MySQL sql優化的一般步驟
MySQL隨著資料量的增多,遇到SQL執行緩慢的問題越來越多。文中介紹幾種常用的SQL優化的一般步驟.
- show status
- explain
- show profile
- trace
show status
show status 主要是檢視各種型別的操作的執行次數。
SHOW STATUS LIKE 'COM%';Variable_name Value Com_admin_commands 0 Com_alter_db 0 Com_alter_db_upgrade 0 Com_alter_event 0 Com_alter_function 0 Com_alter_procedure 0 Com_alter_server 0 Com_alter_table 0 Com_alter_tablespace 0 Com_analyze 0 Com_assign_to_keycache 0 Com_begin 0 Com_binlog 0 Com_call_procedure 0 Com_change_db 1 Com_change_master 0 Com_check 0 Com_checksum 0 Com_commit 0 Com_compound_sql 0 Com_create_db 0 Com_create_event 0 Com_create_function 0 Com_create_index 0 Com_create_procedure 0 Com_create_role 0 Com_create_server 0 Com_create_table 0 Com_create_temporary_table 0 Com_create_trigger 0 Com_create_udf 0 Com_create_user 0 Com_create_view 0 Com_dealloc_sql 0 Com_delete 0 Com_delete_multi 0 Com_do 0 Com_drop_db 0 Com_drop_event 0 Com_drop_function 0 Com_drop_index 0 Com_drop_procedure 0 Com_drop_role 0 Com_drop_server 0 Com_drop_table 0 Com_drop_temporary_table 0 Com_drop_trigger 0 Com_drop_user 0 Com_drop_view 0 Com_empty_query 0 Com_execute_sql 0 Com_flush 0 Com_get_diagnostics 0 Com_grant 0 Com_grant_role 0 Com_ha_close 0 Com_ha_open 0 Com_ha_read 0 Com_help 0 Com_insert 0 Com_insert_select 0 Com_install_plugin 0 Com_kill 0 Com_load 0 Com_lock_tables 0 Com_optimize 0 Com_preload_keys 0 Com_prepare_sql 0 Com_purge 0 Com_purge_before_date 0 Com_release_savepoint 0 Com_rename_table 0 Com_rename_user 0 Com_repair 0 Com_replace 0 Com_replace_select 0 Com_reset 0 Com_resignal 0 Com_revoke 0 Com_revoke_all 0 Com_revoke_role 0 Com_rollback 0 Com_rollback_to_savepoint 0 Com_savepoint 0 Com_select 0 Com_set_option 2 Com_show_authors 0 Com_show_binlog_events 0 Com_show_binlogs 0 Com_show_charsets 0 Com_show_collations 0 Com_show_contributors 0 Com_show_create_db 0 Com_show_create_event 0 Com_show_create_func 0 Com_show_create_proc 0 Com_show_create_table 0 Com_show_create_trigger 0 Com_show_databases 1 Com_show_engine_logs 0 Com_show_engine_mutex 0 Com_show_engine_status 0 Com_show_errors 0 Com_show_events 0 Com_show_explain 0 Com_show_fields 1 Com_show_function_status 0 Com_show_generic 0 Com_show_grants 0 Com_show_keys 0 Com_show_master_status 0 Com_show_open_tables 0 Com_show_plugins 0 Com_show_privileges 0 Com_show_procedure_status 0 Com_show_processlist 0 Com_show_profile 