B-樹/B+樹/B*樹詳解(查詢+插入)
前言:
為了能夠更好的理解什麼是B樹,這裡先對所有的動態查詢樹做下總結:
動態二叉樹總共分為:二叉查詢樹(Binary Search Tree),平衡二叉查詢樹(Balanced Binary Search Tree),紅黑樹(Red-Black Tree ),B-tree/B+tree/B*tree。前三者是典型的二叉查詢樹結構,其查詢的時間複雜度O(log2N)與樹的深度相關,那麼降低樹的高度自然就可以提高查詢效率。那麼如何解決降低樹的高度的問題?
現在假設這麼個場景咱們有面對這樣一個實際問題:就是大規模資料儲存中,實現索引查詢這樣一個實際背景下,樹節點儲存的元素數量是有限的(如果元素數量非常多的話,查詢就退化成節點內部的線性查找了),這樣導致二叉查詢樹結構由於
對於多叉樹主要分為三種:B-tree/B+tree/B*tree
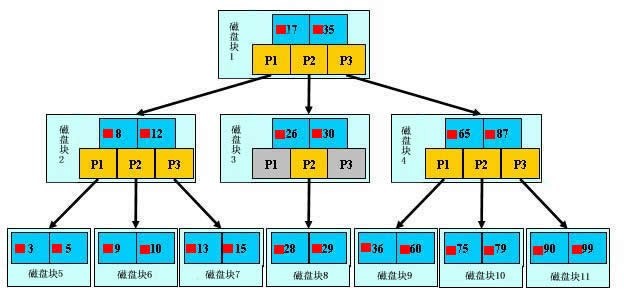
一、Btree:
一棵M階(M>2)的B樹,是一棵平衡的M路平衡搜尋樹,可以是空樹或者滿足一下性質:
1. 根節點至少有兩個孩子
2.
每個非根節點有[ ,M]個孩子
3.
每個非根節點有[ -1,M-1]個關鍵字,並且以升序排列
4. key[i]和key[i+1]之間的孩子節點的值介於key[i]、key[i+1]之間
5. 所有的葉子節點都在同一層
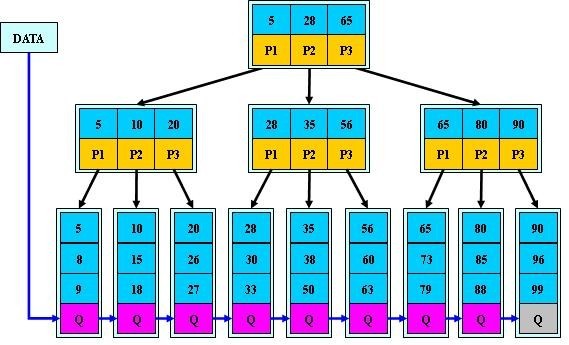
二、B+樹
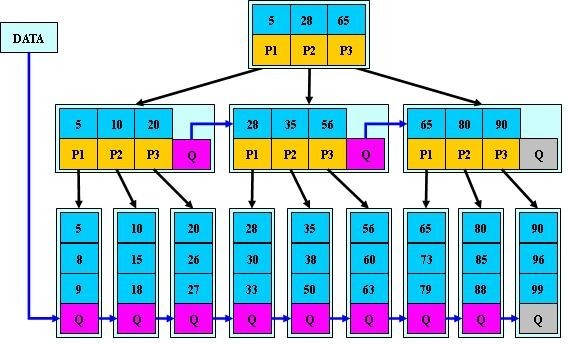
這裡只分別講一下他們的區別於聯絡
他們的結構如下面三個圖所示:B樹還算是正常的多叉樹,B+樹和B*樹是在B樹的基礎上發展的。
B樹與B+樹的區別:
1.所有的葉子節點包含了全部關鍵子資訊,及指向含有這些關鍵字記錄的指標,且葉子結點本身依關鍵字的大小自小而大的順序連結。 (而B 樹的葉子節點並沒有包括全部需要查詢的資訊)
2.所有的非終端結點可以看成是索引部分,結點中僅含有其子樹根結點中最大(或最小)關鍵字。 (而B 樹的非終節點也包含需要查詢的有效資訊)
B+樹與B*樹的區別:
B+樹的分裂:當一個結點滿時,分配一個新的結點,並將原結點中
B*樹的分裂:當一個結點滿時,如果它的下一個兄弟結點未滿,那麼將一部分資料移到兄弟結點中,再在原結點插入關鍵字,最後修改父結點中兄弟結點的關鍵字(因為兄弟結點的關鍵字範圍改變了);如果兄弟也滿了,則在原結點與兄弟結點之間增加新結點,並各複製1/3的資料到新結點,最後在父結點增加新結點的指標。
所以,B*樹分配新結點的概率比B+樹要低,空間使用率更高;
B樹的插入和查詢
#ifndef __BTREE_H__
#define __BTREE_H__
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class K,int M = 3>
struct BTreeNode
{
K _key[M]; //多放一個空間方便分裂
BTreeNode<K, M>* _subs[M + 1];
BTreeNode<K, M>* _parent;
size_t _size;
BTreeNode()
:_size(0)
{
_parent = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i <= M; i++)
{
_subs[i] = NULL;
}
}
};
template<class K,class V>
struct Pair
{
K _first;
V _second;
Pair(const K& key, const V& value)
:_first(key)
, _second(value)
{}
};
template<class K,int M = 3>
class BTree
{
typedef BTreeNode<K, M> Node;
public:
BTree()
:_root(NULL)
{}
Pair<K, int> Find(const K& key)
{
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = NULL;
int index = 0;
while (cur)
{
