六、JDBC--獲取自動生成的主鍵值&處理Blob&資料庫事務處理
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-18
【孤立的技術是沒有價值的】,我們這裡只是為了瞭解具體的實現步驟:我們在插入資料的時候,經常會需要獲取我們插入的這一行資料對應的主鍵值。
具體的程式碼實現:
/** * 獲取資料庫自動生成的主鍵 */ @Test public void testGetKeyValues(){ Connection connection=null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null; ResultSet rs=null; try { connection=JDBCTools.getConnection(); String sql="insert into customers(name,email,birth)"+ " values(?,?,?)"; // preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql); //我們這裡使用過載的prepareStatement(sql,flag)方法 //來生成prepareStatement物件 preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS); preparedStatement.setString(1, "ABCDE"); preparedStatement.setString(2, "[email protected]"); preparedStatement.setDate(3, new Date(new java.util.Date().getTime())); preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //通過getGeneratedKeys方法獲取包含了新生成的主鍵的ResultSet物件 //在ResultSet結果集中,只包含一列,列名:GENERATED_KEY,用於存放新生成的主鍵值 rs=preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys(); if(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getObject(1)); } ResultSetMetaData rsmd=rs.getMetaData(); for(int i=0;i<rsmd.getColumnCount();i++){ System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnName(i+1)); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ JDBCTools.release(rs,preparedStatement,connection); } }
處理Blob
Blob的基本概念
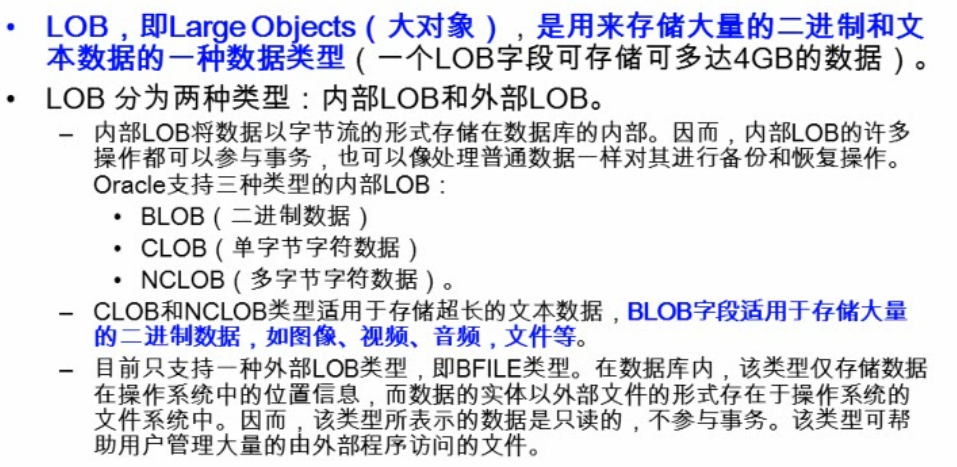
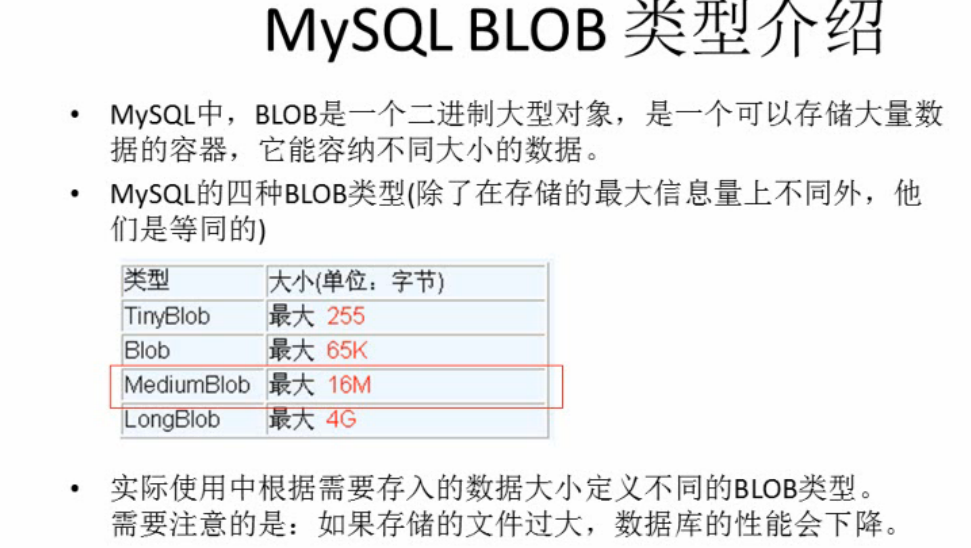
1).插入Blob型別資料
/**
* 插入Blob型別的資料必須使用PreparedStatement
* 因為Blob型別的資料是無法使用字串拼寫的
*
* 呼叫setBlob(int index,InputStream inputStream)
*/@Test
public void testInsertBlod(){
Connection connection=null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
try {
connection=JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql="insert into customers(name,email,birth,picture)"+
" values(?,?,?,?)";
// preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//我們這裡使用過載的prepareStatement(sql,flag)方法
//來生成prepareStatement物件
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "ABCDE");
preparedStatement.setString(2, " 2).讀取Blob型別資料
/**
* 讀取Blob資料:
* 1.使用getBlob方法,讀取Blod物件
* 2.呼叫Blob的getBinaryStream()方法得到輸入流,再使用IO操作即可
*/@Test
public void testReadBlob(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCTools.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name,email,birth,picture"+
" from customers where id =18";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
int id=resultSet.getInt(1);
String name=resultSet.getString(2);
String email=resultSet.getString(3);
System.out.println(id+":"+name+":"+email);
Blob pictureBlob=resultSet.getBlob(5);
InputStream inputStream=pictureBlob.getBinaryStream();
OutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("flo.png");
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len =0;
while((len=inputStream.read(buffer))!=-1){
out.write(buffer,0,len);
}
out.close();
inputStream.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCTools.release(resultSet, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}資料庫事務
資料庫事務概述

