演算法導論 之 B樹(B-樹)
- 作者:鄒祁峰
- 郵箱:[email protected]
-
日期:2014.03.13 18:00
- 轉載請註明來自"祁峰"的CSDN部落格
1 引言
In computer science, a B-tree is a tree data structure that keeps data sorted and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree is a generalization of a binary search tree in that a node can have more than two
children (Comer 1979, p. 123). Unlike self-balancing binary search trees, the B-tree is optimized for systems that read and write large blocks of data. It is commonly used in databases and filesystems.
在電腦科學中,B樹在查詢、訪問、插入、刪除操作上時間複雜度為O(log2~n)(2為底數 n為對數),與自平衡二叉查詢樹不同的是B樹對大塊資料讀寫的操作有更優的效能,其通常在資料庫和檔案系統中被使用。
一棵m階的B樹,或為空樹,或為滿足下列特徵的m叉樹:
①、樹中每個結點至多有m棵子樹;
②、若根結點不是終端結點,則至少有2棵子樹;
③、除根之外,所有非終端結點至少有
④、所有的非終端結點中包含下列資訊資料:
[n, C0, K0, C1, K1, C2, K2, ...., Kn-1, Cn]
其中:Ki[i=0,1,...,n-1]為關鍵字,且K
2 編碼實現
2.1 結構定義
根據m階B樹的性質,B樹的相關結構定義如下:
/* B樹結點結構 */ typedef struct _btree_node_t { int num; /* 關鍵字個數 */ int *key; /* 關鍵字:所佔空間為(max+1) - 多出來的1個空間用於交換空間使用 */ struct _btree_node_t **child; /* 子結點:所佔空間為(max+2)- 多出來的1個空間用於交換空間使用 */ struct _btree_node_t *parent; /* 父結點 */ }btree_node_t;
程式碼1 結點結構
/* B樹結構 */
typedef struct
{
int max; /* 單個結點最大關鍵字個數 - 階m=max+1 */
int min; /* 單個結點最小關鍵字個數 */
int sidx; /* 分裂索引 = (max+1)/2 */
btree_node_t *root; /* B樹根結點地址 */
}btree_t;程式碼2 B樹結構
2.2 建立B樹
此過程主要是完成btree_t中最大關鍵字個數max、最小關鍵字個數min、分裂索引sidx的設定,並建立一顆空樹,為後續的構造B樹做好準備條件。
/******************************************************************************
**函式名稱: btree_creat
**功 能: 建立B樹
**輸入引數:
** _btree: B樹
** m: 階 - 取值範圍m>=3
**輸出引數: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失敗
**實現描述:
**注意事項:
** 注意:引數max的值不能小於2.
**作 者: # Qifeng.zou # 2014.03.12 #
******************************************************************************/
int btree_creat(btree_t **_btree, int m)
{
btree_t *btree = NULL;
if(m < 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Parameter 'max' must geater than 2.\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
btree = (btree_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(btree_t));
if(NULL == btree) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
btree->max= m - 1;
btree->min = m/2;
if(0 != m%2) {
btree->min++;
}
btree->min--;
btree->sidx = m/2;
btree->root = NULL; /* 空樹 */
*_btree = btree;
return 0;
}
2.3 插入操作
B樹是從空樹起,逐個插入關鍵字而建立起來的,由於B樹結點中的關鍵字個數num必須>=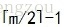 ,因此,每次插入一個關鍵字不是在樹中新增一個終端結點,而是首先在最底層的某個非終端結點中插入一個關鍵字,若該結點的關鍵字個數不超過m-1,則插入完成,否則要進行結點的“分裂”。
假設結點node的關鍵字個數num>max,則需進行分裂處理,其大體處理流程如下:
1) 結點node以sidx關鍵字為分割點,索引(0 ~ sidx-1)關鍵字繼續留在結點node中,索引(sidx+1 ~ num-1)關鍵字放入新結點node2中
,因此,每次插入一個關鍵字不是在樹中新增一個終端結點,而是首先在最底層的某個非終端結點中插入一個關鍵字,若該結點的關鍵字個數不超過m-1,則插入完成,否則要進行結點的“分裂”。
假設結點node的關鍵字個數num>max,則需進行分裂處理,其大體處理流程如下:
1) 結點node以sidx關鍵字為分割點,索引(0 ~ sidx-1)關鍵字繼續留在結點node中,索引(sidx+1 ~ num-1)關鍵字放入新結點node2中2) 而索引sidx關鍵字則插入node->parent中,再將新結點node2作為父結點新插入關鍵字的右孩子結點
3) 判斷插入node的sidx關鍵字後,node->parent的關鍵字個數num是否超過max,如果超過,則以parent為操作物件進行1)的處理;否則,處理結束。
以下將通過構造一棵B樹的方式來講解B樹的插入過程:假設現在需要構建一棵4階B樹(即:階m=4、關鍵字最大個數max=3),其插入操作和處理過程如下描述。 1) 插入關鍵字45 剛開始為空樹,因此插入成功後只有一個結點。

圖1 插入結點 2) 插入關鍵字24和53 在圖1的基礎上,插入關鍵字24和53後,該結點關鍵字個數num仍未超過max,因此不會進行“分裂”處理。插入完成後,該結點關鍵字個數num=3已經達到臨界值max。