while (index < cur->_size)
{
if (cur->_key[index] < key)
++index;
else if (cur->_key[index] == key)
{
return Pair<K, M>(cur, index);
}
else
break;
}
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_subs[index];//在當前節點往下找
index = 0;
}
return Pair<K, M>(parent, -1);//如果沒找到就返回父親節點的位置,然後在父親節點的位置插入
}
bool Insert(const K& key)
{
//沒有節點,直接修改root
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node();
_root->_key[0] = key;
_root->_size++;
return true;
}
Pair<K, M> pair = Find(key);
if (pair._second != -1)
{
return -1;//已經存在
}
Node* cur = pair._first;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
K insertKey = key;
while (1)
{
_InsertKey(cur,insertKey);//直接插入
//小於M,無需分裂
if (cur->_size < M)
{
return true;
}
//分裂調整
int mid = (cur->_size - 1) / 2;//減1是為了防止M為偶數
Node* right = new Node();
int index = 0;
//拷貝_key[]
for (int i = mid + 1; i < cur->_size; i++)
{
right->_key[index++] = cur->_key[i];
++right->_size;
}
index = 0;
//拷貝subs[]
for (int i = mid + 1; i < cur->_size; ++i)
{
right->_subs[index++] = cur->_subs[i];
if (cur->_subs[i])
{
cur->_subs[i]->_parent = right;
}
}
insertKey = cur->_key[mid];
cur->_size = (cur->_size - 1) / 2;
if (parent == NULL)//cur為根節點
{
Node* tmp = new Node();
tmp->_key[0] = insertKey;
++tmp->_size;
tmp->_subs[0] = cur;
tmp->_subs[1] = right;
cur->_parent = right->_parent = tmp;
_root = tmp;
break;
}
else
{
right->_parent = parent;
index = M - 1;
while (parent->_subs[index] != cur)
{
parent->_subs[index + 1] = parent->_subs[index];
--index;
}
parent->_subs[index + 1] = right;
cur = parent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
}
return true;
}
void _InsertKey(Node* cur, cosnt K& key)
{
//插入排序
it index = cur->_size - 1;
while (index >= 0 && key < cur->_key[index])
{
cur->_key[index + 1] = cur->_key[index];
--index;
}
cur->_key[index + 1] = key;
++cur->_size;
}
protected:
Node* _root;
};
#endif //__BTREE_H__