資料庫事務的四個屬性

JDBC的資料庫事務

我們做一個小實驗:
先建立一個數據表:
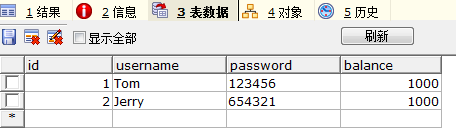
試驗中要用到的更新資料的通用方法update():要保證兩次操作用一個connection連線,否則就不能被稱為一次事務了。
public static void update(Connection connection,String sql,
Object ...args){
/**
* 執行SQL語句,使用PreparedStatement
*/
PreparedStatement preparedStatement=null;
try {
preparedStatement=connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
}
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
JDBCTools.release(null, preparedStatement, null);
}我們要完成的是:Tom->Jerry匯款500元
* 資料庫事務
* 關於事務:
* 1.如果多個操作,每個操作使用的是自己的單獨的連線,則無法保證事務
* 2.具體步驟:
* 1).開始事務,取消預設自動提交行為
* 2).如果事務的操作都成功,則提交事務:connection.commit();
* 3).回滾事務:若出現異常,則在catch塊中回滾事務
我們組織程式碼就按照上面的步驟來進行.
public void testTeansaction() throws Exception{
Connection connection=null;
try {
connection=JDBCTools.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection.getAutoCommit());
String sql="update users set balance=balance-500 where id=1";
//開始事務:取消預設提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
update(connection,sql);
int i=10/0;
System.out.println(i);
sql="update users set balance=balance+500 where id=2";
JDBCTools.update(sql);
//提交事務
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//回滾事務
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}finally{
//關閉連線
JDBCTools.release(null, null, connection);
}
}可以發現,因為我們使用的是同一個connection連線,當異常(除數為0)發生的時候,事務會發生回滾,資料庫的資料會恢復到事務開始之前的狀態.
