Spring 原始碼分析(二) —— 核心容器
容器概述
IoC也被稱作依賴注入(DI)。它是一個處理物件依賴項的過程,也就是將他們一起工作的其他的物件,只有通過構造引數、工廠方法引數或者(屬性注入)通過構造引數例項化或通過工廠方法返回物件後再設定屬性。當建立bean後,IoC容器再將這些依賴項注入進去。這個過程基本上是反轉的,因此得名控制反轉(IoC)。
下圖是 IoC 的高級別檢視
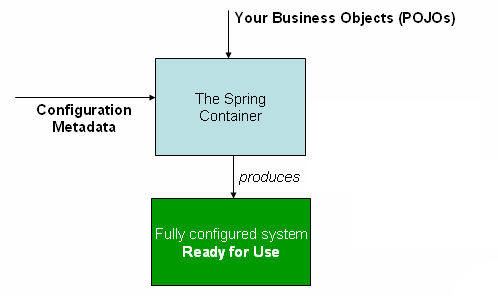
IoC容器利用Java的POJO類和配置元資料來生成 完全配置和可執行 的系統或應用程式。而Bean在Spring中就是POJO,也可以認為Bean就是物件。
設計實現
介面設計
Spring作為面向物件程式設計的集大成之作,我們直接從介面入手可以幫助我們更直觀的瞭解Ioc容器的設計原理。
下圖描述了Ioc容器中的主要介面設計
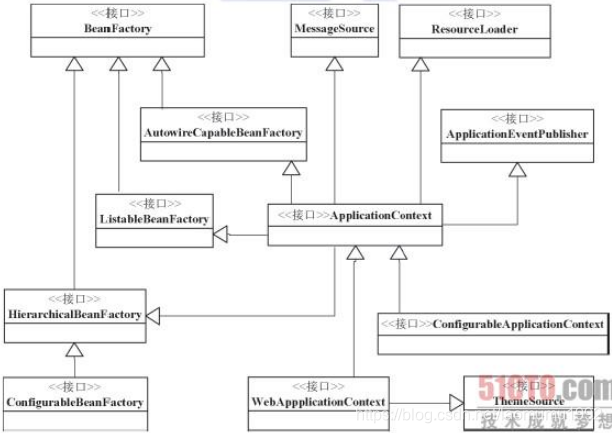
體實現體系,比如DefaultListableBeanFactory就是為了實現ConfigurableBeanFactory,從而成為一個簡單Ioc容器實現。與其他Ioc容器類似,XmlBeanFactory就是為了實現BeanFactory,但都是基於DefaultListableBeanFactory的基礎做了擴充套件。同樣的,ApplicationContext也一樣。
從圖中我們可以簡要的做出以下分析:
1.從介面BeanFactory到HierarchicalBeanFactory,再到ConfigurableBeanFactory,這是一條主要的BeanFactory設計路徑。在這條介面設計路徑中,BeanFactory介面定義了基本的Ioc容器的規範。在這個介面定義中,包括了getBean()這樣的Ioc容器的基本方法(通過這個方法可以從容器中取得Bean)。而HierarchicalBeanFactory介面在繼承了BeanFactory的基本介面後,增加了getParentBeanFactory()的介面功能,使BeanFactory具備了雙親Ioc容器的管理功能。在接下來的ConfigurableBeanFactory介面中,主要定義了一些對BeanFactory的配置功能,比如通過setParentBeanFactory()設定雙親Ioc容器,通過addBeanPostProcessor()配置Bean後置處理器,等等。通過這些介面設計的疊加,定義了BeanFactory就是最簡單的Ioc容器的基本功能。
2.第二條介面設計主線是,以ApplicationContext作為核心的介面設計,這裡涉及的主要介面設計有,從BeanFactory到ListableBeanFactory,再到ApplicationContext,再到我們常用的WebApplicationContext或者ConfigurableApplicationContext介面。我們常用的應用基本都是org.framework.context 包裡的WebApplicationContext或者ConfigurableApplicationContext實現。在這個介面體現中,ListableBeanFactory和HierarchicalBeanFactory兩個介面,連線BeanFactory介面定義和ApplicationContext應用的介面定義。在ListableBeanFactory介面中,細化了許多BeanFactory的介面功能,比如定義了getBeanDefinitionNames()介面方法;對於ApplicationContext介面,它通過繼承MessageSource、ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher介面,在BeanFactory簡單Ioc容器的基礎上添加了許多對高階容器的特性支援。
3.這個介面系統是以BeanFactory和ApplicationContext為核心設計的,而BeanFactory是Ioc容器中最基本的介面,在ApplicationContext的設計中,一方面,可以看到它繼承了BeanFactory介面體系中的ListableBeanFactory、AutowireCapableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory等BeanFactory的介面,具備了BeanFactory Ioc容器的基本功能;另一方面,通過繼承MessageSource、ResourceLoadr、ApplicationEventPublisher這些介面,BeanFactory為ApplicationContext賦予了更高階的Ioc容器特性。對於ApplicationContext而言,為了在Web環境中使用它,還設計了WebApplicationContext介面,而這個介面通過繼承ThemeSource介面來擴充功能。
BeanFactory容器的設計
恩,我們與其寫繁瑣的文字,不如直接閱讀程式碼來的直接的多。
