Spring Websocket+SockJS+STOMP 實現即時通訊(四)—— MessageChannel
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-18
兩種MessageChannel實現
TemporaryReplyChannel
- 用於接收單個回覆訊息的臨時通道。在整個斷點除錯過程中沒有追蹤到,所以在這裡不詳細說明。
ExecutorSubscribableChannel
- 正如字面上所表示的這樣Executor(執行緒池)Subscribable(可訂閱的)Channel(通道)——一個通過執行緒池將訊息傳送給每個訂閱者的通道。這也是Spring-Messaging功能的核心,理解了這個實現類的構成,就很容易掌握《Spring Websocket+SockJS+STOMP 實現即時通訊》
剖析ExecutorSubscribableChannel
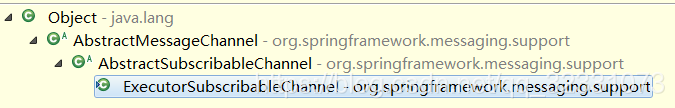 ExecutorSubscribableChannel類,通過繼承父類方法或直接宣告,可以看作由
ExecutorSubscribableChannel類,通過繼承父類方法或直接宣告,可以看作由 六 部分構成
- beanName:主要用作日誌記錄,用來區分ExecutorSubscribableChannel的不同例項;
- handlers:MessageHandler集合,作為MessageChannel的訂閱者,用來處理Messages;
- SendTask :一個內部類,是MessageHandlingRunnable的子類,將一個Message與一個MessageHandler封裝成執行緒任務,丟入執行緒池執行;
- executor: 用來執行SendTask任務的TaskPoolExecutor執行緒池;
- interceptors :普通ChannelInterceptor集合;
- executorInterceptors:ExecutorChannelInterceptor執行緒池攔截器集合;
ExecutorSubscribableChannel:
public class ExecutorSubscribableChannel extends AbstractSubscribableChannel {
private String beanName;
private final Set<MessageHandler> handlers = new CopyOnWriteArraySet 三個ExecutorSubscribableChannel例項
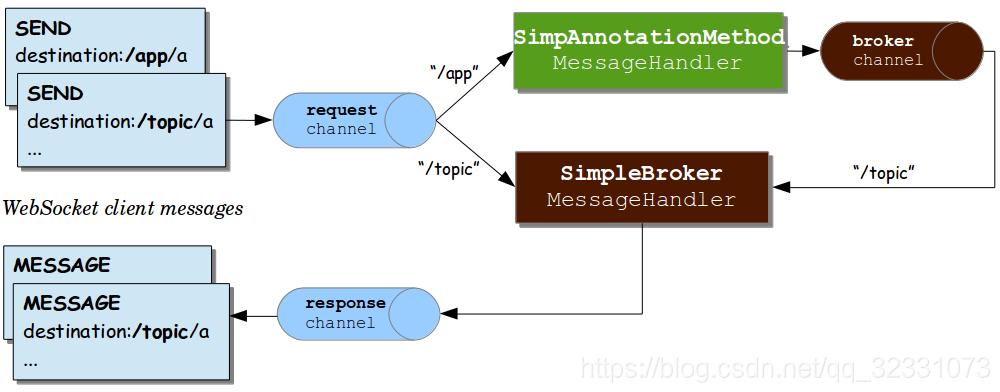
在啟用STOMP的時候——@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker,Spring框架會自動構造三個ExecutorSubscribableChannel例項:
- “clientInboundChannel” — 用於傳遞從WebSocket客戶端接收到的訊息。
- “clientOutboundChannel” — 用於向WebSocket客戶端傳送伺服器訊息。
- “brokerChannel” — 用於從伺服器端的應用程式程式碼中向message broker或 stomp broker relay傳送訊息。
工作方式如下圖所示:
啟用簡單的訊息代理:config.enableSimpleBroker
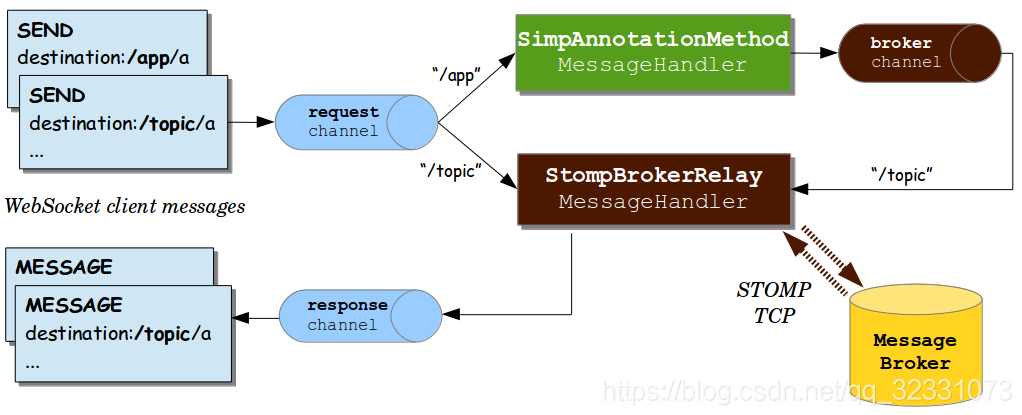
啟用STOMP代理中繼:config.enableStompBrokerRelay
自定義配置MessageChannel
- 啟用STOMP,並配置MessageChannel。從方法的名字上我們可以確定分別是對brokerChannel、clientInboundChannel、clientOutboundChannel進行自定義配置。
WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer實現類:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebSocketConfigurer implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry config) {
config.configureBrokerChannel().taskExecutor();
}
@Override
public void configureClientInboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
}
@Override
public void configureClientOutboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
}
}
- 一直說通過@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker來啟用STOMP,那麼它是如何啟用STOMP的呢?當然,它是通過匯入相關配置來實現STOMP啟用的。
EnableWebSocketMessageBroker:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(DelegatingWebSocketMessageBrokerConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebSocketMessageBroker {
}
- 配置clientInboundChannel。其中有
一個相關成員變數和四個相關方法:- 一個成員變數: clientInboundChannelRegistration:用來登記“clientInboundChannel”的配置資訊。
- 一個鉤子方法:
configureClientInboundChannel(registration):留給它的子類,用來獲取
WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer提供的自定義配置資訊。 - 三個Bean方法:
- clientInboundChannel():通過
clientInboundChannelExecutor()獲得Executor例項,通過getClientInboundChannelRegistration()獲得通道的其他配置資訊,用來構造一個ExecutorSubscribableChannel例項做為“clientInboundChannel”; - clientInboundChannelExecutor():通過
getClientInboundChannelRegistration()獲得通道配置資訊,再從通道配置資訊中獲得TaskExecutorRegistration執行緒池配置資訊,最後從TaskExecutorRegistration獲得ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 例項,作為“clientInboundChannel”的支撐; - getClientInboundChannelRegistration():如果成員變數
