EPOLL使用的簡單總結2——ET模式
註明!此篇博文全部搬運於ChinaUnix網站大佬的系列博文,主要摘自:
·徹底學會epoll(3)——ET讀操作例項分析
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4288802.html
·徹底學會epoll(4)——ET寫操作例項分析
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4296180.html
·徹底學會epoll(5)——ET模式下注意事項
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4308612.html
·徹底學會epoll(6)——關於ET若干問題總結
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4324338.html
0. 接著上一篇的博文,為什麼要用ET不用LT。
當然很多時候也用LT(編碼簡單所以安全)。如果想讓程式更為高效,就可以使用ET模式了。
1. ET與LT的區別
所以問題來了,ET比LT高效在哪裡?
從核心核心實現分析:
在核心的實現中,倆者這是在返回時有區別。
再讀操作時,
LT模式下,如果讀操作就緒(核心讀緩衝區有資料,EPOLLIN事件)就會把核心中的rlist拷貝一次,如果一次沒有處理完讀快取的資料就還會讀操作就緒(依然觸發EPOLLIN事件),又會把rlist拷貝一次。
ET模式下,讀操作就緒只拷貝一次(觸發一次EPOLLIN事件)。
所以在LT模式下在核心拷貝的次數是n(n>=1),ET模式是1。
上篇博文講道了效能殺手包括資料拷貝,而且還發生在核心。
所以ET模式在一定條件下比LT高效。
區別:
大體上如下面的腦圖。
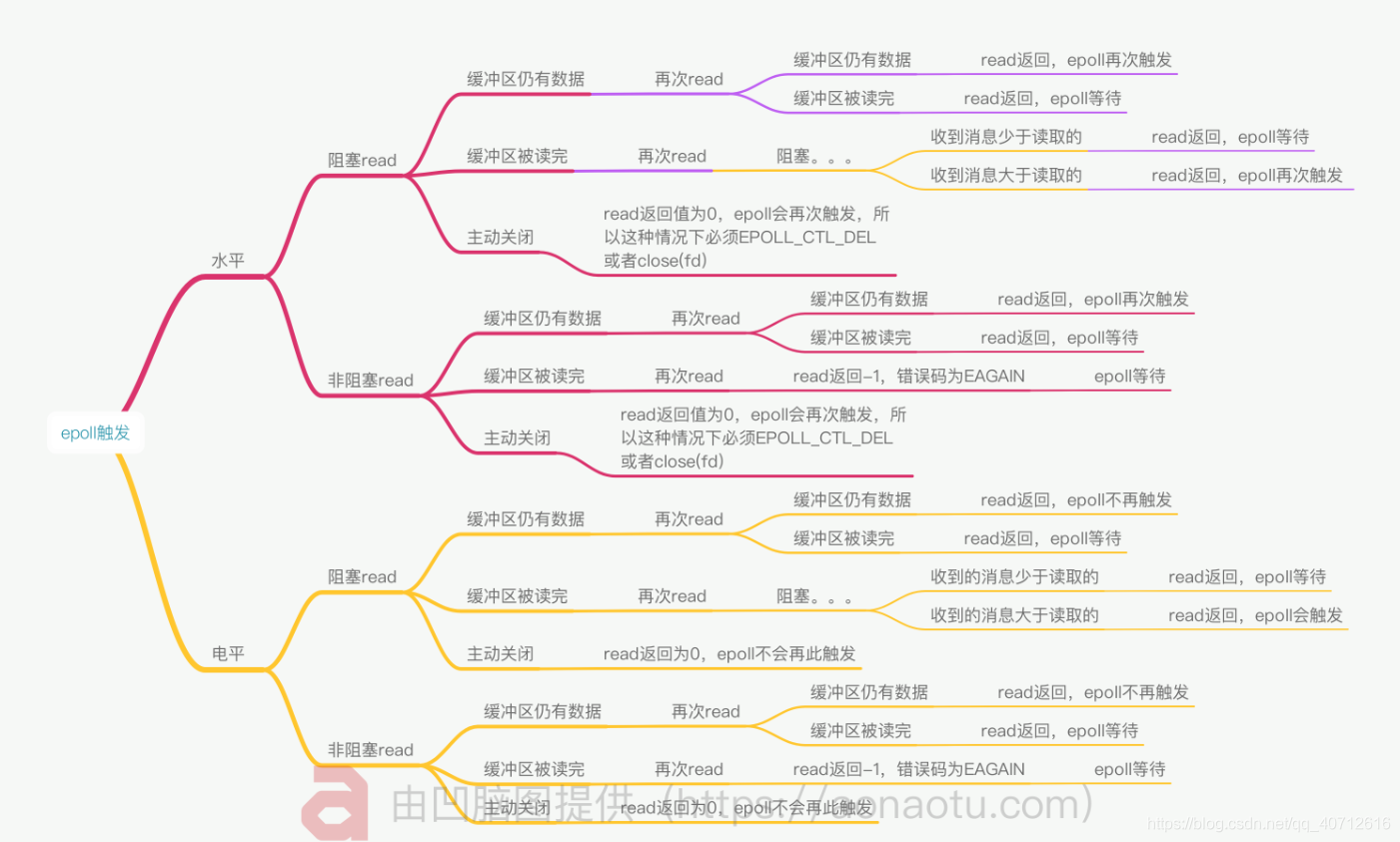
讀操作時EP和LT觸發EPOLLIN事件的區別:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4288802.html
寫操作時ET和LT觸發EPOLLOUT的區別:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4296180.html
·對於讀取操作:
(1) 當buffer由不可讀狀態變為可讀的時候,即由空變為不空的時候。
(2) 當有新資料到達時,即buffer中的待讀內容變多的時候。
另外補充一點:
(3) 當buffer中有資料可讀(即buffer不空)且使用者對相應fd進行epoll_mod IN事件時。
·l 對於寫操作:
(1) 當buffer由不可寫變為可寫的時候,即由滿狀態變為不滿狀態的時候。
(2) 當有舊資料被髮送走時,即buffer中待寫的內容變少得時候。
另外補充一點:
(3) 當buffer中有可寫空間(即buffer不滿)且使用者對相應fd進行epoll_mod OUT事件時。
2. 實現過程中的區別(c++, 面向過程)
結構與上一篇博文一樣,只做一些改動。
也可以看大佬的博文中的程式碼:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-28541347-id-4324338.html
#include "myepollserver.h"
int main()
{
int listenfd;
listenfd = Socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_NONBLOCK | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0); // fei zu se IO fu yong
struct sockaddr_in serveraddr;
bzero(&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr));
serveraddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
serveraddr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
serveraddr.sin_port = htons(8000);
int opt = 1;
setsockopt(listenfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
Bind(listenfd, (struct sockaddr *)&serveraddr, sizeof(serveraddr));
Listen(listenfd, 20);
// clinet init date
struct sockaddr_in clientaddr;
socklen_t clientlen;
int connfd;
//epoll
typedef std::vector<struct epoll_event> EpollList;
