(C語言)簡單明瞭的 陣列模擬棧+ (C++)陣列模擬棧
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-23
C語言資料結構中的很多東西都能夠通過陣列和連結串列來實現,所以熟練陣列和連結串列是很有必要的。
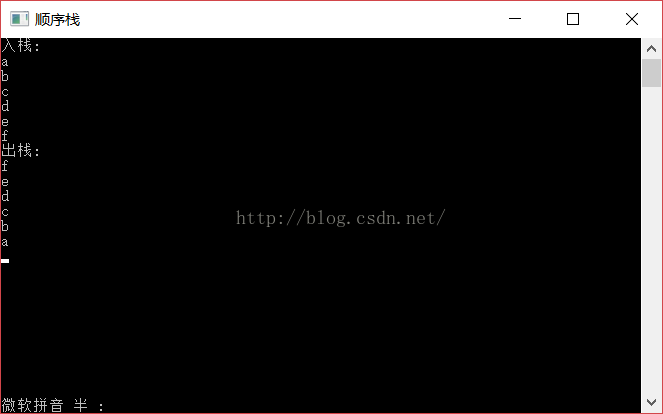
棧的特點就是先進後出,如圖輸出。
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h>//memset庫源 using namespace std; struct Stack { char space[1024]; int top; }; void init(Stack *s) { s->top=0; memset(s->space,0,1024); } bool Isfull(Stack *s) { return s->top==1024; } char pop(Stack *s) { return s->space[--s->top]; } void push(Stack *s,char c) { s->space[s->top++]=c; } int Is_empty(Stack *s) { if(s->top==0) return 1; return 0; } int main() { Stack st; init(&st); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'a'); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'b'); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'c'); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'d'); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'e'); if(!Isfull(&st)) push(&st,'f'); while(!Is_empty(&st)) cout<<pop(&st)<<endl; return 0; }
如果在純C下,把cout輸出改用printf
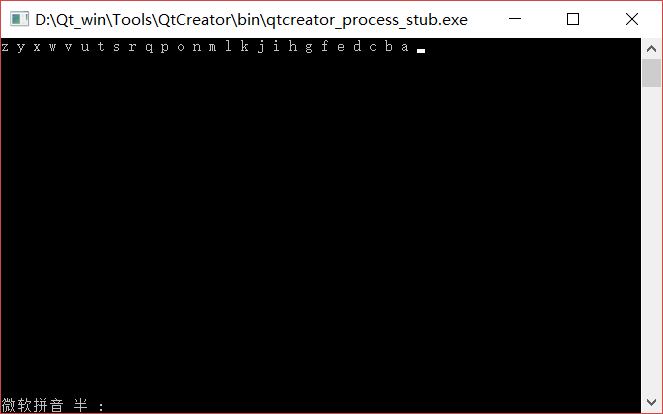
#include <iostream> #include <memory.h> using namespace std; struct Stack { void init(); bool isEmpty(); bool isFull(); char pop(); void push(char c); private: char space[1024]; int top; }; void Stack::init() { top=0; memset(space,0,1024); } bool Stack::isEmpty() { return top==0; } bool Stack::isFull() { return top==1024; } char Stack::pop() { return space[--top]; } void Stack::push(char c) { space[top++]=c; } int main() { Stack st; st.init(); for(char v='a';!st.isFull()&&v!='z'+1;++v) { st.push(v); } while(!st.isEmpty()) cout<<st.pop()<<" "; return 0; }
下面是 C++連結串列模擬棧/
#include <iostream> #include <memory.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; struct Node * next; }; class List { public: List *createList(); void insertList(int d); void traverseList(); private: Node * head; }; List * List::createList() { head=new Node; head->next = NULL; } void List::insertList(int d) { Node * cur = new Node; cur->data=d; cur->next = head->next; head->next=cur; } void List::traverseList() { Node * ph = head->next; while(ph!=NULL) { cout<<ph->data<<endl; ph = ph->next; } } int main() { List list; list.createList(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { list.insertList(i); } list.traverseList(); return 0; }