clientInboundChannelRegistration為null,那麼將直接new一個ChannelRegistration例項,並賦值給成員變數clientInboundChannelRegistration,同時呼叫configureClientInboundChannel(registration)鉤子方法,獲取WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer提供的自定義配置資訊,否則就說明不是第一次呼叫該方法,直接返回成員變數;
- clientInboundChannel():通過
AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration :
public abstract class AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
private ChannelRegistration clientInboundChannelRegistration;
@Bean
public AbstractSubscribableChannel clientInboundChannel() {
ExecutorSubscribableChannel channel = new ExecutorSubscribableChannel(clientInboundChannelExecutor());
ChannelRegistration reg = getClientInboundChannelRegistration();
if (reg.hasInterceptors()) {
channel.setInterceptors(reg.getInterceptors());
}
return channel;
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor clientInboundChannelExecutor() {
TaskExecutorRegistration reg = getClientInboundChannelRegistration().taskExecutor();
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = reg.getTaskExecutor();
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("clientInboundChannel-");
return executor;
}
protected final ChannelRegistration getClientInboundChannelRegistration() {
if (this.clientInboundChannelRegistration == null) {
ChannelRegistration registration = new ChannelRegistration();
configureClientInboundChannel(registration);
registration.interceptors(new ImmutableMessageChannelInterceptor());
this.clientInboundChannelRegistration = registration;
}
return this.clientInboundChannelRegistration;
}
/**
* A hook for subclasses to customize the message channel for inbound messages
* from WebSocket clients.
*/
protected void configureClientInboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
}
}
- 配置clientOutboundChannel。其中也有
一個相關成員變數和四個相關方法,在此不做詳述,可以直接類比上面的“配置clientInboundChannel”。
AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration :
public abstract class AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
private ChannelRegistration clientOutboundChannelRegistration;
@Bean
public AbstractSubscribableChannel clientOutboundChannel() {
ExecutorSubscribableChannel channel = new ExecutorSubscribableChannel(clientOutboundChannelExecutor());
ChannelRegistration reg = getClientOutboundChannelRegistration();
if (reg.hasInterceptors()) {
channel.setInterceptors(reg.getInterceptors());
}
return channel;
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor clientOutboundChannelExecutor() {
TaskExecutorRegistration reg = getClientOutboundChannelRegistration().taskExecutor();
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = reg.getTaskExecutor();
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("clientOutboundChannel-");
return executor;
}
protected final ChannelRegistration getClientOutboundChannelRegistration() {
if (this.clientOutboundChannelRegistration == null) {
ChannelRegistration registration = new ChannelRegistration();
configureClientOutboundChannel(registration);
registration.interceptors(new ImmutableMessageChannelInterceptor());
this.clientOutboundChannelRegistration = registration;
}
return this.clientOutboundChannelRegistration;
}
/**
* A hook for subclasses to customize the message channel for messages from
* the application or message broker to WebSocket clients.
*/
protected void configureClientOutboundChannel(ChannelRegistration registration) {
}
}
-
在看brokerChannel之前,有必要先要了解下
ChannelRegistration——通道配置資訊類。該類共持有兩個例項:- TaskExecutorRegistration例項:
我們知道
ExecutorSubscribableChannel實際上是由ThreadPoolTaskExecutor執行緒池作為支撐,而TaskExecutorRegistration所持有的就是通道的ThreadPoolTaskExecutor執行緒池配置資訊; - ChannelInterceptor集合: 用來儲存一系列的通道攔截器;
另外我們需要理解taskExecutor(taskExecutor)方法:
- 如果
taskExecutor()方法不是第一次被呼叫,那麼TaskExecutorRegistration將不為null,說明執行緒池已經被配置,將直接返回配置資訊; - 如果
TaskExecutorRegistration為null,那麼繼續判斷; - 引數
taskExecutor如果不為null,那麼將把taskExecutor繫結到TaskExecutorRegistration——new TaskExecutorRegistration(taskExecutor); - 引數
taskExecutor如果為null,那麼直接new TaskExecutorRegistration();
- TaskExecutorRegistration例項:
我們知道
ChannelRegistration:
public class ChannelRegistration {
@Nullable
private TaskExecutorRegistration registration;
private final List<ChannelInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Configure the thread pool backing this message channel.
*/
public TaskExecutorRegistration taskExecutor() {
return taskExecutor(null);
}
/**
* Configure the thread pool backing this message channel using a custom
* ThreadPoolTaskExecutor.
* @param taskExecutor the executor to use (or {@code null} for a default executor)
*/
public TaskExecutorRegistration taskExecutor(@Nullable ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
if (this.registration == null) {
this.registration = (taskExecutor != null ? new TaskExecutorRegistration(taskExecutor) :
new TaskExecutorRegistration());
}
return this.registration;
}
/**
* Configure the given interceptors for this message channel,
* adding them to the channel's current list of interceptors.
* @since 4.3.12
*/
public ChannelRegistration interceptors(ChannelInterceptor... interceptors) {
this.interceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
return this;
}
/**
* Configure interceptors for the message channel.
* @deprecated as of 4.3.12, in favor of {@link #interceptors(ChannelInterceptor...)}
*/
@Deprecated
public ChannelRegistration setInterceptors(@Nullable ChannelInterceptor... interceptors) {
if (interceptors != null) {
this.interceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
return this;
}
protected boolean hasTaskExecutor() {
return (this.registration != null);
}
protected boolean hasInterceptors() {
return !this.interceptors.isEmpty();
}
protected List<ChannelInterceptor> getInterceptors() {
return this.interceptors;
}
}
- 接著再看
TaskExecutorRegistration這個類,這個類持有一個ThreadPoolTaskExecutor例項。這個類有兩個構造方法:- TaskExecutorRegistration(taskExecutor):
將傳入的
taskExecutor繫結到成員變數上。 - TaskExecutorRegistration():
無參的構造方法,在該構造方法中,會直接
new一個ThreadPoolTaskExecutor例項,其coreSize核心執行緒數為Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2 —— 兩倍CPU
- TaskExecutorRegistration(taskExecutor):
將傳入的
TaskExecutorRegistration:
public class TaskExecutorRegistration {
private final ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor;
/**
* Create a new {@code TaskExecutorRegistration} for a default
* {@link ThreadPoolTaskExecutor}.
*/
public TaskExecutorRegistration() {
this.taskExecutor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
this.taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2);
this.taskExecutor.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
}
/**
* Create a new {@code TaskExecutorRegistration} for a given
* {@link ThreadPoolTaskExecutor}.