最原始的容器:BeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.core.ResolvableType;
/**
* BeanFactory作為最原始同時也最重要的Ioc容器,它主要的功能是為依賴注入 (DI) 提供支援,
* BeanFactory 和相關的介面,比如,BeanFactoryAware、 DisposableBean、InitializingBean,
* 仍舊保留在 Spring 中,主要目的是向後相容已經存在的和那些 Spring 整合在一起的第三方框架。在
* Spring 中,有大量對 BeanFactory 介面的實現。其中,最常被使用的是 XmlBeanFactory 類。
* 這個容器從一個 XML 檔案中讀取配置元資料,由這些元資料來生成一個被配置化的系統或者應用。
* 在資源寶貴的移動裝置或者基於applet的應用當中, BeanFactory 會被優先選擇。否則,一般使用的是
* ApplicationContext.
* 這裡定義的只是一系列的介面方法,通過這一系列的BeanFactory介面,可以使用不同的Bean的檢索方法很
* 方便地從Ioc容器中得到需要的Bean,從而忽略具體
* 的Ioc容器的實現,從這個角度上看,這些檢索方法代表的是最為基本的容器入口。
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 13 April 2001
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* 轉定義符"&" 用來引用例項,或把它和工廠產生的Bean區分開,就是說,如果一個FactoryBean的名
* 字為a,那麼,&a會得到那個Factory
*
* FactoryBean和BeanFactory 是在Spring中使用最為頻繁的類,它們在拼寫上很相似。一個是
* Factory,也就是Ioc容器或物件工廠;一個是Bean。在Spring中,所有的Bean都是由
* BeanFactory(也就是Ioc容器)來進行管理的。但對
* FactoryBean而言,這個Bean不是簡單的Bean,而是一個能產生或者修飾物件生成的工廠Bean,它的
* 實現與設計模式中的工廠模式和修飾器模式類似。
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* 五個不同形式的getBean方法,獲取例項
* @param name 檢索所用的Bean名
* @return Object(<T> T) 例項物件
* @throws BeansException 如果Bean不能取得
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
/**
* 讓使用者判斷容器是否含有指定名字的Bean.
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @return boolean 是否包含其中
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/**
* 查詢指定名字的Bean是否是Singleton型別的Bean.
* 對於Singleton屬性,可以在BeanDefinition指定.
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @return boolean 是否包是Singleton
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 沒有找到Bean
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 查詢指定名字的Bean是否是Prototype型別的。
* 與Singleton屬性一樣,可以在BeanDefinition指定.
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @return boolean 是否包是Prototype
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 沒有找到Bean
*/
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 查詢指定了名字的Bean的Class型別是否是特定的Class型別.
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @param typeToMatch 匹配型別
* @return boolean 是否是特定型別
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 沒有找到Bean
*/
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 查詢指定名字的Bean的Class型別.