0 Com_show_profiles 0 Com_show_relaylog_events 0 Com_show_slave_hosts 0 Com_show_slave_status 0 Com_show_status 2 Com_show_storage_engines 0 Com_show_table_status 0 Com_show_tables 1 Com_show_triggers 0 Com_show_variables 1 Com_show_warnings 0 Com_shutdown 0 Com_signal 0 Com_start_all_slaves 0 Com_start_slave 0 Com_stmt_close 0 Com_stmt_execute 0 Com_stmt_fetch 0 Com_stmt_prepare 0 Com_stmt_reprepare 0 Com_stmt_reset 0 Com_stmt_send_long_data 0 Com_stop_all_slaves 0 Com_stop_slave 0 Com_truncate 0 Com_uninstall_plugin 0 Com_unlock_tables 0 Com_update 0 Com_update_multi 0 Com_xa_commit 0 Com_xa_end 0 Com_xa_prepare 0 Com_xa_recover 0 Com_xa_rollback 0 Com_xa_start 0 Compression OFF
看幾個常用的com_update、com_select、com_insert、com_delete,這些CRUD的次數統計能直觀的看到資料庫服務是讀多、還是寫多。可根據具體的業務指定不同的方案。
當然對於innodb儲存引擎,可檢視其對應的資訊:
SHOW STATUS LIKE 'innodb_rows_%';Variable_name Value -------------------- ------------- Innodb_rows_deleted 933911 Innodb_rows_inserted 1715972 Innodb_rows_read 30210424768 Innodb_rows_updated 235151
表示對應的操作影響的行數。這樣的話,資料庫的讀多寫少的型別會看的更直觀。也可以直接查詢SESSION_STATUS表來檢視mysql的統計資訊。
SELECT * FROM information_schema.`SESSION_STATUS` s WHERE s.`VARIABLE_NAME` LIKE 'INNODB_ROWS_%';;
注意區分變數名的大小寫。
VARIABLE_NAME VARIABLE_VALUE -------------------- ---------------- INNODB_ROWS_DELETED 933911 INNODB_ROWS_INSERTED 1716071 INNODB_ROWS_READ 30211179934 INNODB_ROWS_UPDATED 235155
定位慢查詢
首先要開啟慢查詢日誌,預設是關閉的。
預設的慢查詢時間為10s,超過這個值的sql會記錄到慢查詢的日誌檔案中,可對這些SQL進行對應的優化。
Variable_name Value
long_query_time 10.000000
slow_query_log OFF
slow_query_log_file LAPTOP-3T4D6I5F-slow.log有這兩種開啟方式:
- 在my.cnf 裡 通過 log-slow-queries[=file_name]
- 在mysqld程序啟動時,指定--log-slow-queries[=file_name]
我們通過在my.cnf中配置來開啟慢查詢:
#啟用慢查詢日誌
slow_query_log=1
#指定慢查詢檔名稱
slow-query-log-file=mysql-slow.log
#慢查詢時間,超過這個值的會記錄到慢查詢日誌中
long_query_time=1
#SQL語句檢測的記錄數少於設定值的語句不會被記錄到慢查詢日誌,即使這個語句執行時間超過了long_query_time的閾值
min_examined_row_limit=100 重啟資料庫,檢視配置引數
Variable_name Value
long_query_time 1.000000
slow_query_log ON
slow_query_log_file mysql-slow.log這樣就開啟了慢查詢日誌,通常用mysqldumpslow這個工具來分析慢查詢日誌資訊。
show processlist
慢查詢需要等到SQL執行完成後才會寫入到日誌檔案中,要查詢當前正在執行的程序、是否鎖表等資訊慢查詢就不行了。需要processlist來檢視資訊了,當然需要有PROCESS許可權才可以看到所有的執行緒資訊,否則只能看到你自己的執行緒。
show processlit;Id User Host db Command Time State Info Progress
2 root localhost:10716 \N Query 0 init show processlist 0.000
3 root localhost:10717 \N Sleep 410 \N 0.000explain