* @param taskExecutor the executor to use
*/
public TaskExecutorRegistration(ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor) {
Assert.notNull(taskExecutor, "ThreadPoolTaskExecutor must not be null");
this.taskExecutor = taskExecutor;
}
protected ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getTaskExecutor() {
if (this.corePoolSize != null) {
this.taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(this.corePoolSize);
}
if (this.maxPoolSize != null) {
this.taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(this.maxPoolSize);
}
if (this.keepAliveSeconds != null) {
this.taskExecutor.setKeepAliveSeconds(this.keepAliveSeconds);
}
if (this.queueCapacity != null) {
this.taskExecutor.setQueueCapacity(this.queueCapacity);
}
return this.taskExecutor;
}
}
- 配置brokerChannel。與clientInboundChannel、clientOutboundChannel不同的是,配置brokerChannel用
getBrokerRegistry()代替了getClient**boundChannelRegistration()、用configureMessageBroker(registry)代替了configureClient**boundChannel(registration),主要是因為前兩者只需要配置MessageChannel,而後者既需要配置MessageChannel同時需要配置MessageBroker,所以這裡用MessageBrokerRegistry代替了ChannelRegistration,而MessageBrokerRegistry持有了ChannelRegistration例項,相當於多加了一層;
AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration :
public abstract class AbstractMessageBrokerConfiguration implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Nullable
private MessageBrokerRegistry brokerRegistry;
@Bean
public AbstractSubscribableChannel brokerChannel() {
ChannelRegistration reg = getBrokerRegistry().getBrokerChannelRegistration();
ExecutorSubscribableChannel channel = (reg.hasTaskExecutor() ?
new ExecutorSubscribableChannel(brokerChannelExecutor()) : new ExecutorSubscribableChannel());
reg.interceptors(new ImmutableMessageChannelInterceptor());
channel.setInterceptors(reg.getInterceptors());
return channel;
}
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor brokerChannelExecutor() {
ChannelRegistration reg = getBrokerRegistry().getBrokerChannelRegistration();
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor;
if (reg.hasTaskExecutor()) {
executor = reg.taskExecutor().getTaskExecutor();
}
else {
// Should never be used
executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(0);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(1);
executor.setQueueCapacity(0);
}
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("brokerChannel-");
return executor;
}
/**
* An accessor for the {@link MessageBrokerRegistry} that ensures its one-time creation
* and initialization through {@link #configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry)}.
*/
protected final MessageBrokerRegistry getBrokerRegistry() {
if (this.brokerRegistry == null) {
MessageBrokerRegistry registry = new MessageBrokerRegistry(clientInboundChannel(), clientOutboundChannel());
configureMessageBroker(registry);
this.brokerRegistry = registry;
}
return this.brokerRegistry;
}
/**
* A hook for subclasses to customize message broker configuration through the
* provided {@link MessageBrokerRegistry} instance.
*/
protected void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry registry) {
}
}
- 值得注意的是,
brokerChannel()方法在構造ExecutorSubscribableChannel例項時,繫結ThreadPoolTaskExecutor的邏輯與前兩者有所不同,結合上面的分析不難理解下列內容;- clientInboundChannel、clientOutboundChannel
這兩個通道的執行緒池一定會被設定,所以Messages總會由新的執行緒非同步處理,首先考慮自定義配置執行緒池,如果沒有,那麼將配置預設執行緒池 —— 其coreSize核心執行緒數為
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2—— 兩倍CPUExecutorSubscribableChannel channel = new ExecutorSubscribableChannel(client**boundChannelExecutor()); - brokerChannel
如果沒有自定義配置執行緒池,那麼
brokerChannel的執行緒池將被設為null,Messages將會被使用當前執行緒同步處理,所以在生產環境中一定要配置brokerChannel的執行緒池ExecutorSubscribableChannel channel = (reg.hasTaskExecutor() ? new ExecutorSubscribableChannel(brokerChannelExecutor()) : new ExecutorSubscribableChannel());
- clientInboundChannel、clientOutboundChannel
這兩個通道的執行緒池一定會被設定,所以Messages總會由新的執行緒非同步處理,首先考慮自定義配置執行緒池,如果沒有,那麼將配置預設執行緒池 —— 其coreSize核心執行緒數為
ExecutorSubscribableChannel :
public class ExecutorSubscribableChannel extends AbstractSubscribableChannel {
@Nullable
private final Executor executor;
/**
* Create a new {@link ExecutorSubscribableChannel} instance
* where messages will be sent in the callers thread.
*/
public ExecutorSubscribableChannel() {
this(null);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link ExecutorSubscribableChannel} instance
* where messages will be sent via the specified executor.
* @param executor the executor used to send the message,
* or {@code null} to execute in the callers thread.
*/
public ExecutorSubscribableChannel(@Nullable Executor executor) {
this.executor = executor;
}
}