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @return 指定的Bean或者null(沒有找到合適的Bean)
* @throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 沒有找到Bean
*/
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/**
* 查詢指定了名字的Bean的所有別名,這些都是在BeanDefinition中定義的
* @param name 搜尋所用的Bean名
* @return 指定名字的Bean的所有別名 或者一個空的陣列
*/
String[] getAliases(String name);
}容器的基礎:XmlBeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory.xml;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* XmlBeanFactory是BeanFactory的最簡單實現類
*
* XmlBeanFactory的功能是建立在DefaultListableBeanFactory這個基本容器的基礎上的,
* 並在這個基本容器的基礎上實行了其他諸如XML讀取的附加功能。XmlBeanFactory使用了
* DefaultListableBeanFactory作為基礎類,DefaultListableBeanFactory是一個很重
* 要的Ioc實現,會在下一章進行重點論述。
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 15 April 2001
*/
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
/**
* 根據給定來源,建立一個XmlBeanFactory
* @param resource Spring中對與外部資源的抽象,最常見的是對檔案的抽象,特別是XML檔案。而且Resource裡面通常
* 是儲存了Spring使用者的Bean定義,比如applicationContext.xml在被載入時,就會被抽象為Resource來處理。
* @throws BeansException 載入或者解析中發生錯誤
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
/**
* 根據給定來源和BeanFactory,建立一個XmlBeanFactory
* @param resource Spring中對與外部資源的抽象,最常見的是對檔案的抽象,特別是XML檔案。而且Resource裡面通常
* 是儲存了Spring使用者的Bean定義,比如applicationContext.xml在被載入時,就會被抽象為Resource來處理。
* @param parentBeanFactory 父類的BeanFactory
* @throws BeansException 載入或者解析中發生錯誤
*/
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}最原始Ioc容器的使用
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
/**
* 最原始的Ioc容器使用,當然這也是Spring容器中效率最高的用法,比起繁瑣的文字,閱讀原始碼來得直觀得多。
* 只需要寫兩行程式碼就行了,當然前提是要準備好Spring的配置檔案
*
* @author kay
* @since 1.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class SimpleBeanFactory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
Message message = beanFactory.getBean("message", Message.class); //Message是自己寫的測試類
message.printMessage();
}
}下面是XmlBeanFactory在使用過程中涉及到的類的關係圖
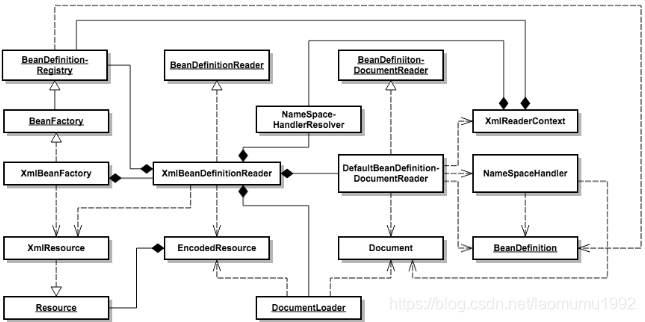
圖中空心三角加實線代表繼承、空心三角加虛線代表實現、實線箭頭加虛線代表依賴、實心菱形加實線代表組合。這裡用下劃線代表介面,沒有下劃線的代表類。
看著非常複雜是吧,不要緊,我們以程式碼來做簡要說明
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
/**
* 這是與SimpleBeanFactory等效的程式設計式使用Ioc容器
*
* 從中我也可以看到一些Ioc的基本原理,同時也揭示了Ioc實現中的一些關鍵類:如Resource、DefaultListableBeanFactory
* 以及BeanDefinitionReader等等
*
* @author kay
* @since 1.0
*/
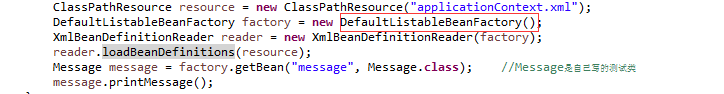
public class ProgramBeanFactory{
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(factory);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
Message message = factory.getBean("message", Message.class); //Message是自己寫的測試類
