VS2015呼叫matlab Plot函式
最近經常採用Matlab模擬,然後C語言實現,最後需要將計算結果使用Qt的qwt或者matlab中的plot函式繪圖。
因此想借用matlab的plot函式介面,使用VS2015來編寫訊號處理程式碼,最後通過繪圖來驗證。
參考部落格:
https://blog.csdn.net/shouzang/article/details/80795945
https://blog.csdn.net/libing403/article/details/79135220
非常感謝!
一、VS2015呼叫Matlab2016a進行繪圖
執行環境
Windows 10 64bit
Visual Studio Community 2015/2017
Matlab 2016a
1.1 檢查Matlab對C++編譯器的支援情況
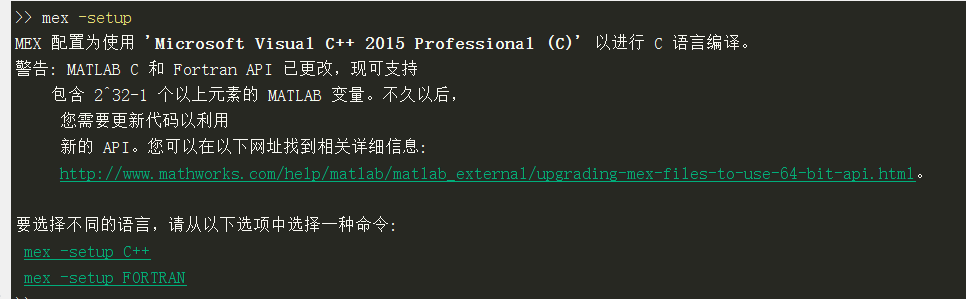
開啟Matlab,在命令列中輸入
mex -setup
如下圖所示,此時Matlab已經可以識別VC++ 2015。
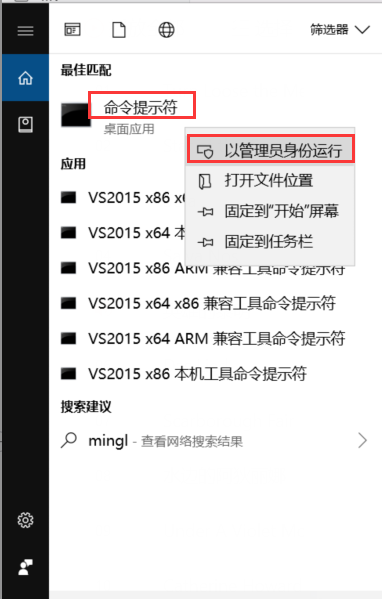
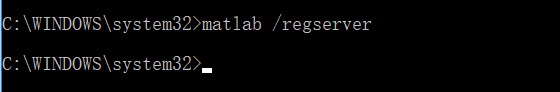
以管理員身份執行命令提示符,切換到"matlab.exe"的路徑,輸入下方命令進行註冊。
若不註冊,在使用engOpen()開啟Matlab引擎會提示失敗。
二、VS配置及程式碼示例
測試Demo
#include<cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include"engine.h"
const int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024;
char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE];
void test()
{
Engine* ep;
mxArray *x1 = NULL;
mxArray *y1 = NULL;
if ((ep = engOpen("")) == NULL)
{
printf("Engine Fail\n");
}
engOutputBuffer(ep, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE);
printf("Init Success\n");
double x[5] = { 1.0, 2.5,3.7,4.4,5.1 };
double y[5] = { 3.3,4.7,9.6,15.6,21.3 };
x1 = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, 5, mxREAL);
y1 = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, 5, mxREAL);
memcpy((char*)mxGetPr(x1), (void *)x, 5 * sizeof(double));
memcpy((char*)mxGetPr(y1), (void *)y, 5 * sizeof(double));
engPutVariable(ep, "x", x1);
engPutVariable(ep, "y", y1);
engEvalString(ep, "plot(x,y)");
getchar();
engClose(ep);
}
int main()
{
test();
}
值得注意的是,由於matlab是在64位環境下安裝的,對應的庫檔案也只有64位的,因此我們的vs工程是在X64平臺的。
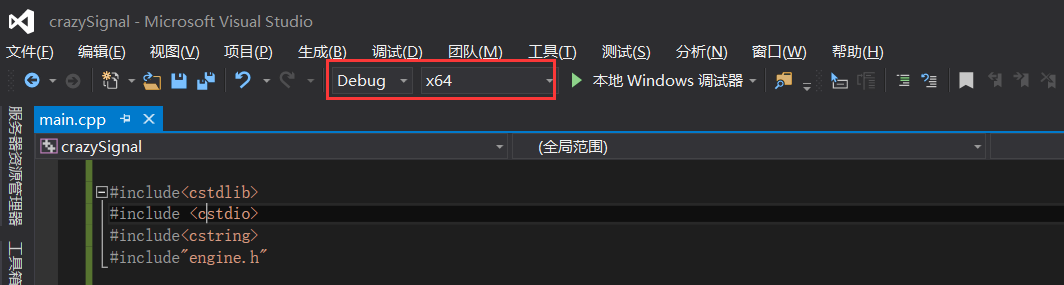
