Angular2中Input和Output用法及示例
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-21
對於angular2中的Input和Output可以和angularjs中指令作類比。
Input相當於指令的值繫結,無論是單向的(@)還是雙向的(=)。都是將父作用域的值“輸入”到子作用域中,然後子作用域進行相關處理。
Output相當於指令的方法繫結,子作用域觸發事件執行響應函式,而響應函式方法體則位於父作用域中,相當於將事件“輸出到”父作用域中,在父作用域中處理。
看個angular2示例吧,我們定義一個子元件,獲取父作用域的陣列值並以列表形式顯示,然後當點選子元件的元素時呼叫父元件的方法將該元素刪除。
//app.component.html<app-child [values]="data" - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
以上是跟元件app-root的元件類及模板,可以我們把data輸入到子元件app-child中,然後接收childEvent事件並對其進行響應。
//app-child.component.html<p *ngFor="let item of values; let i = index" (click)="fireChildEvent(i)"> {{item}}</p>//app-child.component.ts@Component({ selector: 'app-child', templateUrl: './child.component.html' - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
子元件定義了values接收了父元件的輸入,這裡就是data值,然後使用ngFor指令顯示。
當點選每個元素的時候觸發了click事件,執行fireChildEvent函式,該函式要將元素的index值“輸出”到父元件中進行處理。
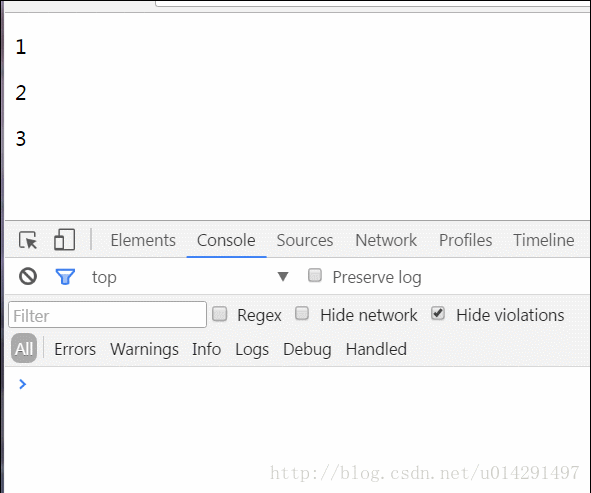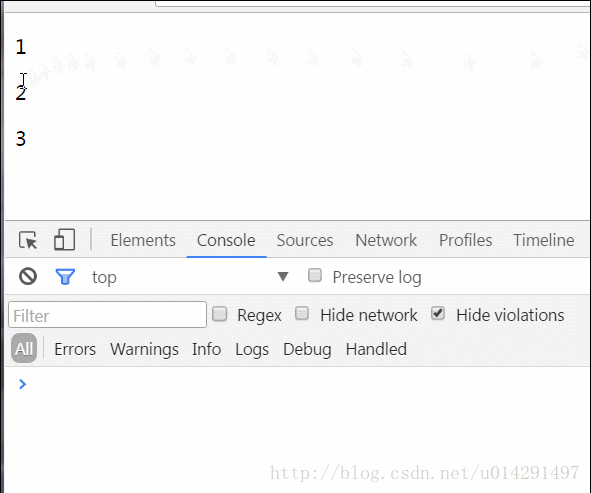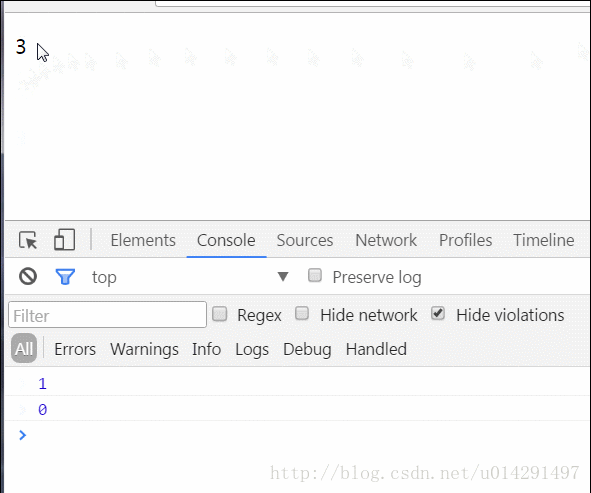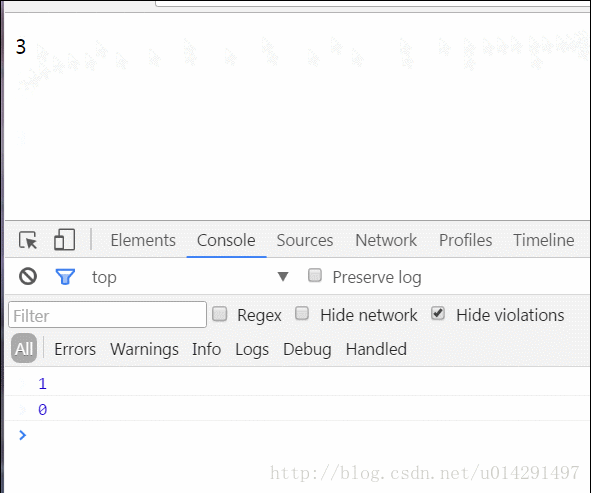
Output一般都是一個EventEmitter的例項,使用例項的emit方法將引數emit到父元件中,觸發父元件的childEvent事件。
然後父元件監聽到該事件的發生,執行對應的處理函式getChildEvent,刪除傳遞的元素索引指向的資料,同時,檢視更新。
實際效果: