第3章 函式 (2)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-18
文章目錄
一、巢狀與遞迴
1、函式的巢狀
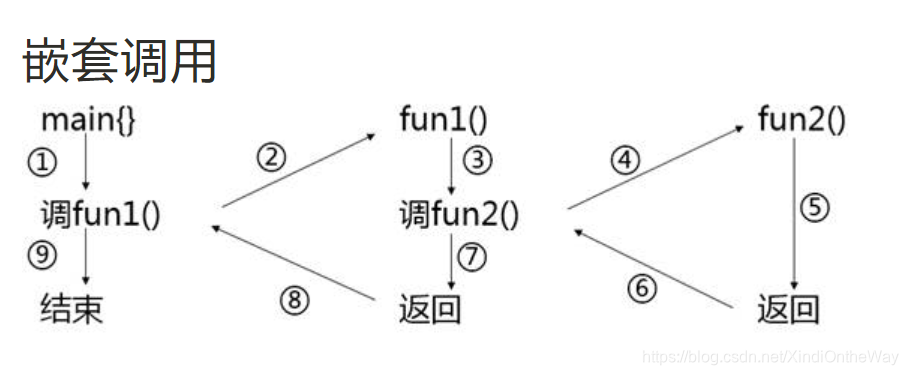
2、函式的遞迴呼叫
定義:函式直接或者間接地呼叫自身。
例題1:計算n的階乘
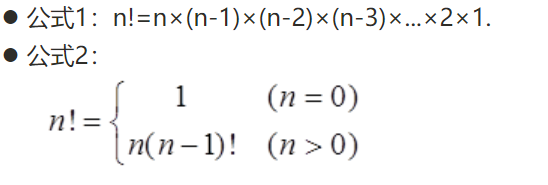
#include <iostream> 例題2:用遞迴法計算從n個人中選k個人組成一個委員會的不同組合數。
分析
- 由n個人裡選k個人的組合數= 由n-1個人裡選k個人的組合數+由n-1個人裡選k-1個人的組合數;
- 當n = k或k = 0時,組合數為1。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
unsigned combination(unsigned n, unsigned k) {
unsigned results;
if (k > n)
results = 0;
else if (n == k || k == 0)
results = 1;
else
results = combination(n - 1, k) + combination(n - 1, k - 1);
return results;
}
int main() {
int n, k;
cout << "please enter n and k: " << endl;
cin >> n >> k;
cout << "C(n,k)="<<combination(n,k) << endl;
return 0;
}
例題3 漢諾塔

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void move(char src, char dest) {
cout << src << " ----> " << dest << endl;
}
void hanoi(int m, char src, char medium, char dest) {
//m: 盤子個數 src:源 dest: 目的地 medium: 中介
if (m == 1) {
move(src, dest);
}
else {
hanoi(m - 1, src, dest, medium);
move(src, dest);
hanoi(m - 1, medium, src, dest);
}
}
int main() {
hanoi(10, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
二、函式的引數傳遞

