SpringSecurity學習記錄__HelloWorld案例__01
Spring Security 簡介
Spring Security是一個能夠為基於Spring的企業應用系統提供宣告式的安全訪問控制解決方案的安全框架。
一個能夠為基於Spring的企業應用系統提供宣告式的安全訪問控制解決方式的安全框架(簡單說是對訪問許可權進行控制),應用的安全性包括使用者認證(Authentication)和使用者授權(Authorization)兩個部分。使用者認證指的是驗證某個使用者是否為系統中的合法主體,也就是說使用者能否訪問該系統。使用者認證一般要求使用者提供使用者名稱和密碼。系統通過校驗使用者名稱和密碼來完成認證過程。使用者授權指的是驗證某個使用者是否有許可權執行某個操作。在一個系統中,不同使用者所具有的許可權是不同的。比如對一個檔案來說,有的使用者只能進行讀取,而有的使用者可以進行修改。一般來說,系統會為不同的使用者分配不同的角色,而每個角色則對應一系列的許可權。 spring security的主要核心功能為 認證和授權
,架構也是基於這兩個核心功能去實現的。
本文演示了Spring Security的最最基本用法
步驟1: 工程目錄結構

第2步:建立Maven工程更新pom.xml,新增所需依懶
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.study</groupId> <artifactId>SpringSecurity-HelloWorld-XML</artifactId> <name>SpringSecurity-HelloWorld-XML</name> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0</version> <properties> <jdk.version>1.6</jdk.version> <spring.version>3.2.8.RELEASE</spring.version> <spring.security.version>3.2.3.RELEASE</spring.security.version> <jstl.version>1.2</jstl.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- Spring dependencies --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-core</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-expression</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-context-support</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Spring Security --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-core</artifactId> <version>${spring.security.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-web</artifactId> <version>${spring.security.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-config</artifactId> <version>${spring.security.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- jstl for jsp page --> <dependency> <groupId>jstl</groupId> <artifactId>jstl</artifactId> <version>${jstl.version}</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <artifactId>maven-eclipse-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.9</version> <configuration> <additionalProjectnatures> <projectnature>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springnature</projectnature> </additionalProjectnatures> <additionalBuildcommands> <buildcommand>org.springframework.ide.eclipse.core.springbuilder</buildcommand> </additionalBuildcommands> <downloadSources>true</downloadSources> <downloadJavadocs>true</downloadJavadocs> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.5.1</version> <configuration> <source>1.6</source> <target>1.6</target> <compilerArgument>-Xlint:all</compilerArgument> <showWarnings>true</showWarnings> <showDeprecation>true</showDeprecation> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId> <artifactId>exec-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.2.1</version> <configuration> <mainClass>org.test.int1.Main</mainClass> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
主要還是在springweb開發所需jar上新增三個Spring Security所需jar:

相關配置檔案:
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app version="2.5" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> <!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- Processes application requests --> <servlet> <servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- Spring Security --> <filter> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
root-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- Root Context: defines shared resources visible to all other web components -->
<import resource="spring-security.xml" />
</beans>
此配置其實包含了“配置模組化”的思想,通過import,把跟Security相關的配置,單獨放在另一個xml檔案中,然後import進來,配置檔案特別多的時候,這樣可以使Spring的配置看上去更有條理
spring-security.xml
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.2.xsd">
<http auto-config="true">
<intercept-url pattern="/admin" access="ROLE_USER" />
<!-- <http-basic /> -->
</http>
<authentication-manager>
<authentication-provider>
<user-service>
<user name="dk" password="123456" authorities="ROLE_USER" />
</user-service>
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
</beans:beans>這才是Security的精華所在,8-10行,表示“/admin”請求需要ROLE_USER角色的使用者才能訪問,12-18行配置了一個使用者dk以及密碼123456,並將該使用者授於ROLE_USER角色(當然:這裡只是演示,實際應用中,更常見的做法是將使用者名稱、密碼放到資料庫中)
servlet-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- DispatcherServlet Context: defines this servlet's request-processing infrastructure -->
<!-- Enables the Spring MVC @Controller programming model -->
<annotation-driven />
<!-- Handles HTTP GET requests for /resources/** by efficiently serving up static resources in the ${webappRoot}/resources directory -->
<resources mapping="/resources/**" location="/resources/" />
<!-- Resolves views selected for rendering by @Controllers to .jsp resources in the /WEB-INF/views directory -->
<beans:bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<beans:property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" />
<beans:property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</beans:bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.csdn.dk" />
</beans:beans>
主要用來處理Spring-MVC的相關內容,跟Security其實沒啥關係
第3步:前端檢視頁面部分
通用頁面(所以角色都可以訪問)
hello.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" session="false"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>${title}</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Title:${title}</h1>
<h1>Message:${message}</h1>
</body>
</html>特定頁面(不是所以角色都可以訪問)
admin.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" session="true"%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>${title}</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Title : ${title}</h1>
<h1>Message : ${message}</h1>
<c:if test="${pageContext.request.userPrincipal.name != null}">
<h2>
Welcome : ${pageContext.request.userPrincipal.name} | <a
href="<c:url value="/j_spring_security_logout" />"> Logout</a>
</h2>
</c:if>
</body>
</html>第4步 :後端JAVA部分
HelloController.java
對應前端兩個頁面的請求控制
package com.csdn.dk;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = { "/", "/welcome" }, method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView welcome() {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView();
model.addObject("title", "Welcome - Spring Security Hello World");
model.addObject("message", "This is welcome page!");
model.setViewName("hello");
return model;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/admin", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView admin() {
ModelAndView model = new ModelAndView();
model.addObject("title", "Admin - Spring Security Hello World");
model.addObject("message", "This is protected page!");
model.setViewName("admin");
return model;
}
}
第5步 :新增javaee支援(也可以單獨新增javaee.jar支援)
載入專案到Tomcat後執行起來,錄入登入使用者名稱與密碼進行測試
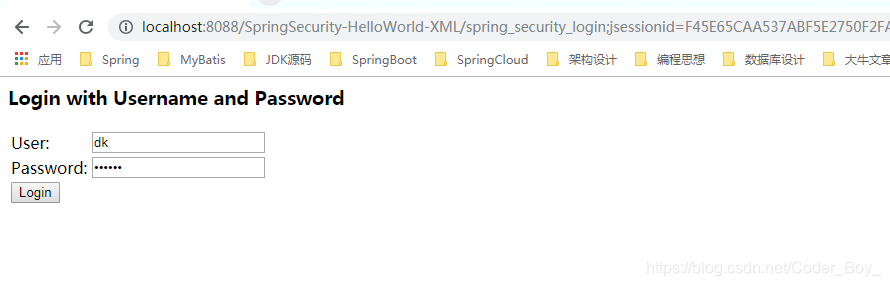
登入成功頁面的截圖:

登入失敗頁面的截圖:

在上面的案例中,有一些框架預設的配置:
admin.jsp中退出的a連結: j_spring_security_logout,是Spring Security預設生成的logout地址,除非開發人員有其它設定,否則預設退出地址就是它
還有就是我們訪問/admin時,會重定向到Spring Security自動生成的login頁面 spring_security_login
也就是沒有編寫登入表單form,系統提示一個預設的登入表單。

這種預設約定配置,在springBoot中體現的最明顯,也就是現在流行的“約定大於配置”的思想。
