java 併發程式設計學習筆記(一)之 併發基礎
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-22
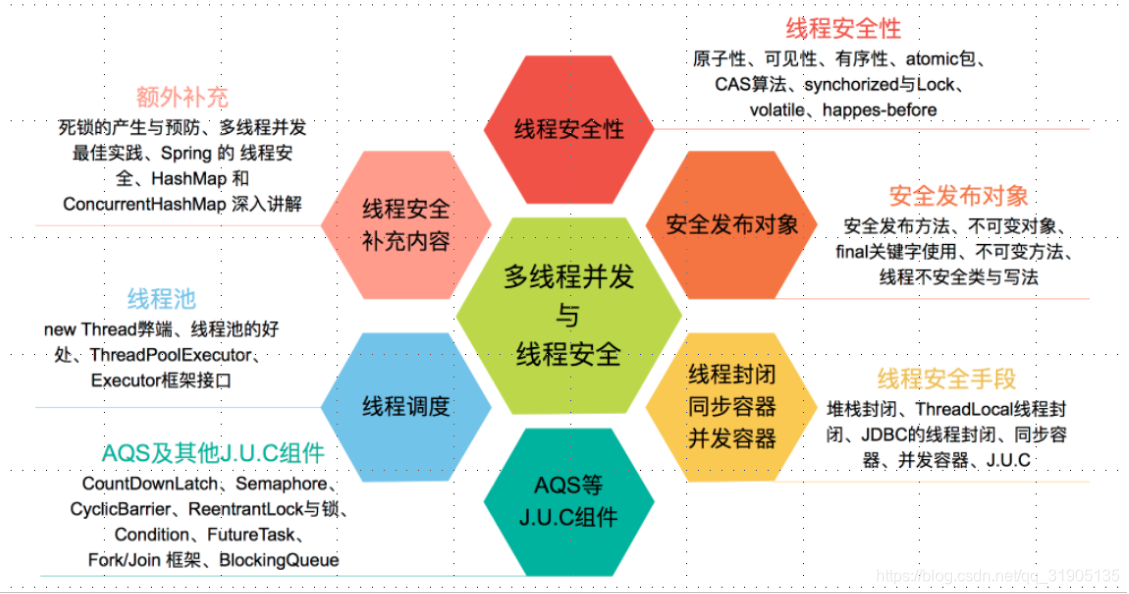
併發基礎
- 併發小測試
java.util.concurrent.Semaphore 類
public class SemTest { /** * Semaphore 通常用來控制同時有多少個執行緒在執行 */ private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1); // private static Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3); static class car implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { try { semaphore.acquire(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "start "); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "end"); semaphore.release(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Thread thread = new Thread(new car(), "小汽車1"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new car(), "小汽車2"); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new car(), "小汽車3"); List<Thread> list = new ArrayList<Thread>(); list.add(thread); list.add(thread2); list.add(thread3); for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { service.execute(list.get(i)); } } }
@Slf4j public class CountExample { private static int threadTotal = 1; private static int clientTotal = 5000; private static long count = 0; public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService exec = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal); for (int index = 0; index < clientTotal; index++) { exec.execute(() -> { try { semaphore.acquire(); add(); semaphore.release(); } catch (Exception e) { log.error("exception", e); } }); } exec.shutdown(); log.info("count:{}", count); } private static void add() { count++; } }
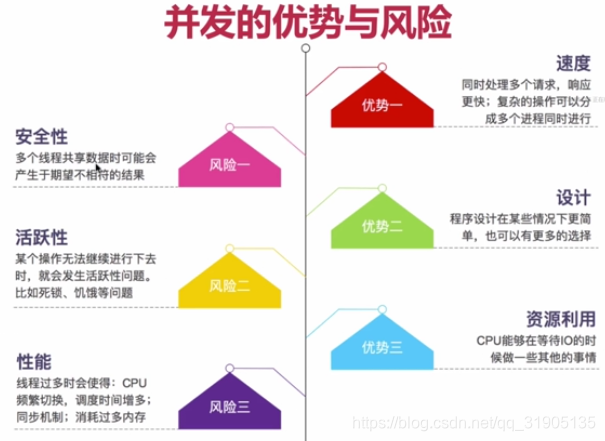
併發: 多個執行緒操作相同的資源,保證執行緒安全,合理使用資源
高併發: 伺服器同時處理很多請求,提高程式效能