Java NIO——selector
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-18
文章目錄
Java NIO程式設計例項之三Selector
1.概念
選擇器(Selector) 是 SelectableChannle 物件的多路複用器, Selector 可以同時監控多個 SelectableChannel 的 IO 狀況,也就是說,利用 Selector可使一個單獨的執行緒管理多個 Channel。 Selector 是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
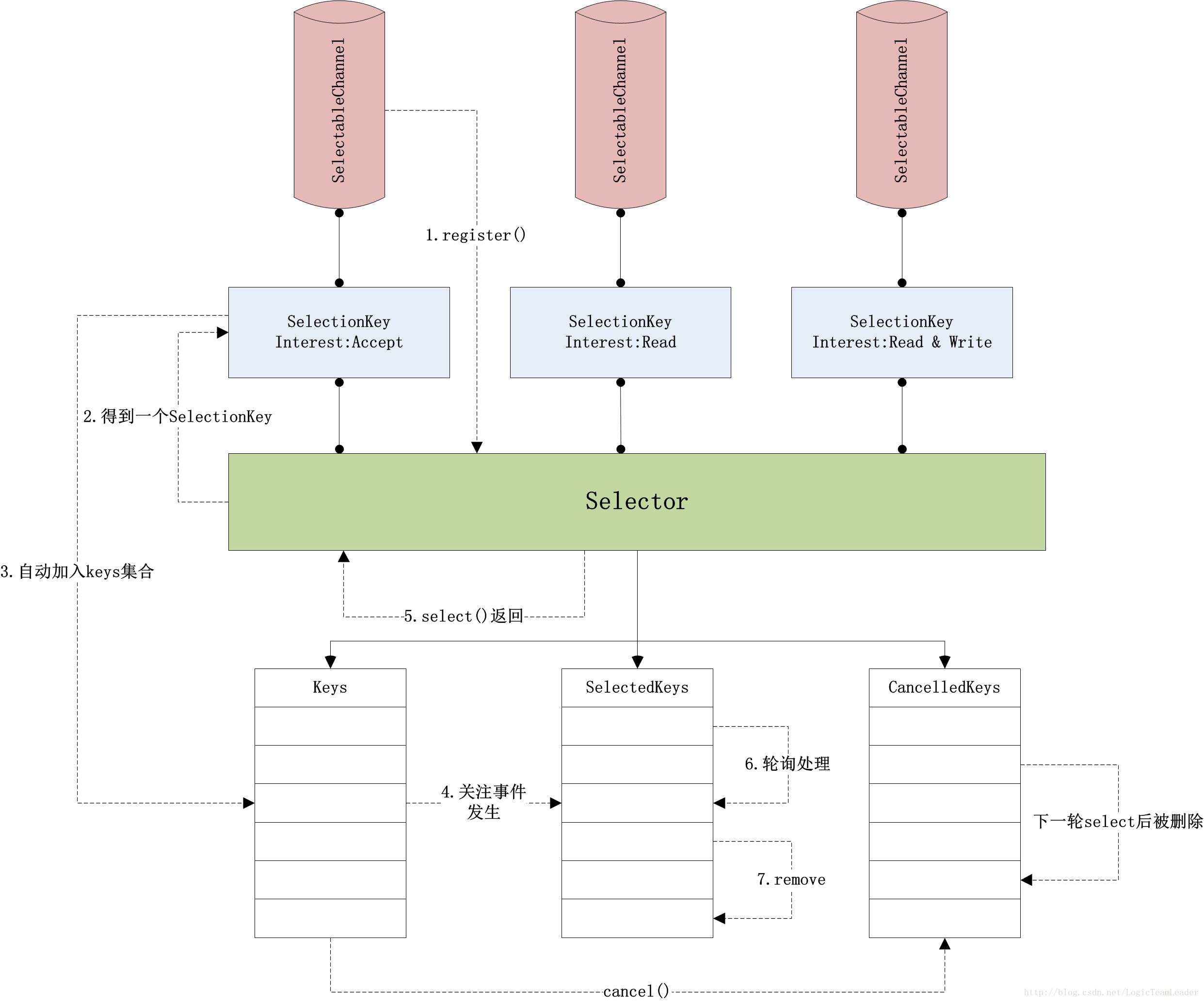
Selector、SelectionKey和SelectableChannel,它們之間的關係如下圖所示:
SelectableChannel是一類可以與Selector進行配合的通道,例如Socket相關通道以及Pipe產生的通道都屬於SelectableChannel。這類通道可以將自己感興趣的操作(例如read、write、accept和connect)註冊到一個
Selector是一個控制器,它負責管理已註冊的多個SelectableChannel,當這些通道的某些狀態改變時,Selector會被喚醒(從select()方法的阻塞中),並對所有就緒的通道進行輪詢操作。
2 selectionKey
當呼叫 register(Selector sel, int ops) 將通道註冊選擇器時,選擇器對通道的監聽事件,需要通過第二個引數 ops 指定可以監聽的事件型別(可使用 SelectionKey 的四個常量表示):
- 讀 : SelectionKey.OP_READ (1)
- 寫 : SelectionKey.OP_WRITE (4)
- 連線 : SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT (8)
- 接收 : SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT (16)
若註冊時不止監聽一個事件,則可以使用“位或”操作符連線。
int interestSet = SelectionKey.OP_READ|SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;
selectionKey常用方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| int interestOps() | 返回所感興趣的事件集合 |
| int readyOps() | 返回已經準備就緒的集合 |
| boolean isAcceptable() | 接收是否就緒 |
| boolean isConnectable() | 連線是否就緒 |
| boolean isReadable() | 讀操作是否就緒 |
| boolean isWritable | 寫操作是否就緒 |
| Channel channel | 獲取通道 |
| Selector selector | 獲取選擇器 |
| attach(Object o) | 將物件或資料附著到SelectionKey上 |
| Object attachment() | 獲取附著物件 |
3 常用方法
3.1 register(Selector selector,int ops)
SelectionKey register(Selector sel, int ops)
方法的返回值是一個SelectionKey,這個物件會被自動加入Selector的keys集合,因此不必特意保留這個SelectionKey的物件引用,需要時可以使用Selector的keys()方法得到所有的SelectionKey物件引用。
註冊完成後,該通道就與Selector保持關聯了。當通道的狀態改變時,其改變會自動被Selector感知,並在Selector的三個集合中反應出來。
3.2 三個集合
- Set keys(),獲取keys集合,儲存了所有與selector關聯的Selectionkey物件
- Set selectedKeys(),獲取selectedKeys集合,儲存了在一次select()方法呼叫後,所有狀態改變的通道關聯的SelectionKey物件
- cancelledKeys集合,儲存了一輪select()方法呼叫過程中,所有被取消但還未從keys中刪除的SelectionKey物件
3.3 select方法
- int select(),會一直阻塞,直到至少有一個註冊的通道狀態改變,才會被喚醒
- int select(long timeout),一直阻塞,直到時間耗盡,或者有通道的狀態改變。
3.4 wakeUp
3.5 close
4 demo
public class SelectorServer {
private static final int PORT = 1234;
private static ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