開啟工程屬性頁,在“除錯”選項中,新增“PATH=<Matlab安裝路徑\bin\win64>”,否則會提示找不到dll。 (PATH=D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2016a\bin\win64)
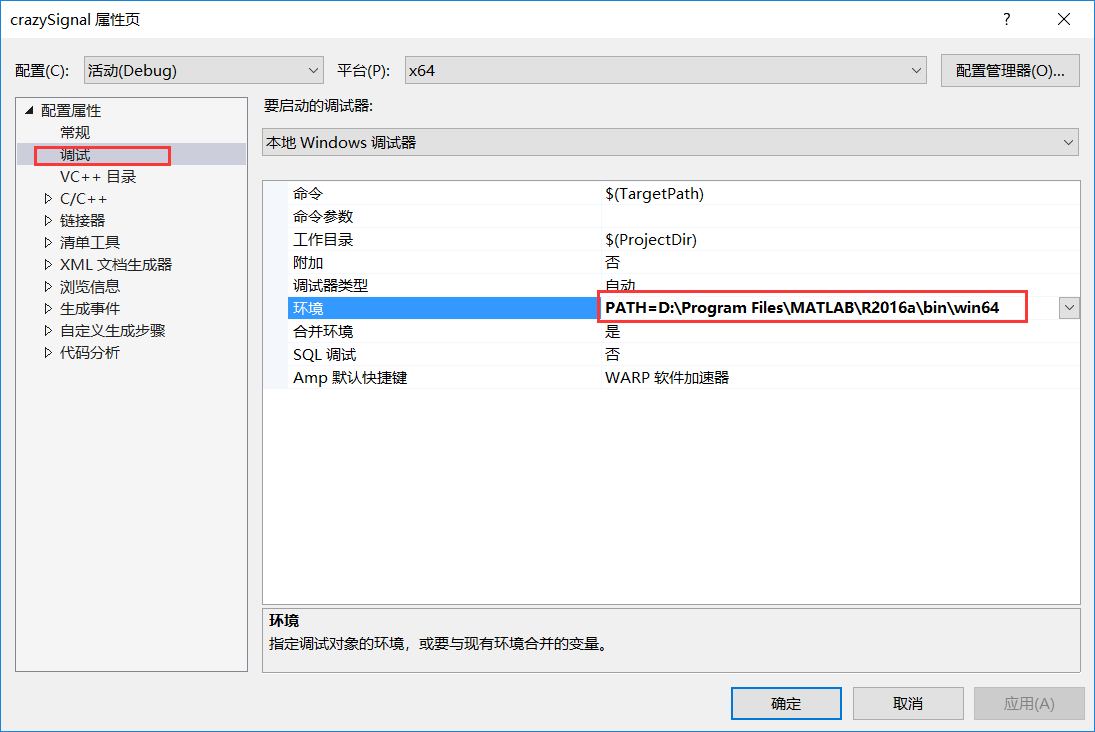
在“VC++目錄”中:
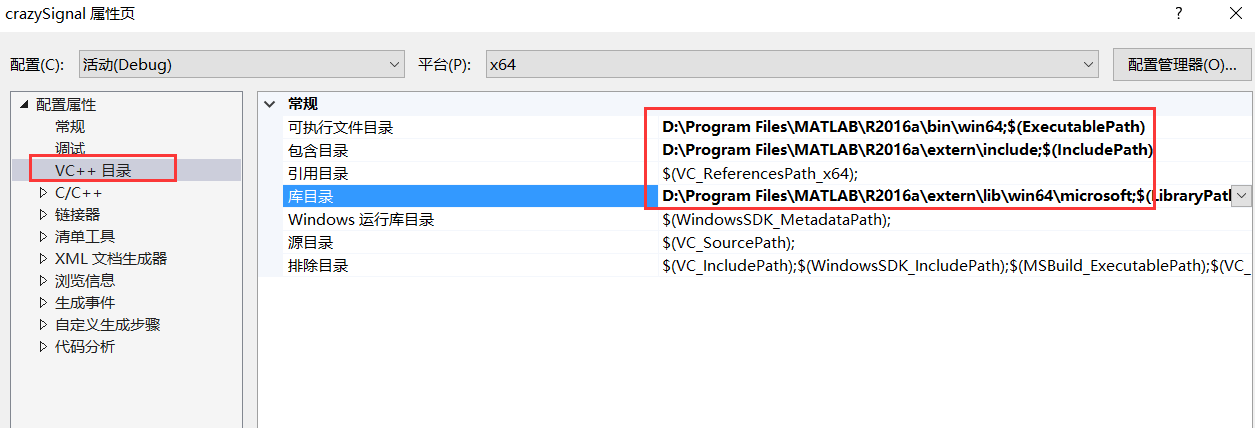
“可執行檔案目錄”中新增“Matlab安裝路徑\bin\win64”,(D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2016a\bin\win64) “包含目錄”中新增“Matlab安裝路徑\extern\include”, (D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2016a\extern\include) “庫目錄”中新增“Matlab安裝路徑\extern\lib\win64\microsoft” (D:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2016a\extern\lib\win64\microsoft)
如下圖所示。
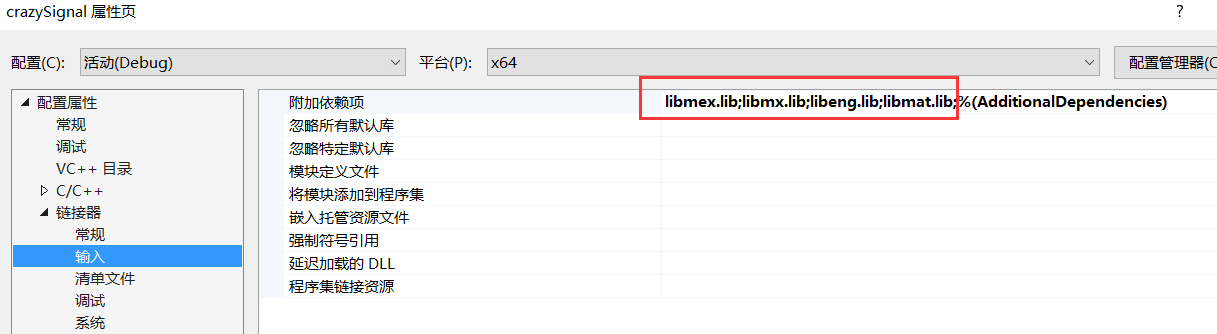
在“連結器”-“輸入”中,“附加依賴項”中新增“libmat.lib”,“libeng.lib”,“libmx.lib”,“libmex.lib”,如下圖所示。
Demo編譯後即可呼叫Matlab進行畫圖,如下圖所示。
三、引擎講解
在VS中呼叫matlab引擎
包含標頭檔案
#include "engine.h"
開啟引擎
Engine* pEng = NULL;
if (!(pEng = engOpen(NULL)))
{
printf("Open matlab enging fail!");
getchar();
return -1;
}
向matlab工作空間設定/獲取資料常用的函式
int engPutVariable(Engine *ep, const char *name, const mxArray *pm)
設定一個變數陣列的值
mxArray *engGetVariable(Engine *ep, const char *name)獲取一個變數 int engEvalString(Engine* ep, const char* string)執行Matlab表示式
關閉引擎
if(pEng)
engClose(pEng);
正弦波程式碼示例:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<engine.h>
#define dataNum 100
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
Engine* eg = NULL;
if (!(eg = engOpen(NULL)))
{
printf("Open matlab enging fail!");
return 1;
}
double xtemp[dataNum] = { 0 };
double ytemp[dataNum] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < dataNum; i++)
{
xtemp[i] = i * 2.0 * 3.1415926 / 100.0;
ytemp[i] = sin(xtemp[i]);
}
mxArray *X = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, dataNum, mxREAL);//建立matlab儲存資料的指標
mxArray *Y = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, dataNum, mxREAL);
memcpy(mxGetPr(X), xtemp, dataNum * sizeof(double)); //資料複製
memcpy(mxGetPr(Y), ytemp, dataNum * sizeof(double));
if ((ret = engPutVariable(eg, "X", X)) != 0) //把資料傳遞到matlab工作空間,並命名為X
printf("engPutVariable error:%d\n", ret);
if ((ret = engPutVariable(eg, "Y", Y)) != 0)
printf("engPutVariable error:%d\n", ret);
engEvalString(eg, "plot(X,Y)");//執行繪圖命令
getchar();
if(eg)
engClose(eg);
return 0;
}
編寫matlab命令封裝函式
從上面的程式設計可以看出,呼叫matlab進行繪圖過程也顯得比較繁瑣,例如要建立變數,複製記憶體資料,執行命令表示式等一系列操作。為了像在matlab中一樣呼叫執行matlab命令的體驗,可以把matlab的命令封裝成c語言的函式。例如,下面是對plot命令的封裝:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<engine.h>
#define dataNum 100
//忽略4096錯誤
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
int mat_plot(Engine *eg, double *x, double *y, int N, char *LineStyle, double LineWidth, double MarkerSize)
{
int ret = 0;
mxArray *X = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, N, mxREAL);
mxArray *Y = mxCreateDoubleMatrix(1, N, mxREAL);
mxArray *MS = mxCreateDoubleScalar(MarkerSize);
memcpy(mxGetPr(X), x, N * sizeof(double));
memcpy(mxGetPr(Y), y, N * sizeof(double));
if ((ret = engPutVariable(eg, "X", X)) != 0)
printf("engPutVariable error:%d\n", ret);
if ((ret = engPutVariable(eg, "Y", Y)) != 0)
printf("engPutVariable error:%d\n", ret);
//gennerate the plot command
char plotCommand[256] = "fig=plot(X,Y,'";
//set line style and marker
if (strlen(LineStyle) > 0)
strncat(plotCommand, LineStyle, strlen(LineStyle));
else
{
strncat(plotCommand, "-", strlen("-"));
}
strncat(plotCommand, "',", strlen(LineStyle));
char temp[20] = "";
//set line width
if (LineWidth < 1.0)
LineWidth = 1.0;
strncat(plotCommand, "'LineWidth',", strlen("'LineWidth',"));
memset(temp, 0, sizeof(temp));
sprintf(temp, "%f,", LineWidth);
strncat(plotCommand, temp, strlen(temp));
//set marker size
strncat(plotCommand, "'MarkerSize',", strlen("'MarkerSize',"));
sprintf(temp, "%f", MarkerSize);
strncat(plotCommand, temp, strlen(temp));
strncat(plotCommand, ");", strlen(temp));
//plot
if ((ret = engEvalString(eg, plotCommand)) != 0)
{
printf("\nplot Command error:%s\n", plotCommand);
return ret;
}
engEvalString(eg, "set(gcf,'color','w');");
printf("plot Command ok:%s\n", plotCommand);
//destroy mxArray,but they are still in matlab workspace
mxDestroyArray(X);
mxDestroyArray(Y);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Engine* eg = NULL;
if (!(eg = engOpen(NULL)))
{
printf("Open matlab enging fail!");
return 1;
}
int ret = 0;
double xtemp[dataNum] = { 0 };
double ytemp[dataNum] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < dataNum; i++)
{
xtemp[i] = i * 2.0 * 3.1415926 / 100.0;
ytemp[i] = sin(xtemp[i]);
}
mat_plot(eg, xtemp, ytemp, dataNum, "-r", 1, 5);
getchar();
if (eg)
engClose(eg);
return 0;
}
這樣使用起matlab命令就方便多了,例如我要用c語言裡運算的資料來畫圖,直接呼叫封裝的函式就可以了
mat_plot(eg, xtemp, ytemp, dataNum, "-r", 1, 5);
上面引數含義
eg:指向開啟的matlab引擎指標
xtemp:x座標資料
ytemp:y軸座標資料
dataNum:資料個數
“-r”:線型,顏色(還可以設定標記例如“–r*”)
1:線寬
5:標記大小
這樣就不用關心資料是怎樣傳遞資料到matlab和怎樣執行畫圖命令的。封裝函式寫得好些,就可以像matlab裡面使用更像,例如直接設定線型,線寬。
四、小結
以前對c演算法進行測試時,需要把c產生的資料導數到matlab,再進行繪圖,看效果。這樣既要寫c語言程式,還得專門寫matlab程式進行測試,而且要繪製動態圖形就特別麻煩。現在這樣通過直接在c/c++呼叫matlab引擎進行資料視覺化處理,可以在C語言環境裡,呼叫matlab幾乎所有命令。要是把matlab命令封裝好,就跟在matlab裡畫圖一樣方便,可以極大提高開發效率。
