升,而且引數量大,當然不能以偏概全);
5. 使用CUDA利用GPU加速深度卷積網路的訓練。
6. 資料增強。通過隨機裁剪、旋轉、翻轉等操作,減輕過擬合,提升模型泛化效能。
程式碼實現
本文使用Keras實現Alexnet網路。
from keras.layers import Input from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Dense, Flatten, Dropout, Lambda from keras.models import Model from keras import optimizers from keras.utils import plot_model from keras import backend as K def LRN(alpha=1e-4, k=2, beta=0.75, n=5): """ LRN for cross channel normalization in the original Alexnet parameters default as original paper. """ def f(X): b, r, c, ch = X.shape half = n // 2 square = K.square(X) extra_channels = K.spatial_2d_padding(square, ((0, 0), (half, half)), data_format='channels_first') scale = k for i in range(n): scale += alpha * extra_channels[:,:,:,i:i+int(ch)] scale = scale ** beta return X / scale return Lambda(f, output_shape=lambda input_shape: input_shape) def alexnet(input_shape=(224,224,3), nclass=1000): """ build Alexnet model using keras with TensorFlow backend. :param input_shape: input shape of network, default as (224,224,3) :param nclass: numbers of class(output shape of network), default as 1000 :return: Alexnet model """ input_ = Input(shape=input_shape) x = Conv2D(96, kernel_size=(11, 11), strides=(4, 4), activation='relu')(input_) x = LRN()(x) x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x) x = Conv2D(256, kernel_size=(5, 5), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = LRN()(x) x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x) x = Conv2D(384, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = Conv2D(384, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = Conv2D(256, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(1, 1), activation='relu', padding='same')(x) x = MaxPool2D(pool_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(x) x = Flatten()(x) x = Dense(4096, activation='relu')(x) x = Dropout(0.5)(x) x = Dense(4096, activation='relu')(x) x = Dropout(0.5)(x) output_ = Dense(nclass, activation='softmax')(x) model = Model(inputs=input_, outputs=output_) model.summary() opti_sgd = optimizers.sgd(lr=0.01, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True) model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=opti_sgd, metrics=['accuracy']) return model if __name__ == '__main__': model = alexnet() plot_model(model, 'Alexnet.png', show_shapes=True) # 儲存模型圖