message.printMessage();
}
}以上,可以簡單說明我們在使用Ioc容器時,需要如下幾個步驟:
1,建立Ioc配置檔案的抽象資源,這個抽象資源包含了BeanDefinition的定義資訊。
2,建立一個BeanFactory,這裡使用了DefaultListableBeanFactory。
3,建立一個載入BeanDefinition的讀取器,這裡使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader來載入XML檔案形式的BeanDefinition,通過一個回撥配置給BeanFactory。
4,從定義好的資源位置讀入配置資訊,具體的解析過程由XmlBeanDefinitionReader來完成。完成整個載入和註冊Bean定義之後,需要的Ioc容器就建立起來了。這個時候我們就可以直接使用Ioc容器了。
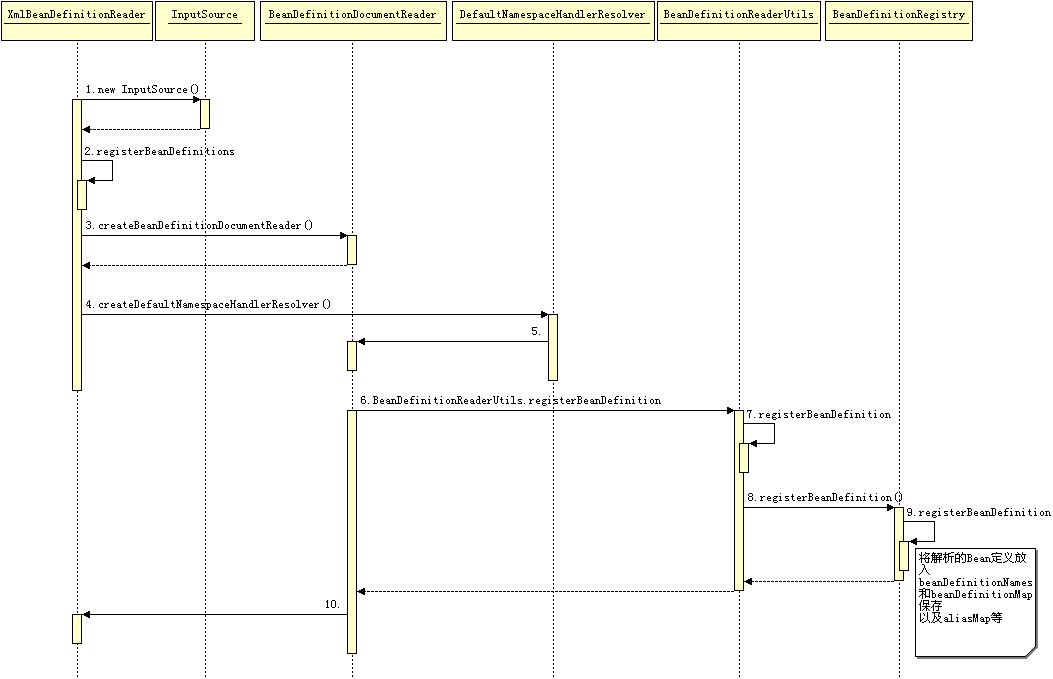
恩,以下是Bean在使用過程中的解析、註冊時效圖,我們來一步一步分析,它是怎麼在原始碼中實現的。
配置檔案封裝類:ClassPathResource
在Java中,將不同來源的資源抽象成URL,通過註冊不同的handler(URLStreamHandler)來處理不同來源間的資源讀取邏輯。而URL中卻沒有提供一些基本方法來實現自己的抽象結構。因而Spring對其內部資源,使用了自己的抽象結構:Resource介面來封裝。而ClassPathResource實現類即是對Resource的實現。
Resource介面體系
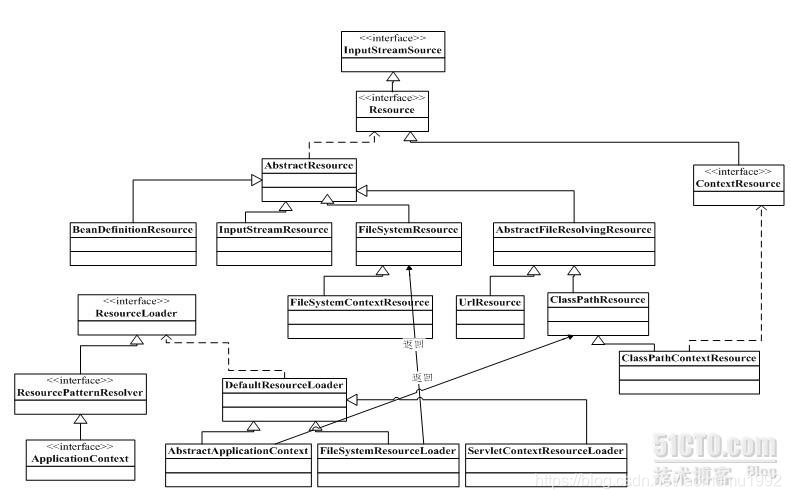
資源的原始介面為Resource,它繼承自InputStreamResource,實現了其getInstream方法,這樣所有的資源就是通過該方法來獲取輸入流的。對於資源的載入,也實現了統一,定義了一個資源載入頂級介面ResourceLoader,它預設的載入就是DefaultResourceLoader。
InputStreamSource介面
package org.springframework.core.io;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* InputStreamSource 封裝任何能返回InputStream的類,比如File、Classpath下的資源和Byte Array等
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 20.01.2004
*/
public interface InputStreamSource {
/**
* 返回InputStream的類,比如File、Classpath下的資源和Byte Array等
* @return InputStream 返回一個新的InputStream的物件
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}Resource介面
package org.springframework.core.io;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* Resource介面抽象了所有Spring內部使用到的底層資源:File、URL、Classpath等。
* 同時,對於來源不同的資原始檔,Resource也有不同實現:檔案(FileSystemResource)、Classpath資源(ClassPathResource)、
* URL資源(UrlResource)、InputStream資源(InputStreamResource)、Byte陣列(ByteArrayResource)等等。
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 28.12.2003
*/
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 判斷資源是否存在
* @return boolean 是否存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 判斷資源是否可讀
* @return boolean 是否可讀
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* 是否處於開啟狀態
* @return boolean 是否開啟
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* 得到URL型別資源,用於資源轉換
* @return URL 得到URL型別
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 得到URI型別資源,用於資源轉換
* @return URI 得到URI型別
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 得到File型別資源,用於資源轉換
* @return File 得到File型別
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 獲取資源長度
* @return long 資源長度
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 獲取lastModified屬性
* @return long 獲取lastModified