//1.register()
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("REGISTER CHANNEL , CHANNEL NUMBER IS:" + selector.keys().size());
while (true) {
//2.select()
int n = selector.select();
if (n == 0) {
continue;
}
//3.輪詢SelectionKey
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = (Iterator) selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//如果滿足Acceptable條件,則必定是一個ServerSocketChannel
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel sscTemp = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//得到一個連線好的SocketChannel,並把它註冊到Selector上,興趣操作為READ
SocketChannel socketChannel = sscTemp.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("REGISTER CHANNEL , CHANNEL NUMBER IS:" + selector.keys().size());
}
//如果滿足Readable條件,則必定是一個SocketChannel
if (key.isReadable()) {
//讀取通道中的資料
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
readFromChannel(channel);
}
//4.remove SelectionKey
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void readFromChannel(SocketChannel channel) {
buffer.clear();
try {
while (channel.read(buffer) > 0) {
buffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[buffer.remaining()];
buffer.get(bytes);
System.out.println("READ FROM CLIENT:" + new String(bytes));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
首先註冊了一個ServerSocketChannel,它用來監聽1234埠上的連線;當監聽到連線時,把連線上的SocketChannel再註冊到Selector上,這些SocketChannel註冊的是SelectionKey.OP_READ事件;當這些SocketChannel狀態變為可讀時,讀取資料並顯示。
public class SelectorClient {
static class Client extends Thread {
private String name;
private Random random = new Random(47);
Client(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(1234));
while (!channel.finishConnect()) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100);
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(100 * random.nextInt(10));
String str = "Message from " + name + ", number:" + i;
buffer.put(str.getBytes());
buffer.flip();
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
channel.write(buffer);
}
buffer.clear();
}
channel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
executorService.submit(new Client("Client-1"));
executorService.submit(new Client("Client-2"));
executorService.submit(new Client("Client-3"));
executorService.shutdown();
}
}