int epollfd;
epollfd = epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC);
//Creates a handle to epoll, the size of which tells the kernel how many listeners there are.
/*ET模式的下的第一處改動, epfd.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET ; 增加EPOLLET事件*/
struct epoll_event epfd;
epfd.data.fd = listenfd;
epfd.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET ;
epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, listenfd, &epfd);
EpollList events(16);//You can listen for 16 at first
int nready;
while(1)
{
nready = epoll_wait(epollfd, &*events.begin(), static_cast<int>(events.size()), -1);
if (nready == -1)
{
if(errno == EINTR)
continue;
perror("epoll_wait");
}
if(nready == 0)
continue;
if ((size_t)nready == events.size())
{
events.resize(events.size() * 2);
}
for(int i=0; i < nready; ++i)
{
/*ET模式的下的第二處改動,把讀寫操作分開後,重新確定一些變數的作用域*/
char buf[100];
bzero(buf, sizeof(buf));
int n=0, nread, nwrite;
if (events[i].data.fd == listenfd)
{
clientlen = sizeof(clientaddr);
connfd = Accept4(listenfd, (struct sockaddr*)&clientaddr, &clientlen,
SOCK_NONBLOCK | SOCK_CLOEXEC);// fei zu se IO fu yong
std::cout << connfd << "is come!" << std::endl;
/*ET模式的下的第三處改動,監聽與使用者到來時新增EPOLLET事件,epfd.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;*/
epfd.data.fd = connfd;
epfd.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, connfd, &epfd);
}else if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN)
{
connfd = events[i].data.fd;
if (connfd < 0)
{
continue;
}
/*ET模式的下的第四處改動,修改讀操作,一次性讀完*/
while((nread = read(connfd, buf, 100)) > 0) //read to over
{
n += nread;
}
if (n > 0)
{
std::cout << "::" << connfd <<" Date: ["<< buf <<"]" << std::endl;
/*ET*/
epfd.data.fd = connfd;
epfd.events = events[i].events | EPOLLOUT;
epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_MOD, connfd, &epfd);
}else if (n == 0)
{
std::cout << connfd << "is go" << std::endl;
close(connfd);
epfd = events[i];
epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, connfd, &epfd);
}
}
/*ET模式的下的第五處改動,讀寫分開,一次性寫完*/
if (events[i].events & EPOLLOUT)
{
while(n > 0)//write ot over
{
nwrite = write(connfd, buf, n);
n -= nwrite;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