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 建立一個相對的資源方法
* @param relativePath 相對路徑
* @return Resource 返回一個新的資源
* @throws IOException 如果資源不能開啟則丟擲異常
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 獲取檔名稱
* @return String 檔名稱或者null
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* 得到錯誤處理資訊,主要用於錯誤處理的資訊列印
* @return String 錯誤資源資訊
*/
String getDescription();
}根據上面的推論,我們可以理解為這兩段程式碼,在某種程度來說是完全等效的
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml");
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();這樣得到InputStream以後,我們可以拿來用了。值得一提是,不同的實現有不同的呼叫方法,這裡就不展開了。下面是ClassPathResource的具體實現:
ClassPathResource.java
private final String path;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader) null); //這裡是入口,直接跳入下面的ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) 中
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}忽略給定介面:DefaultListableBeanFactory
這裡 DefaultListableBeanFactory 所起到的是忽略給定介面自動裝配功能。簡單來說,一般 bean 中的功能 A 如果沒有初始化,那麼Spring會自動初始化A,這是Spring的一個特性。但當某些特殊情況時,B不會初始化,比如:B已經實現了 BeanNameAware介面。可以說,就是通過其他方式來解析依賴,類似於 BeanFactory 的 BeanFactoryAware。下面是具體實現:
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
public DefaultListableBeanFactory() {
super(); //直接指向下面 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory()
}AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
private final Set<Class<?>> ignoredDependencyInterfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>();
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class); //忽略給定介面自動裝配功能的主要實現處
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
public void ignoreDependencyInterface(Class<?> ifc) {
this.ignoredDependencyInterfaces.add(ifc);
}BeanDefinition的載入、解析和註冊:XmlBeanDefinitionReader
這裡是BeanDefinition真正被載入的地方。這個載入過程就是把使用者定義好的Bean表示成Ioc容器內部的資料結構,當然這個資料結構就是BeanDefinition。而BeanDefinition實際上就是POJO物件在Ioc容器中的抽象,通過這個BeanDefinition定義的資料結構,讓Ioc容器能夠對POJO物件也就是Bean進行管理。

XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//loadBeanDefinitions的具體實現,而EncodedResource主要用於對資原始檔的處理,
//而其主要實現方法getReader()在下面有所介紹
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
//通過屬性來記錄已經載入的資源
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
// 呼叫DefaultResourceLoader的getResources方法完成具體的Resource定位
try {
//從EncodedResource中獲取已經封裝的Resource物件並再次從Resource中獲取inputStream
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); //真正的邏輯核心
}
finally {
inputStream.close(); //關閉inputStream
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
/**
* 真正的核心處理部分
* 如果不考慮冗餘的程式碼,其實只做三件事:
* 1.獲取XML檔案的驗證模式
* 2.載入XML,並獲取Document.
* 3.返回的Document,註冊Bean
*/
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
// 取得XML檔案的Document物件, 這個解析過程由DefaultDocumentLoader完成
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
// 啟動對BeanDefinition解析的詳細過程, 解析過程中會使用到Spring的Bean配置規則
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
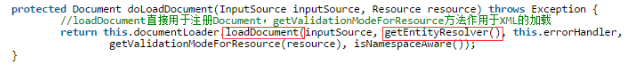
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
//loadDocument直接用於註冊Document,getValidationModeForResource方法作用於XML的載入
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}EncodedResource.java
public Reader getReader() throws IOException {
if (this.charset != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.charset);
}
else if (this.encoding != null) {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream(), this.encoding);
}
else {
return new InputStreamReader(this.resource.getInputStream());
}
}XML檔案驗證
獲取XML檔案的驗證模式,一般分為兩步:首先,是XML檔案驗證,然後,就是驗證模式的讀取。
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd"> //XSD方式,用於驗證XML檔案的正確性
<bean id="..">...</bean>
</beans>常用的XML檔案驗證方法有兩種:DTD和XSD,DTD現在基本不用了,而上圖中的spring-beans-4.0.xsd對應在原始碼中的org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.spring-beans-4.0.xsd。這裡就不具體介紹了,有興趣可以自己去研究。
載入XML
Spring中通過getValidationModeForResource方法來獲取上面講的DTD和XSD驗證方法,不過就程式設計而言,還是非常簡單的。只是要特別需要注意的是自動檢測驗證模式的實現。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
public static final int VALIDATION_AUTO = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_AUTO;
public static final int VALIDATION_XSD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD;
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode();
//如果手動指定了驗證模式則使用指定的驗證模式
if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return validationModeToUse;
}
//如果沒有指定,則自動檢測
int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource); //自動檢測主要是在detectValidationMode(Resource resource)完成的
if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return detectedMode;
}
return VALIDATION_XSD;
}
protected int detectValidationMode(Resource resource) {
if (resource.isOpen()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Passed-in Resource [" + resource + "] contains an open stream: " +
"cannot determine validation mode automatically. Either pass in a Resource " +
"that is able to create fresh streams, or explicitly specify the validationMode " +
"on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance.");
}
InputStream inputStream;
try {
inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: cannot open InputStream. " +
"Did you attempt to load directly from a SAX InputSource without specifying the " +
"validationMode on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance?", ex);
}
try {
return this.validationModeDetector.detectValidationMode(inputStream); //自動檢測則是給detectValidationMode完成的
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unable to determine validation mode for [" +
resource + "]: an error occurred whilst reading from the InputStream.", ex);
}
}XmlValidationModeDetector.java
public static final int VALIDATION_NONE = 0;
public static final int VALIDATION_AUTO = 1;
public static final int VALIDATION_DTD = 2;
public static final int VALIDATION_XSD = 3;
private static final String DOCTYPE = "DOCTYPE";
public int detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
try {
boolean isDtdValidated = false;
String content;
while ((content = reader.readLine()) != null) {
content = consumeCommentTokens(content);
//空或註釋略過
if (this.inComment || !StringUtils.hasText(content)) {
continue;
}
if (hasDoctype(content)) {
isDtdValidated = true;
break;
}
//讀取<前的資訊
if (hasOpeningTag(content)) {
break;
}
}
return (isDtdValidated ? VALIDATION_DTD : VALIDATION_XSD);
}
catch (CharConversionException ex) {
return VALIDATION_AUTO;
}
finally {
reader.close();
}
}
private boolean hasDoctype(String content) {
return content.contains(DOCTYPE);
}
private boolean hasOpeningTag(String content) {
if (this.inComment) {
return false;
}
int openTagIndex = content.indexOf('<');
return (openTagIndex > -1 && (content.length() > openTagIndex + 1) &&
Character.isLetter(content.charAt(openTagIndex + 1)));
}獲取Document
通過以上的驗證準備,就可以進行載入了,而XmlBeanDefinitionReader並沒有自己去完成,而是給了DocumentLoader介面去完成的,而他呼叫的是DefaultDocumentLoader.loadDocument方法。loadDocument沒有太多可描述的。所以。。。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
private DocumentLoader documentLoader = new DefaultDocumentLoader();
//EntityResolver主要用於處理前面提到的DTD方法的處理
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() {
if (this.entityResolver == null) {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader != null) {