圖2 插入結點
3) 插入關鍵字90
在圖2基礎上,插入關鍵字90後,該結點關鍵字個數num=4超過max值,需要進行“分裂”處理。

圖3 分裂處理
當結點關鍵字個數num達到max時,則需要進行“分裂”處理,分割序號為num/2。圖3中的[4| 24, 45, 53, 90]的分割序號為num/2 = 4/2 = 2,序號從0開始計數,因此關鍵字53為分割點,分裂過程如下:
->1) 以序列號idx=num/2為分割點,原結點分裂為2個結點A[2| 24, 45]和B[1| 90];
->2) 原結點無父結點,則新建一個結點P,並將關鍵字插入到新結點P中;
->3) 將結點A和B作為結點P的子結點,並遵循B樹特徵④;
->4) 因結點P的結點數未超過max,則分裂結束。
4) 插入關鍵字46和47
在圖3右圖的基礎上,插入關鍵字46和47後,得到圖4左圖,此時結點[4| 24, 45, 46, 47]已經達到分裂條件。
圖4 分裂處理
連續插入關鍵字46、47後,該結點[2| 24, 45]變為[4| 24, 45, 46, 47],因此其達到了“分裂”的條件,其分裂流程如下:
->1) 以序列號idx=num/2為分割點,結點[2| 24, 45, 46, 47]分裂為兩個結點A[2| 24, 45]和B[1| 47];
->2) 分割點關鍵字46被插入到父結點P中,得到結點P[2| 46, 53]
->3) 新結點B[1| 47]加入到結點P[2| 46, 53]的子結點序列中 - 遵循特徵④
->4) 因結點P[2| 46, 53]的關鍵字個數num為超過max,因為分裂結束。
5) 插入關鍵字15和18
在圖4右圖的基礎上,插入關鍵字15和18後,得到圖5左圖,此時結點[4| 15, 18, 24, 45]已經達到分裂條件。其處理過程同4),在此不再贅述。
圖5 分裂處理
6) 插入關鍵字48、49、50
在圖5右圖的基礎上插入48、49、50,可得到圖6左圖,此時結點[1| 47, 48, 49, 50]已達到分裂條件。
圖6 分裂處理
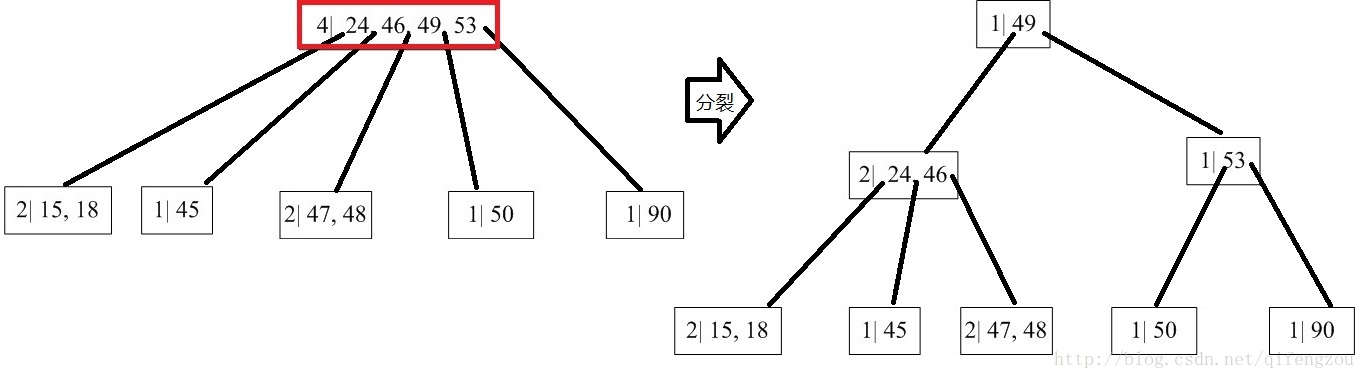
完成第一步分裂處理之後,父結點P[4| 24, 46, 49, 53]此時也達到了分裂條件。
圖7 進一步分裂
通過對1) ~ 6)的插入操作過程的理解和分析,可使用如下程式碼實現:
/******************************************************************************
**函式名稱: btree_insert
**功 能: 插入關鍵字(對外介面)
**輸入引數:
** btree: B樹
** key: 被插入的關鍵字
**輸出引數: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失敗
**實現描述:
**注意事項:
**作 者: # Qifeng.zou # 2014.03.12 #
******************************************************************************/
int btree_insert(btree_t *btree, int key)
{
int idx = 0;
btree_node_t *node = btree->root;
/* 1. 構建第一個結點 */
if(NULL == node) {
node = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == node) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create node failed!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
node->num = 1;
node->key[0] = key;
node->parent = NULL;
btree->root = node;
return 0;
}
/* 2. 查詢插入位置:在此當然也可以採用二分查詢演算法,有興趣的可以自己去優化 */
while(NULL != node) {
for(idx=0; idx<node->num; idx++) {
if(key == node->key[idx]) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] The node is exist!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
else if(key < node->key[idx]) {
break;
}
}
if(NULL != node->child[idx]) {
node = node->child[idx];
}
else {
break;
}
}
/* 3. 執行插入操作 */
return _btree_insert(btree, node, key, idx);
}/******************************************************************************
**函式名稱: _btree_insert
**功 能: 插入關鍵字到指定結點
**輸入引數:
** btree: B樹
** node: 指定結點
** key: 被插入的關鍵字
** idx: 指定位置
**輸出引數: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失敗
**實現描述:
**注意事項:
**作 者: # Qifeng.zou # 2014.03.12 #
******************************************************************************/
static int _btree_insert(btree_t *btree, btree_node_t *node, int key, int idx)
{
int i = 0;
/* 1. 移動關鍵字:首先在最底層的某個非終端結點上插入一個關鍵字,因此該結點無孩子結點,故不涉及孩子指標的移動操作 */
for(i=node->num; i>idx; i--) {
node->key[i] = node->key[i-1];
}
node->key[idx] = key; /* 插入 */
node->num++;
/* 2. 分裂處理 */
if(node->num > btree->max) {
return btree_split(btree, node);
}
return 0;
}/******************************************************************************