1、引用型別

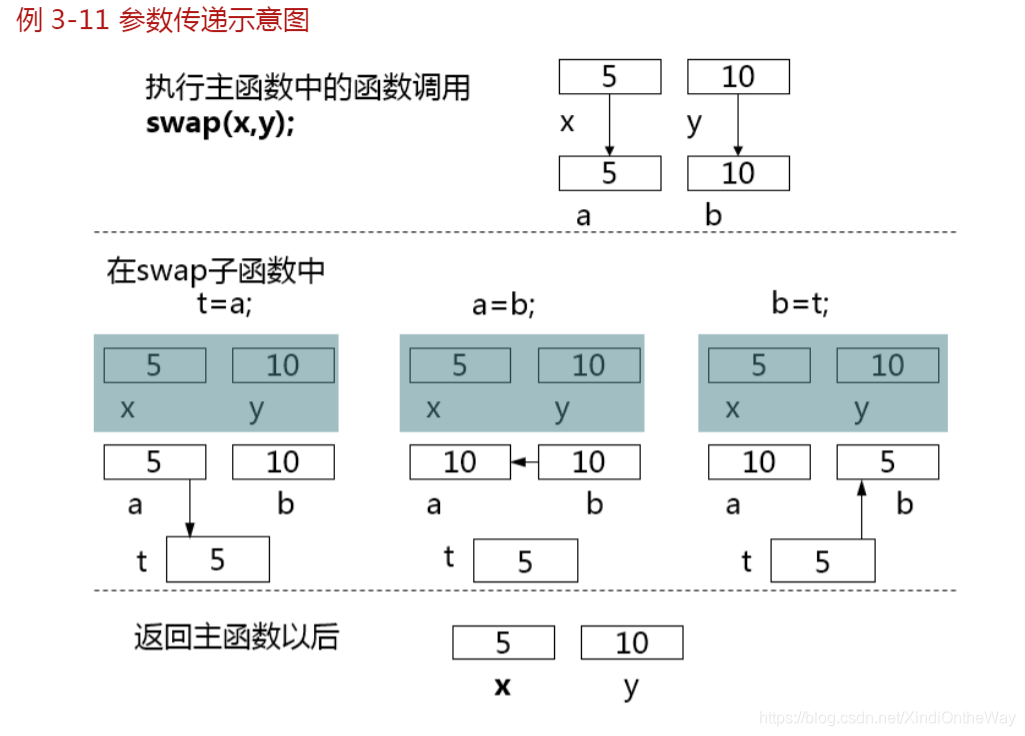
例題1: 值傳遞,交換
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int a, int b) {
int t;
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int main() {
int x = 4, y = 5;
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
swap(x, y);
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
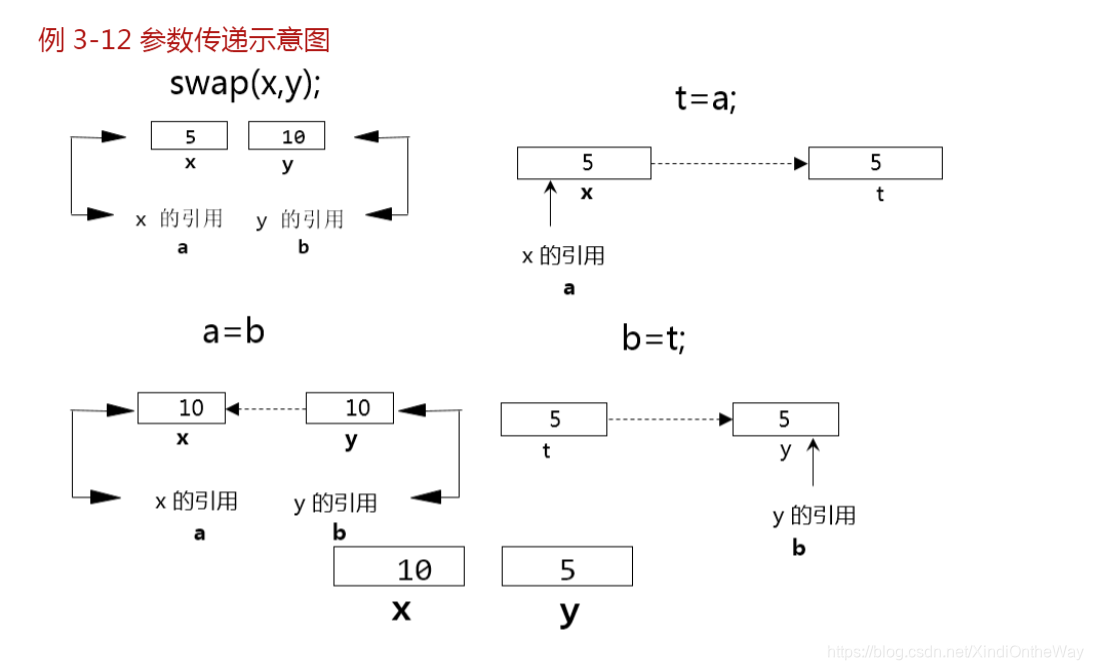
例題2:引用傳遞,交換
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int &a, int &b) {
int t;
t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
}
int main() {
int x = 4, y = 5;
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
swap(x, y);
cout << "x = " << x << " y = " << y << endl;
return 0;
}
三、含有可變引數的函式
含有可變引數的函式

initializer_list提供的操作

initializer_list使用方法

四、行內函數


例題:行內函數應用舉例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.1415926;
inline double calArea(double r) {
return PI * r*r;
}
int main() {
double r = 3.0;
double area = calArea(r);
cout << area << endl;
return 0;
}
五、constexpr函式

六、帶預設引數值的函式
預設引數值
可以預先設定預設的引數值,呼叫時如給出實參,則採用實參值,否則採用預先設定的預設引數值。
例:
int add(int x = 5,int y = 6) {
return x + y;
}
int main() {
add(10,20); //10+20
add(10); //10+6
add(); //5+6
}
預設引數值的說明次序
- 有預設引數的形參必須列在形參列表的最右,即預設引數值的右面不能有無預設值的引數;
- 呼叫時實參與形參的結合次序是從左向右。
例:
int add(int x, int y = 5, int z = 6);//正確
int add(int x = 1, int y = 5, int z);//錯誤
int add(int x = 1, int y, int z = 6);//錯誤
預設引數值與函式的呼叫位置
- 如果一個函式有原型宣告,且原型宣告在定義之前,則預設引數值應在函式原型宣告中給出;如果只有函式的定義,或函式定義在前,則預設引數值可以函式定義中給出。
例:

例題:計算長方體體積
函式getVolume計算體積
有三個形參:length(長)、width(寬)、height(高),其中width和height帶有預設值2和3。
主函式中以不同形式呼叫getVolume函式。
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int getVolume(int length, int width = 2, int height = 3);
int main() {
const int X = 10, Y = 12, Z = 15;
cout << "Some box data is " ;
cout << getVolume(X, Y, Z) << endl;
cout << "Some box data is " ;
cout << getVolume(X, Y) << endl;
cout << "Some box data is " ;
cout << getVolume(X) << endl;
return 0;
}
int getVolume(int length, int width, int height) {
cout << setw(5) << length << setw(5) << width << setw(5)
<< height << '\t';
return length * width * height;
}
七、函式過載
函式過載的概念
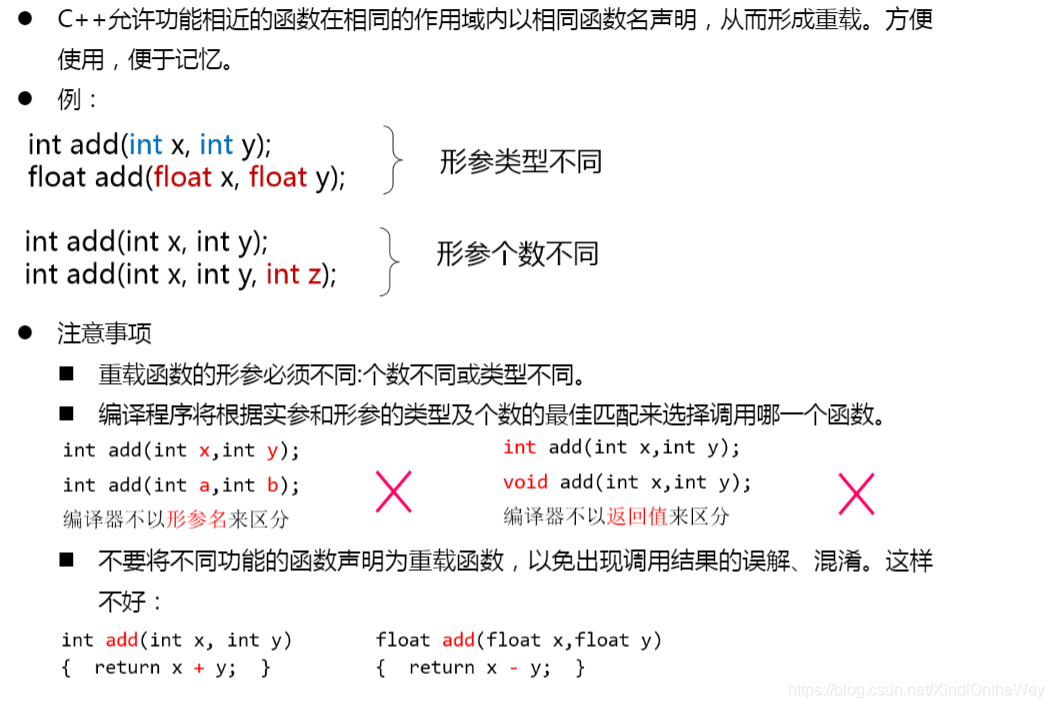
例題:過載函式應用舉例
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sumOfSquare(int a, int b) {
return a * a + b * b;
}
double sumOfSquare(double a, double b) {
return a * a + b * b;
}
int main() {
int m, n;
cout << "Enter two integer: ";
cin >> m >> n;
cout << "Their sum of square: " << sumOfSquare(m, n) << endl;
double x, y;
cout << "Enter two real number: ";
cin >> x >> y;
cout << "Their sum of square: " << sumOfSquare(x, y) << endl;
return 0;
}
八、C++系統函式

#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.14159265358979;
int main() {
double angle;
cout << "Please enter an angle: ";
cin >> angle; //輸入角度值
double radian = angle * PI / 180; //轉化為弧度值
cout << "sin(" << angle << ") = " << sin(radian) <<endl;
cout << "cos(" << angle << ") = " << cos(radian) <<endl;
cout << "tan(" << angle << ") = " << tan(radian) <<endl;
return 0;
}