this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
return this.entityResolver;
}DefaultDocumentLoader.java
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}BeanDefinition的解析
BeanDefinition載入過程其實就是把定義的BeanDefinition在IoC容器中轉化為一個Spring內部表示的資料結構的過程。IoC容器對Bean的管理和依賴注入的實現,都是通過對其持有的BeanDefinition進行各種相關的操作來完成的。這些BeanDefinition資料在IoC容器中通過一個HashMap來維護。

XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
private Class<?> documentReaderClass = DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class;
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 得到BeanDefinitionDocumentReader來對XML的BeanDefinition進行解析
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// 具體的解析過程在BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法中完成
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() {
return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass));
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
public static final String BEAN_ELEMENT = BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.BEAN_ELEMENT;
public static final String NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT = "beans";
public static final String ALIAS_ELEMENT = "alias";
public static final String ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE = "alias";
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); // 獲得Document的根元素
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root); // 解析Bean定義之前, 增強解析過程的可擴充套件性
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate); // 從Document的根元素開始進行Bean定義的Document物件
postProcessXml(root); // 解析Bean定義之前, 增強解析過程的可擴充套件性
this.delegate = parent;
}
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); // 獲取Document物件根元素的所有子節點並迴圈解析
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); // 解析Spring的Bean規則預設元素節點
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele); // 解析自定義元素節點
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root); // 解析自定義元素根節點
}
}
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) { // 解析import元素
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) { // 解析alias元素
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { // 解析bean元素
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) { // 解析內嵌beans元素, 作為根節點遞迴解析
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}恩,直接從程式碼就可以看出,Spring首先獲取Document的根元素(一般為<beans/>),然後取得根元素所有的子節點並迴圈解析這些子節點;如果子節點在Spring預設的名稱空間內,則按照Spring Bean定義規則來解析,否則按照自定義的節點解析。在按照Spring Bean定義規則進行解析的parseDefaultElement方法中,完成了對<import/>、<alias/>、<bean/>、<beans/>等元素的解析。
為了使文章簡短一點,在這裡只關注Spring對<bean>元素的解析過程,其它的解析過程不再分析。DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
// 具體的解析委託給BeanDefinitionParserDelegate來完成
// BeanDefinitionHolder是BeanDefinition的封裝類,
// 封裝了BeanDefinition、Bean的名字和別名, 用它來完成向IoC容器註冊.
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele) {
return parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, null);
}
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
// 解析Bean定義資原始檔中的<Bean>元素,主要處理<Bean>元素的id,name和aliase屬性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
// 如果<Bean>元素中沒有配置id屬性時, 將別名中的第一個值賦值給beanName
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
// 對<bean>元素進行詳細解析
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
//為解析的Bean使用別名註冊時, 為了向後相容(Spring1.2/2.0給別名新增類名字尾)
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
// 這裡只讀取<Bean>元素中配置的class名字, 然後載入到BeanDefinition中去
// 只是記錄配置的class名字, 並不例項化, 物件的例項化在依賴注入時完成
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
// 根據<Bean>元素配置的class名稱和parent屬性值建立BeanDefinition, 為載入Bean定義資訊做準備
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 對當前<Bean>元素中配置的一些屬性進行解析, 如singleton、abstract等
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 對<Bean>元素的meta(元資料)、lookup-method、replaced-method等子元素進行解析
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd); // 解析<Bean>元素的構造方法引數
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd); // 解析<Bean>元素的<property>設定
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}<bean>元素解析已經完了,而<bean>元素屬性及其子元素的解析順序為:1,解析<bean>元素的屬性。2,解析<description>子元素。3,解析<meta>子元素。4,解析<lookup-method/>子元素。5,解析<replaced-method>子元素。6,解析<constructor-arg>子元素。7,解析<property>子元素。8,解析<qualifier>子元素。解析過程中像<meta>、<qualifier>等子元素都很少使用,而下面就直接解析最常用的子元素<property>子元素。
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
// 遍歷<bean>所有的子元素
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd); // 如果是<property>元素, 則對其進行解析
}
}
}
public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE); // <property>元素name屬性
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName));
try {
// 如果同一個Bean中已經有相同名字的<property>存在, 直接返回
// 也就是說, 如果一個Bean中定義了兩個名字一樣的<property>元素, 只有第一個起作用.