**函式名稱: btree_split
**功 能: 結點分裂處理
**輸入引數:
** btree: B樹
** node: 需要被分裂處理的結點
**輸出引數: NONE
**返 回: 0:成功 -1:失敗
**實現描述:
**注意事項:
**作 者: # Qifeng.zou # 2014.03.12 #
******************************************************************************/
static int btree_split(btree_t *btree, btree_node_t *node)
{
int idx = 0, total = 0, sidx = btree->sidx;
btree_node_t *parent = NULL, *node2 = NULL;
while(node->num > btree->max) {
/* Split node */
total = node->num;
node2 = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == node2) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create node failed!\n", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
/* Copy data */
memcpy(node2->key, node->key + sidx + 1, (total-sidx-1) * sizeof(int));
memcpy(node2->child, node->child+sidx+1, (total-sidx) * sizeof(btree_node_t *));
node2->num = (total - sidx - 1);
node2->parent = node->parent;
node->num = sidx;
/* Insert into parent */
parent = node->parent;
if(NULL == parent) {
/* Split root node */
parent = btree_creat_node(btree);
if(NULL == parent) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] Create root failed!", __FILE__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
btree->root = parent;
parent->child[0] = node;
node->parent = parent;
node2->parent = parent;
parent->key[0] = node->key[sidx];
parent->child[1] = node2;
parent->num++;
}
else {
/* Insert into parent node */
for(idx=parent->num; idx>0; idx--) {
if(node->key[sidx] < parent->key[idx-1]) {
parent->key[idx] = parent->key[idx-1];
parent->child[idx+1] = parent->child[idx];
continue;
}
break;
}
parent->key[idx] = node->key[sidx];
parent->child[idx+1] = node2;
node2->parent = parent;
parent->num++;
}
memset(node->key+sidx, 0, (total - sidx) * sizeof(int));
memset(node->child+sidx+1, 0, (total - sidx) * sizeof(btree_node_t *));
/* Change node2's child->parent */
for(idx=0; idx<=node2->num; idx++) {
if(NULL != node2->child[idx]) {
node2->child[idx]->parent = node2;
}
}
node = parent;
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************************************
**函式名稱: btree_creat_node
**功 能: 新建結點
**輸入引數:
** btree: B樹
**輸出引數: NONE
**返 回: 節點地址
**實現描述:
**注意事項:
**作 者: # Qifeng.zou # 2014.03.12 #
******************************************************************************/
static btree_node_t *btree_creat_node(btree_t *btree)
{
btree_node_t *node = NULL;
node = (btree_node_t *)calloc(1, sizeof(btree_node_t));
if(NULL == node) {
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
node->num = 0;
/* More than (max) is for move */
node->key = (int *)calloc(btree->max+1, sizeof(int));
if(NULL == node->key) {
free(node), node=NULL;
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
/* More than (max+1) is for move */
node->child = (btree_node_t **)calloc(btree->max+2, sizeof(btree_node_t *));
if(NULL == node->child) {
free(node->key);
free(node), node=NULL;
fprintf(stderr, "[%s][%d] errmsg:[%d] %s\n", __FILE__, __LINE__, errno, strerror(errno));
return NULL;
}
return node;
}2.4 結果展示
只需寫一個簡單的測試函式,呼叫以上的測試介面。隨機插入n個關鍵字,並列印其樹形結構,便可很方便的判斷出插入操作的正確性。1) 設定B樹階m=3時

圖8 結果展示
2) 設定B樹階m=10時

圖9 結果展示