通過explain命令來檢視SQL的執行計劃。語法很簡單,explain 要執行的SQL即可。
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM sys_role r,sys_user_role ur WHERE r.id= ur.role_id;
id select_type table type possible_keys key key_len ref rows Extra
1 SIMPLE r ALL PRIMARY \N \N \N 1
1 SIMPLE ur ALL \N \N \N \N 1 Using where; Using join buffer (flat, BNL join) 返回的資訊詳解介紹一下,
id
選擇識別符號。這是查詢中SELECT的序號。如果行引用其他行的並集結果,則該值可以為NULL。在本例中,表列顯示了一個值,如<unionM,N>,表示行引用id值為M和N的行的並集。
select_type
- SIMPLE(簡單SELECT,不使用UNION或子查詢等)
- PRIMARY(查詢中若包含任何複雜的子部分,最外層的select被標記為PRIMARY)
- UNION(UNION中的第二個或後面的SELECT語句)
- DEPENDENT UNION(UNION中的第二個或後面的SELECT語句,取決於外面的查詢)
- UNION RESULT(UNION的結果)
- SUBQUERY(子查詢中的第一個SELECT)
- DEPENDENT SUBQUERY(子查詢中的第一個SELECT,取決於外面的查詢)
- DERIVED(派生表的SELECT, FROM子句的子查詢)
- UNCACHEABLE SUBQUERY(一個子查詢的結果不能被快取,必須重新評估外連結的第一行)
table
涉及的表
type
表示MySQL在表中找到所需行的方式,又稱“訪問型別”。
常用的型別有: ALL, index, range, ref, eq_ref, const, system, NULL(從左到右,效能從差到好)
ALL:全表掃描, MySQL將遍歷全表以找到匹配的行
index: 索引全掃描,index與ALL區別為index型別只遍歷索引樹
range: 索引範圍掃描,常見於< 、<= 、>、>=、between等操作。
ref: 使用非唯一索引掃描或唯一索引的字首掃描。返回匹配某個單獨值的記錄行。
eq_ref: 類似ref,區別就在使用的索引是唯一索引,對於每個索引鍵值,表中只有一條記錄匹配,簡單來說,就是多表連線中使用primary key或者 unique key作為關聯條件
const、system: 單表中最多有一個匹配的行,查詢速度很快。所以這個匹配行中的其他列的值可以被優化器在當前查詢中當做常量處理。例如使用primary key或者 unique key來查詢。
NULL: 表示不用訪問表或使用索引就能直接得到結果。
prossible_keys
可能使用到的索引
key
實際使用到的索引,沒有使用到索引就是NULL
key_len
表示索引中使用的位元組數,可通過該列計算查詢中使用的索引的長度(key_len顯示的值為索引欄位的最大可能長度,並非實際使用長度,即key_len是根據表定義計算而得,不是通過表內檢索出的)
不損失精確性的情況下,長度越短越好
ref
ref列顯示將哪些列或常量與key列中指定的索引進行比較,以便從表中選擇行。
如果值是func,則使用的值是某個函式的結果。要檢視哪個函式,請在EXPLAIN之後使用SHOW warning檢視擴充套件的EXPLAIN輸出。這個函式實際上可能是一個運算子,比如算術運算子。
rows
表示MySQL根據表統計資訊及索引選用情況,估算的找到所需的記錄所需要讀取的行數
Extra
該列包含MySQL解決查詢的詳細資訊,有以下幾種情況:
Using where:列資料是從僅僅使用了索引中的資訊而沒有讀取實際的行動的表返回的,這發生在對錶的全部的請求列都是同一個索引的部分的時候,表示mysql伺服器將在儲存引擎檢索行後再進行過濾
Using temporary:表示MySQL需要使用臨時表來儲存結果集,常見於排序和分組查詢
Using filesort:MySQL中無法利用索引完成的排序操作稱為“檔案排序”
Using join buffer:改值強調了在獲取連線條件時沒有使用索引,並且需要連線緩衝區來儲存中間結果。如果出現了這個值,那應該注意,根據查詢的具體情況可能需要新增索引來改進能。
Impossible where:這個值強調了where語句會導致沒有符合條件的行。
Select tables optimized away:這個值意味著僅通過使用索引,優化器可能僅從聚合函式結果中返回一行
有時候使用explain不能定位到問題,可配合profile來聯合分析。
show profile
SHOW PROFILE和SHOW PROFILES語句顯示分析資訊,指示在當前會話過程中執行的語句的資源使用情況。
基本語法:
SHOW PROFILE [type [, type] ... ]
[FOR QUERY n]
[LIMIT row_count [OFFSET offset]]
type: {
ALL
| BLOCK IO
| CONTEXT SWITCHES
| CPU
| IPC
| MEMORY
| PAGE FAULTS
| SOURCE
| SWAPS
}當然,首先要開啟profile.
