C語言實現簡單的雙向迴圈連結串列
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-21
其實連結串列很簡單,跟著我的腳步走,基本是這篇部落格看完,你也就能實現簡單的連結串列操作了
陣列、連結串列是最常見的重要的資料結構,所以掌握連結串列也是很重要的咯。
一般連結串列的操作無外乎增刪改查。 今天就簡單的實現一下雙向迴圈連結串列的增刪
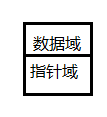
1. 連結串列的資料結構,主要包含指標域和資料域
雙向迴圈連結串列的資料結構包含至少兩個指標和至少一個數據
//用結構體封裝一下連結串列的資料結構 typedef struct _node_t{ struct _node_t *prev; //上一個節點 struct _node_t *next; //下一個節點 uint8_t data; //資料域 }Node,*pNode;
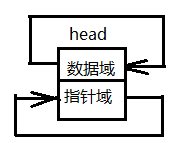
2.連結串列的初始化,即建立一個頭結點
頭結點的prev或next都是其本身,一般建議頭節點只存指標。
//連結串列初始化,即建立一個頭結點 pNode linklist_init(void){ pNode head = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); //申請記憶體 if(NULL == head){ perror("malloc Node failed!"); } head->prev = head; //頭節點的prev指向本身 head->next = head; //頭節點的next指向本身 return head; }
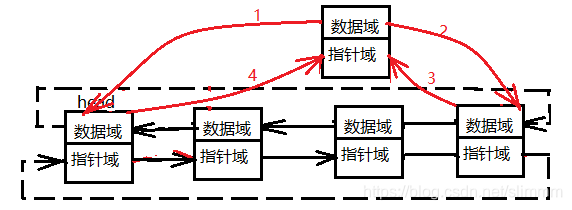
3.連結串列的插入
在前面插入,即在頭結點之後插入:
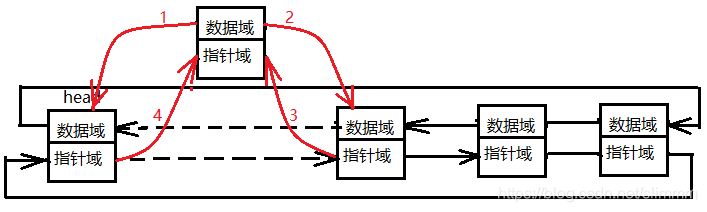
來來來,排隊了,,新來了一個童鞋tmp,個子比較矮的,老師讓他站在排頭的後面;
新來的tmp看了一下前面是排頭(head),後面是某某(head->next),然後他記住了自己的位置,通過自己前面和後面的童鞋定位了自己的位置;
可是還不夠啊,排頭和之前在排頭後面的童鞋不知道啊,所以之前排頭後面的童鞋,重新定位了一下自己的位置(head->next->prev)我原來在排頭後面,但是現在我前面是誰?排頭後面的換了,排頭也定位了一下自己的位置(head->next) 我後面新來的是誰呀。
pNode linklist_addhead(pNode head, uint8_t dat){ pNode tmp = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node)); //申請記憶體 if(tmp == head){ perror("malloc Node failed!"); } tmp->prev = head; //tmp定位自己,看下前面是誰 tmp->next = head->next; //再看看後面是誰 head->next->prev = tmp; //原來在排頭後面的童鞋,看看現在自己前面的是誰 head->next = tmp; //排頭也看了下,現在自己後面的是誰 tmp->data = dat; //新來的童鞋的名字 return head; //排頭的位置不能丟,不然找不到這一隊人馬了 }
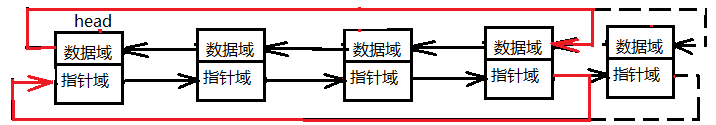
在末尾插入
這裡就不再贅述了,直接上圖,看不懂的,看上圖及描述
pNode linklist_addtail(pNode head, uint8_t dat){
pNode tmp = (pNode)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(tmp == head){
perror("malloc Node failed!");
}
tmp->prev = head->prev; //tmp看下自己前面是誰,主要前面是排頭ing,因為是環形的連結串列
tmp->next = head; //tmp看下自己後面的是誰
head->prev->next = tmp; //原來排頭前面的童鞋的後面是誰,來新人tmp了
head->prev = tmp; //現在排頭前面的換成了tmp了
tmp->data = dat;
return head;
}
還有其他插入方法,但是隻要掌握了頭插尾插,其他的都是浮雲
3.連結串列的刪除
從頭刪除,即將排頭後面的tmp童鞋刪除
先告訴tmp童鞋後面的童鞋(tmp->next),我走了之後你前面的是誰;然後告訴tmp童鞋前面的童鞋(這裡head),我走了之後你後面的是誰;把前後兩個童鞋定位告訴他們後就可以離開了(free);
pNode Linklist_delhead(pNode head){
pNode tmp = head->next;
if(tmp == head){
perror("linklist empty!");
return head;
}
tmp->next->prev = head; //tmp走了,tmp童鞋後面的童鞋的前面變成了排頭
head->next = tmp->next; //tmp走了,排頭後面的童鞋變成了原來排在tmp童鞋後面的童鞋
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->prev = NULL;
free(tmp); //釋放記憶體
}
從尾部刪除
這裡就不再贅述了,直接上圖,看不懂的,看上圖及描述
pNode Linklist_deltail(pNode head){
pNode tmp = head->prev;
if(tmp == head){
perror("linklist empty!");
return head;
}
tmp->prev->next = head;
head->prev = tmp->prev;
tmp->next = NULL;
tmp->prev = NULL;
free(tmp);
}
4. 遍歷顯示連結串列
從排頭依次報數,輪流一圈,回到排頭就完成了
void linklist_show(pNode head){
tmp = head->next; //從排頭後面的童鞋開始遍歷
while(tmp != head){ //沒有遍歷到排頭
printf("%p:%d\n",tmp, tmp->data);
tmp = tmp->next; //指向下一個童鞋
}
}
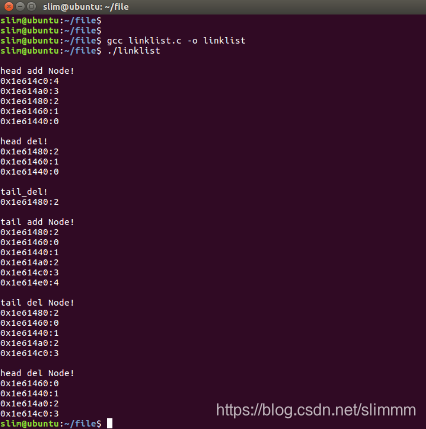
5. 測試
int main(void){
pNode head = linklist_init();
printf("\nhead add Node!\n");
for(uint8_t i=0;i<5;i++){
linklist_addhead(head, i);
}
linklist_show(head);
printf("\nhead del!\n");
for(uint8_t i=0;i<2;i++){
Linklist_delhead(head);
}
linklist_show(head);
printf("\ntail_del!\n");
for(uint8_t i=0;i<2;i++){
Linklist_deltail(head);
}
linklist_show(head);
printf("\ntail add Node!\n");
for(uint8_t i=0;i<5;i++){
linklist_addtail(head, i);
}
linklist_show(head);
printf("\ntail del Node!\n");
Linklist_deltail(head);
linklist_show(head);
printf("\nhead del Node!\n");
Linklist_delhead(head);
linklist_show(head);
return 0;
}
執行結果