spring-data-redis的事務操作深度解析--原來客戶端庫還可以攢夠了事務命令再發?
一、官方文件
簡單介紹下redis的幾個事務命令:
redis事務四大指令: MULTI、EXEC、DISCARD、WATCH。
這四個指令構成了redis事務處理的基礎。
1.MULTI用來組裝一個事務;
2.EXEC用來執行一個事務;
3.DISCARD用來取消一個事務;
4.WATCH類似於樂觀鎖機制裡的版本號。
被WATCH的key如果在事務執行過程中被併發修改,則事務失敗。需要重試或取消。
以後單獨介紹。
下面是最新版本的spring-data-redis(2.1.3)的官方手冊。
https://docs.spring.io/spring-data/redis/docs/2.1.3.RELEASE/reference/html/#tx
這裡,我們注意這麼一句話:
Redis provides support for transactions through the
multi,exec, anddiscardcommands. These operations are available onRedisTemplate. However,RedisTemplateis not guaranteed to execute all operations in the transaction with the same connection.
意思是redis伺服器通過multi,exec,discard提供事務支援。這些操作在RedisTemplate中已經實現。然而,RedisTemplate不保證在同一個連線中執行所有的這些一個事務中的操作。
另外一句話:
Spring Data Redis provides the
SessionCallbackinterface for use when multiple operations need to be performed with the sameconnection, such as when using Redis transactions. The following example uses themultimethod:
意思是:spring-data-redis也提供另外一種方式,這種方式可以保證多個操作(比如使用redis事務)可以在同一個連線中進行。示例如下:
//execute a transaction List<Object> txResults = redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback<List<Object>>() { public List<Object> execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException { operations.multi(); operations.opsForSet().add("key", "value1"); // This will contain the results of all operations in the transaction return operations.exec(); } }); System.out.println("Number of items added to set: " + txResults.get(0));
二、實現事務的方式--RedisTemplate直接操作
在前言中我們說,通過RedisTemplate直接呼叫multi,exec,discard,不能保證在同一個連線中進行。
這幾個操作都會呼叫RedisTemplate#execute(RedisCallback<T>, boolean),比如multi:
public void multi() { execute(connection -> { connection.multi(); return null; }, true); }
我們看看RedisTemplate的execute方法的原始碼:
1 public <T> T execute(RedisCallback<T> action, boolean exposeConnection, boolean pipeline) { 2 3 Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it"); 4 Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); 5 6 RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory(); 7 RedisConnection conn = null; 8 try { 9 --開啟了enableTransactionSupport選項,則會將獲取到的連線繫結到當前執行緒 10 if (enableTransactionSupport) { 11 // only bind resources in case of potential transaction synchronization 12 conn = RedisConnectionUtils.bindConnection(factory, enableTransactionSupport); 13 } else {
-- 未開啟,就會去獲取新的連線 14 conn = RedisConnectionUtils.getConnection(factory); 15 } 16 17 boolean existingConnection = TransactionSynchronizationManager.hasResource(factory); 18 19 RedisConnection connToUse = preProcessConnection(conn, existingConnection);
。。。忽略無關程式碼。。。
26 RedisConnection connToExpose = (exposeConnection ? connToUse : createRedisConnectionProxy(connToUse)); 27 T result = action.doInRedis(connToExpose); -- 使用獲取到的連線,執行定義在業務回撥中的程式碼 28 。。。忽略無關程式碼。。。 33 34 // TODO: any other connection processing? 35 return postProcessResult(result, connToUse, existingConnection); 36 } finally { 37 RedisConnectionUtils.releaseConnection(conn, factory); 38 } 39 }
檢視以上原始碼,我們發現,
- 不啟用enableTransactionSupport,預設每次獲取新連線,程式碼如下:
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.multi(); template.opsForValue().set("test_long", 1); template.opsForValue().increment("test_long", 1); template.exec();
- 啟用enableTransactionSupport,每次獲取與當前執行緒繫結的連線,程式碼如下:
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); template.setEnableTransactionSupport(true); template.multi(); template.opsForValue().set("test_long", 1); template.opsForValue().increment("test_long", 1); template.exec();
三、實現事務的方式--SessionCallback
採用這種方式,預設就會將所有操作放在同一個連線,因為在execute(SessionCallback<T> session)(注意,這裡是過載函式,引數和上面不一樣)原始碼中:
public <T> T execute(SessionCallback<T> session) {
Assert.isTrue(initialized, "template not initialized; call afterPropertiesSet() before using it");
Assert.notNull(session, "Callback object must not be null");
RedisConnectionFactory factory = getRequiredConnectionFactory();
//在執行業務回撥前,手動進行了繫結
RedisConnectionUtils.bindConnection(factory, enableTransactionSupport);
try { // 業務回撥
return session.execute(this);
} finally {
RedisConnectionUtils.unbindConnection(factory);
}
}
四、SessionCallback方式的示例程式碼:
1 RedisStandaloneConfiguration configuration = new RedisStandaloneConfiguration("192.168.19.90"); 2 JedisConnectionFactory factory = new JedisConnectionFactory(configuration); 3 factory.afterPropertiesSet(); 4 5 RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); 6 template.setConnectionFactory(factory); 7 template.setDefaultSerializer(new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer()); 8 StringRedisSerializer serializer = new StringRedisSerializer(); 9 template.setKeySerializer(serializer); 10 template.setHashKeySerializer(serializer); 11 12 template.afterPropertiesSet(); 14 15 try { 16 List<Object> txResults = template.execute(new SessionCallback<List<Object>>() { 17 @Override 18 public List<Object> execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException { 19 20 operations.multi(); 21 22 operations.opsForValue().set("test_long", 1); 23 int i = 1/0; 24 operations.opsForValue().increment("test_long", 1); 25 26 // This will contain the results of all ops in the transaction 27 return operations.exec(); 28 } 29 }); 30 31 } catch (Exception e) { 32 System.out.println("error"); 33 e.printStackTrace(); 34 }
有幾個值得注意的點:
1、為什麼加try catch
先說結論:只是為了防止呼叫的主執行緒失敗。
因為事務裡執行到23行,(int i = 1/0)時,會丟擲異常。
但是在 template.execute(SessionCallback<T> session)中未對其進行捕獲,只在finally塊進行了連線釋放。
所以會導致呼叫執行緒(這裡是main執行緒)中斷。

2.try-catch了,事務到底得到保證了沒
我們來測試下,測試需要,省略非關鍵程式碼
2.1 事務執行過程,丟擲異常的情況:
List<Object> txResults = template.execute(new SessionCallback<List<Object>>() {
@Override
public List<Object> execute(RedisOperations operations) throws DataAccessException {
operations.multi();
operations.opsForValue().set("test_long", 1);
int i = 1/0;
operations.opsForValue().increment("test_long", 1);
// This will contain the results of all ops in the transaction
return operations.exec();
}
});
執行上述程式碼,執行到int i = 1/0時,會丟擲異常。我們需要檢查,丟擲異常後,是否傳送了“discard”命令給redis 伺服器?
下面是我的執行結果,從最後的抓包可以看到,是傳送了discard命令的:

2.2 事務執行過程,不丟擲異常的情況:
這次我們註釋了拋錯的那行,可以看到“EXEC”命令已經發出去了:

3 丟擲異常,不捕獲異常的情況:
有些同學可能比較奇怪,為啥網上那麼多教程,都是沒有捕獲異常的,我這裡要捕獲呢?
其實我也奇怪,但在我目前測試來看,不捕獲的話,執行執行緒就中斷了,因為template.execute是同步執行的。
來,看看:
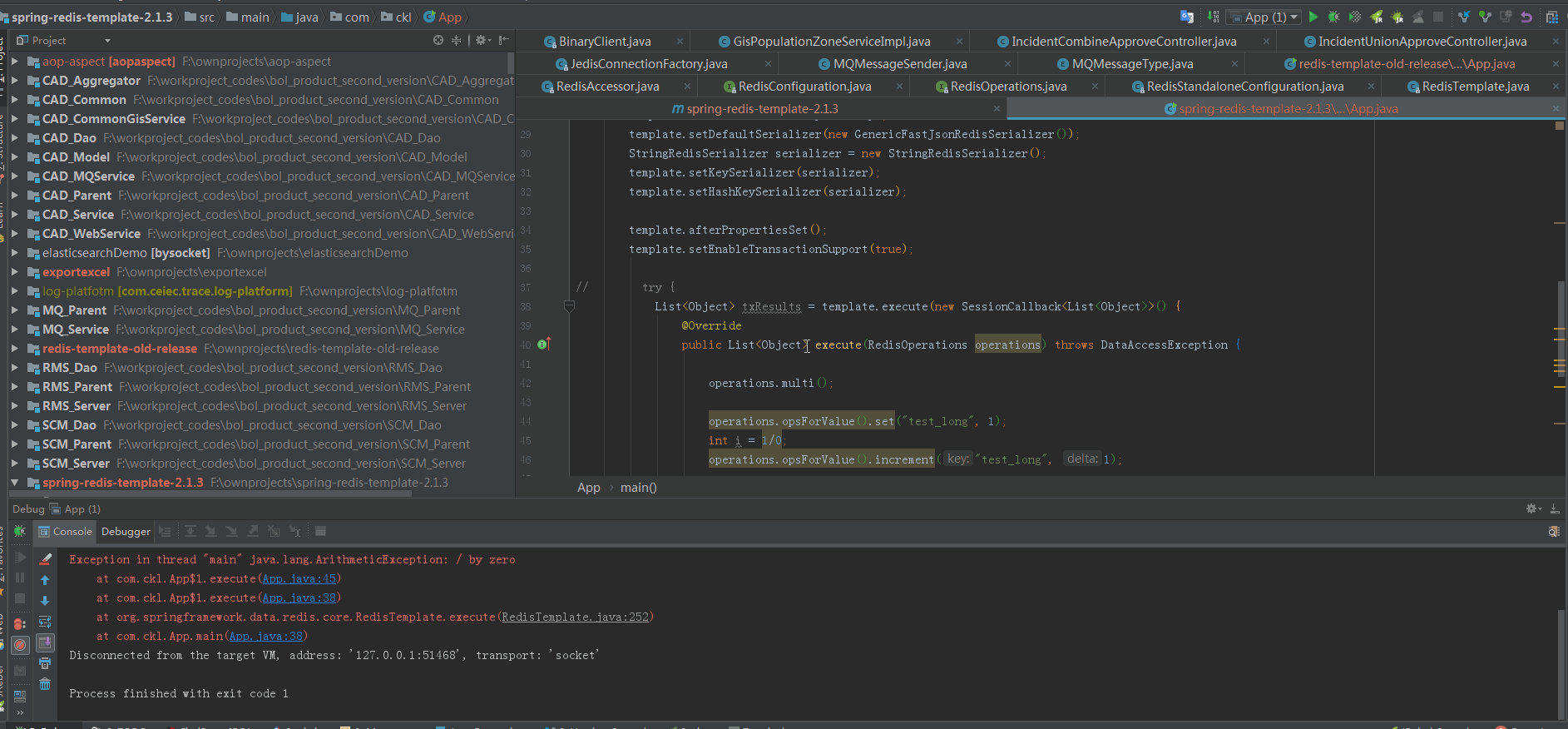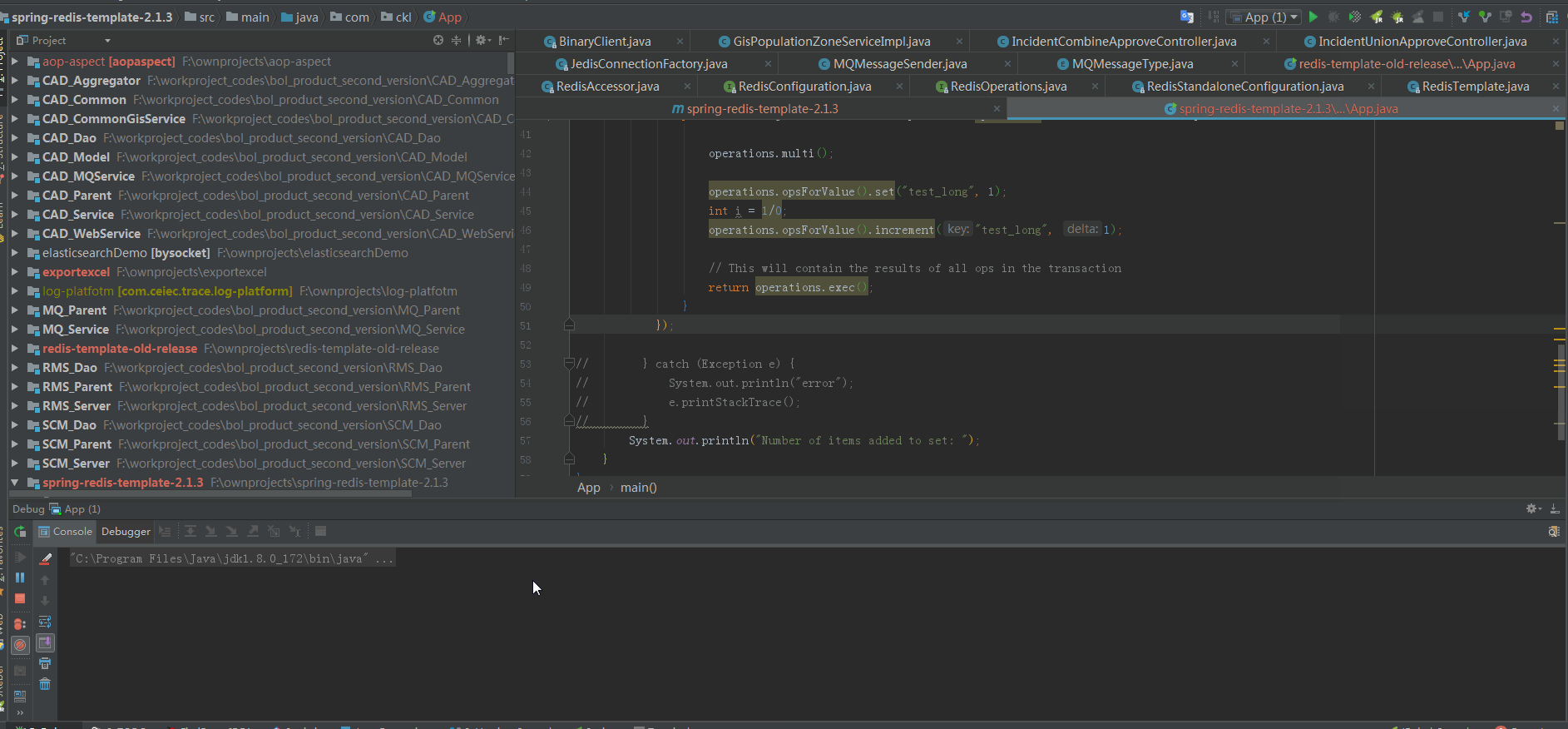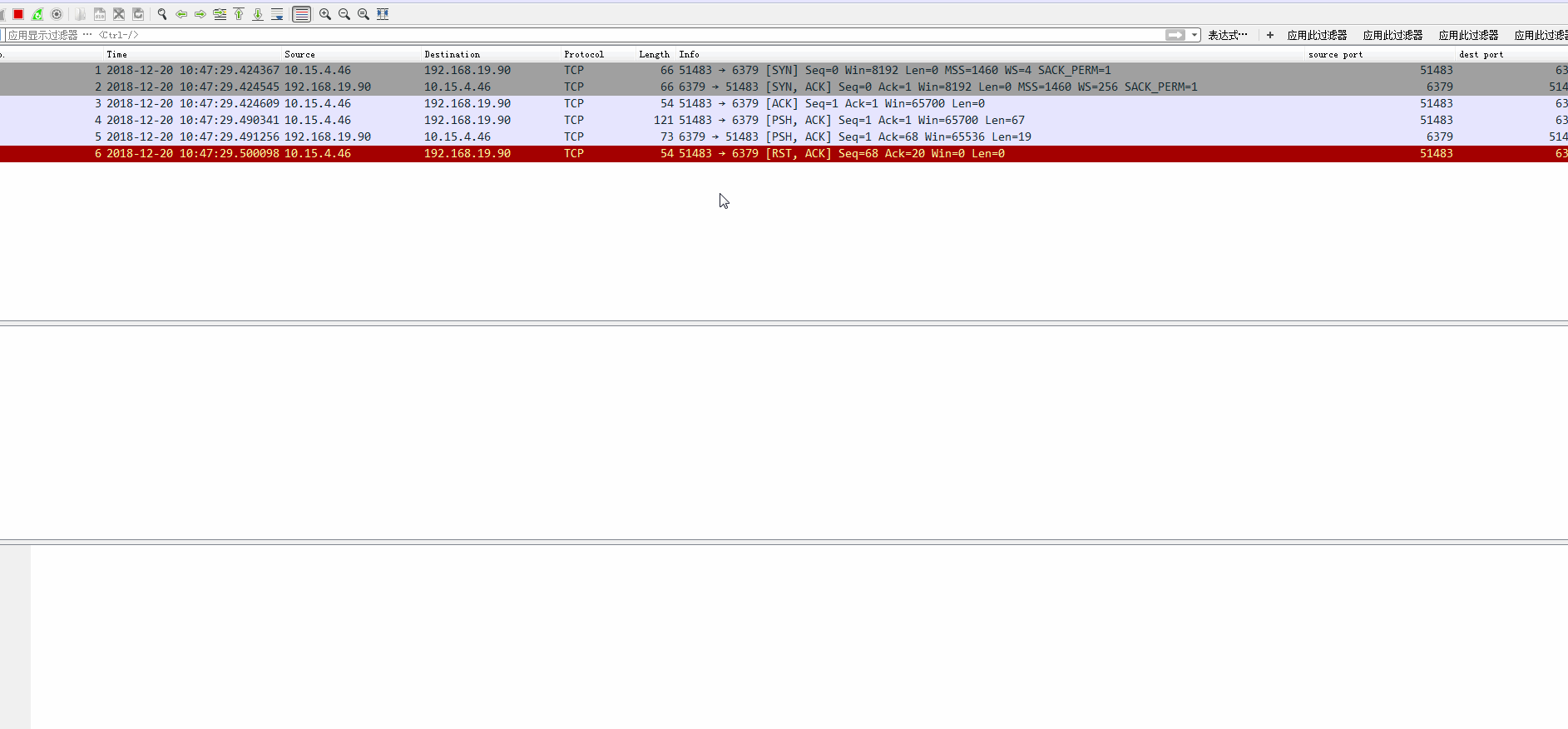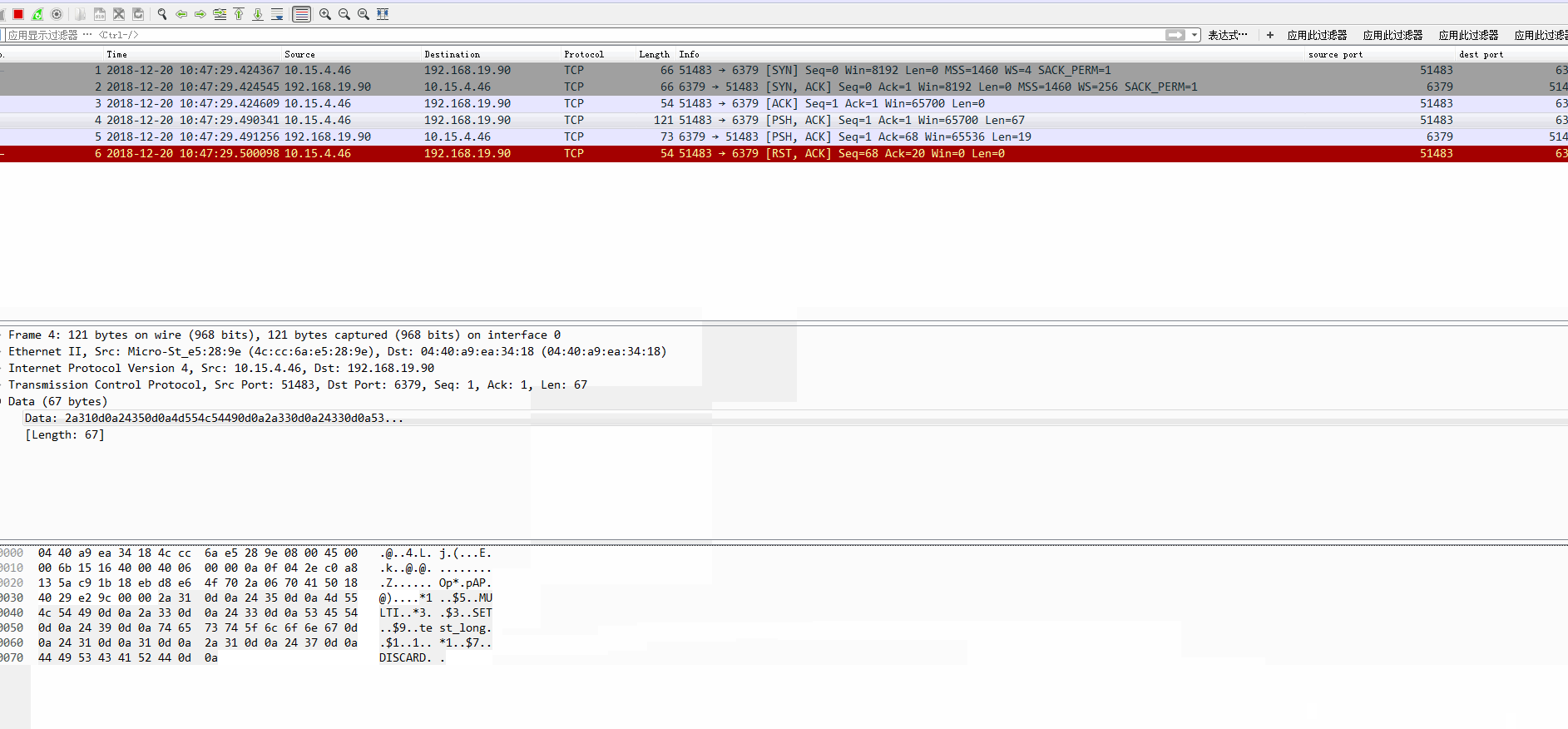
從上圖可以看到,主執行緒被未捕獲的異常給中斷了,但是,檢視網路抓包,發現“DISCARD”命令還是發出去了的。
4.總結
從上面可以看出來,不管捕獲異常沒,事務都能得到保證。只是不捕獲異常,會導致主執行緒中斷。
不保證所有版本如此,在我這,spring-data-redis 2.1.3是這樣的。
我跟了n趟程式碼,發現:
1、在執行sessionCallBack中的程式碼時,我們一般會先執行multi命令。
multi命令的程式碼如下:
public void multi() { execute(connection -> { connection.multi(); return null; }, true); }
即呼叫了當前執行緒繫結的connection的multi方法。
進入JedisConnection的multi方法,可以看到:
private @Nullable Transaction transaction;
public void multi() { if (isQueueing()) { return; } try { if (isPipelined()) { getRequiredPipeline().multi(); return; }
//賦值給了connection的例項變數 this.transaction = jedis.multi(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw convertJedisAccessException(ex); } }
2、在有異常丟擲時,直接進入finally塊,會去關閉connection,當然,這裡的關閉只是還回到連線池。
大概的邏輯如下:

3.在沒有異常丟擲時,執行exec,在exec中會先將狀態變數修改,後邊進入finally的時候,就不會發送discard命令了。

最後的結論就是:
所有這一切的前提是,共有同一個連線。(使用SessionCallBack的方式就能保證,總是共用同一個連線),否則multi用到的連線1裡transcation是有值的,但是後面獲取到的其他連線2,3,4,裡面的transaction是空的,
還怎麼保證事務呢?
五、思考
在不開啟redisTemplate的enableTransactionSupport選項時,每執行一次redis操作,就會向伺服器傳送相應的命令。
但是,在開啟了redisTemplate的enableTransactionSupport選項,或者使用SessionCallback方式時,會像下面這樣傳送命令:

後來,我在《redis實戰》這本書裡的4.4節,Redis事務這一節裡,找到了答案:

歸根到底呢,因為重用同一個連線,所以可以延遲發;如果每次都不一樣的連線,只能馬上發了。
這裡另外說一句,不是所有客戶端都這樣,redis自帶的redis-cli是不會延遲傳送的。
六、原始碼
https://github.com/cctvckl/work_util/tree/master/spring-redis-template-2.1.3