if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {
error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele);
return;
}
// 解析<property>元素, 返回的物件對應<property>元素的解析結果, 最終封裝到PropertyValue中, 並設定到BeanDefinitionHolder中
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
parseMetaElements(ele, pv);
pv.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null) ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element";
// 檢查<property>的子元素, 只能是ref, value, list等(description, meta除外)其中的一個.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
// 判斷property元素是否含有ref和value屬性, 不允許既有ref又有value屬性.
// 同時也不允許ref和value屬性其中一個與子元素共存.
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
// 如果屬性是ref屬性, 建立一個ref的資料物件RuntimeBeanReference, 封裝了ref資訊
if (hasRefAttribute) {
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (hasValueAttribute) { // 如果屬性是value屬性, 建立一個數據物件TypedStringValue, 封裝了value資訊
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
else if (subElement != null) { // 如果當前<property>元素還有子元素
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else { // propery元素既沒有ref或value屬性, 也沒有子元素, 解析出錯返回null
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}恩,其實<property>元素還有子元素。
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
return parsePropertySubElement(ele, bd, null);
}
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultValueType) {
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) { // 如果子元素沒有使用Spring預設名稱空間, 則使用使用者自定義的規則解析
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) { // 如果子元素是bean元素, 則使用解析<bean>元素的方法解析
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) { // 如果子元素是ref, 有且只能有bean、local和parent 3個屬性中的一個
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE); // 引用普通任意的bean
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
refName = ele.getAttribute(LOCAL_REF_ATTRIBUTE); // 引用同一個XML配置檔案中的bean
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE); // 引用父容器中的bean
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean', 'local' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
}
// ref元素沒有bean、local和parent 3個屬性中的一個, 返回null.
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) { // 如果子元素是<idref>, 使用解析idref元素的方法解析
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<value>
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<null>
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<array>
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<list>
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<set>
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<map>
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) { // 子元素是<props>
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else { // 以上都不是, 說明配置錯誤, 返回null.
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}我們以<list>子元素進行分析
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public List<Object> parseListElement(Element collectionEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
// 獲取<list>元素中的value-type屬性, 即集合元素的資料型別
String defaultElementType = collectionEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = collectionEle.getChildNodes(); // <list>元素所有子節點
ManagedList<Object> target = new ManagedList<Object>(nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(collectionEle));
target.setElementTypeName(defaultElementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(collectionEle));
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, defaultElementType); // 具體解析List元素中的值
return target;
}
protected void parseCollectionElements(
NodeList elementNodes, Collection<Object> target, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultElementType) {
// 遍歷集合所有子節點
for (int i = 0; i < elementNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = elementNodes.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)) {
// 如果子節點是Element且不是<description>節點, 則新增進ManagedList.
// 同時觸發對下層子元素的解析, 遞迴呼叫.
target.add(parsePropertySubElement((Element) node, bd, defaultElementType));
}
}
}不好意思,沒子類了,BeanDefinition就被載入到IoC容器後,就可以在容器中建立了資料映射了。剩下的就是BeanDefinition註冊了。
BeanDefinition的註冊
BeanDefinition資訊已經在IoC容器內部建立起了自己的資料結構,但這些資料還不能供IoC容器直接使用,需要在IoC容器中對這些BeanDefinition資料進行註冊。不同的解析元素解析方式都不同但最後的註冊的方式是一樣的,我們還是以上面提到的<bean>元素為例。

BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.java
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 向IoC容器註冊BeanDefinition
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// 如果解析的BeanDefinition有別名, 向容器為其註冊別名.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}上面的registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition())是呼叫的註冊位置,而BeanDefinitionRegistry僅僅是一個介面,而真正實現它的卻是最原本的DefaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition方法,值得一提的是DefaultListableBeanFactory.registerBeanDefinition方法在最新的Spring 4.0中穩定性方面做了很大改善。
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
// 對解析得到的BeanDefinition校驗
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition oldBeanDefinition;
oldBeanDefinition = this.