mysql> SELECT @@profiling;
+-------------+
| @@profiling |
+-------------+
| 0 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> SET profiling = 1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)檢視所有的profiles。
SHOW profiles;Query_ID Duration Query
30 0.00010284 SET profiling_history_size = 15
31 0.00350268 SHOW STATUS
32 0.00011305 select @@profiling
33 0.00262382 SHOW STATUS
34 0.00048830 select state, round(sum(duration),5) as `duration (summed) in sec` from information_schema.profiling where query_id = 32 group by state order by `duration (summed) in sec` desc檢視指定id的profile,檢視具體執行緒的時間消耗。
SHOW profile FOR QUERY 34;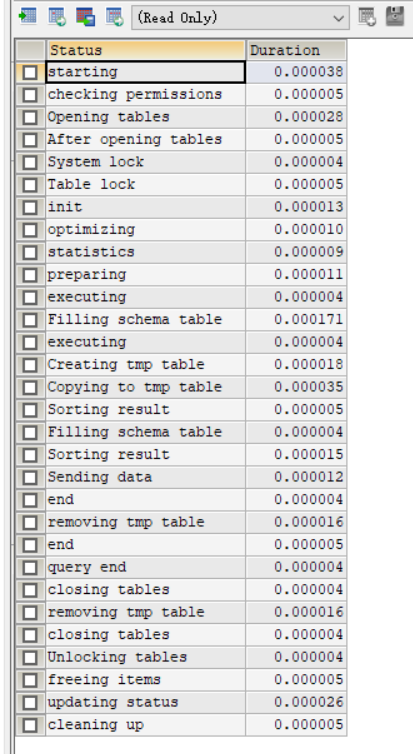
其中sending data狀態是需要大量磁碟io操作的,比較耗費時間。其他的資訊參考mysql官網的說明。
trace
MySQL從5.6加入了SQL的跟蹤trace。通過trace檔案可以看到優化器為何選擇這個執行計劃而不是其他的。
首先要開啟跟蹤trace,
-- 開啟並且設定資料格式為JSON
SET OPTIMIZER_TRACE="enabled=on",END_MARKERS_IN_JSON=ON;
-- 設定記憶體
SET OPTIMIZER_TRACE_MAX_MEM_SIZE=1000000; 檢視是否開啟
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%optimizer_trace%';Variable_name Value
optimizer_trace enabled=on,one_line=off
optimizer_trace_features greedy_search=on,range_optimizer=on,dynamic_range=on,repeated_subselect=on
optimizer_trace_limit 1
optimizer_trace_max_mem_size 1000000
optimizer_trace_offset -1開始執行SQL
mysql> select * from version;
+--------+----------------+----------------------------+
| VER_ID | SCHEMA_VERSION | VERSION_COMMENT |
+--------+----------------+----------------------------+
| 1 | 2.3.0 | Hive release version 2.3.0 |
+--------+----------------+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
檢視跟蹤資訊,
select * from information_schema.optimizer_trace\G
檢視TRACE欄位中對應的json資訊。
{
"steps": [
{
"join_preparation": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"expanded_query": "/* select#1 */ select `version`.`VER_ID` AS `VER_ID`,`version`.`SCHEMA_VERSION` AS `SCHEMA_VERSION`,`version`.`VERSION_COMMENT` AS `VERSION_COMMENT` from `version`"
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_preparation */
},
{
"join_optimization": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
{
"table_dependencies": [
{
"table": "`version`",
"row_may_be_null": false,
"map_bit": 0,
"depends_on_map_bits": [
] /* depends_on_map_bits */
}
] /* table_dependencies */
},
{
"rows_estimation": [
{
"table": "`version`",
"table_scan": {
"rows": 1,
"cost": 1
} /* table_scan */
}
] /* rows_estimation */
},
{
"considered_execution_plans": [
{
"plan_prefix": [
] /* plan_prefix */,
"table": "`version`",
"best_access_path": {
"considered_access_paths": [
{
"rows_to_scan": 1,
"access_type": "scan",
"resulting_rows": 1,
"cost": 1.2,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_access_paths */
} /* best_access_path */,
"condition_filtering_pct": 100,
"rows_for_plan": 1,
"cost_for_plan": 1.2,
"chosen": true
}
] /* considered_execution_plans */
},
{
"attaching_conditions_to_tables": {
"original_condition": null,
"attached_conditions_computation": [
] /* attached_conditions_computation */,
"attached_conditions_summary": [
{
"table": "`version`",
"attached": null
}
] /* attached_conditions_summary */
} /* attaching_conditions_to_tables */
},
{
"refine_plan": [
{
"table": "`version`"
}
] /* refine_plan */
}
] /* steps */
} /* join_optimization */
},
{
"join_execution": {
"select#": 1,
"steps": [
] /* steps */
} /* join_execution */
}
] /* steps */
}當然這只是一個簡單的查詢的跟蹤資訊,其他更復雜的SQL的跟蹤資訊會更加詳盡,不過大概的結構就是這個樣子的。
小結
通過上述步驟,一般可以定位到問題,剩下的就是對症下藥。索引優化、批量資料優化、表碎片、具體的SQL操作的優化等等具體情況具體分析。
