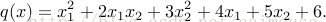黑塞矩陣 Hessian Matrix
在機器學習課程裡提到了這個矩陣,那麼這個矩陣是從哪裡來,又是用來作什麼用呢?先來看一下定義:
黑塞矩陣(Hessian Matrix),又譯作海森矩陣、海瑟矩陣、海塞矩陣等,是一個多元函式的二階偏導數構成的方陣,描述了函式的局部曲率。黑塞矩陣最早於19世紀由德國數學家Ludwig Otto Hesse提出,並以其名字命名。黑塞矩陣常用於牛頓法解決優化問題。
一般來說, 牛頓法主要應用在兩個方面, 1, 求方程的根; 2, 最優化.
在機器學習裡,可以考慮採用它來計算n值比較少的資料,在影象處理裡,可以抽取影象特徵,在金融裡可以用來作量化分析。
影象處理可以看這個連線:
量化分析可以看這個:
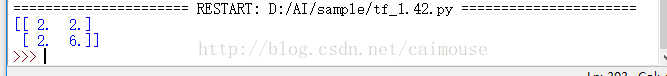
下面使用TensorFlow並且使用黑塞矩陣來求解下面的方程:
程式碼如下:
#python 3.5.3 蔡軍生 #http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/2592 # import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npdef cons(x): return tf.constant(x, dtype=tf.float32)def compute_hessian(fn, vars): mat = [] for v1 in vars: temp = [] for v2 in vars: # computing derivative twice, first w.r.t v2 and then w.r.t v1 再來舉多一個例子的原始碼,它就是用來計算量化分析,這個程式碼很值錢啊,如下:
#python 3.5.3 蔡軍生 #http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/2592 # import numpy as npimport scipy.stats as statsimport scipy.optimize as opt#構造Hessian矩陣def rosen_hess(x): x = np.asarray(x) H = np.diag(-400*x[:-1],1) - np.diag(400*x[:-1],-1) diagonal = np.zeros_like(x) diagonal[0] = 1200*x[0]**2-400*x[1]+2 diagonal[-1] = 200 diagonal[1:-1] = 202 + 1200*x[1:-1]**2 - 400*x[2:] H = H + np.diag(diagonal) return Hdef rosen(x): """The Rosenbrock function""" return sum(100.0*(x[1:]-x[:-1]**2.0)**2.0 + (1-x[:-1])**2.0)def rosen_der(x): xm = x[1:-1] xm_m1 = x[:-2] xm_p1 = x[2:] der = np.zeros_like(x) der[1:-1] = 200*(xm-xm_m1**2) - 400*(xm_p1 - xm**2)*xm - 2*(1-xm) der[0] = -400*x[0]*(x[1]-x[0]**2) - 2*(1-x[0]) der[-1] = 200*(x[-1]-x[-2]**2) return derx_0 = np.array([0.5, 1.6, 1.1, 0.8, 1.2])res = opt.minimize(rosen, x_0, method='Newton-CG', jac=rosen_der, hess=rosen_hess, options={'xtol': 1e-8, 'disp': True})print("Result of minimizing Rosenbrock function via Newton-Conjugate-Gradient algorithm (Hessian):")print(res)====================== RESTART: D:/AI/sample/tf_1.43.py ======================Optimization terminated successfully. Current function value: 0.000000 Iterations: 20 Function evaluations: 22 Gradient evaluations: 41 Hessian evaluations: 20Result of minimizing Rosenbrock function via Newton-Conjugate-Gradient algorithm (Hessian): fun: 1.47606641102778e-19 jac: array([ -3.62847530e-11, 2.68148992e-09, 1.16637362e-08, 4.81693414e-08, -2.76999090e-08]) message: 'Optimization terminated successfully.' nfev: 22 nhev: 20 nit: 20 njev: 41 status: 0 success: True x: array([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])>>>
可見hessian矩陣可以使用在很多地方了吧。
1. C++標準模板庫從入門到精通
2.跟老菜鳥學C++
3. 跟老菜鳥學python
4. 在VC2015裡學會使用tinyxml庫
5. 在Windows下SVN的版本管理與實戰
7.在VC2015裡使用protobuf協議
8.在VC2015裡學會使用MySQL資料庫
可以看更多的網站:
http://blog.csdn.net/ubunfans/article/details/41520047
http://blog.csdn.net/baimafujinji/article/details/51167852
http://jacoxu.com/jacobian%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5%E5%92%8Chessian%E7%9F%A9%E9%98%B5/
http://www.cnblogs.com/logosxxw/p/4651413.html