Python入門19
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-23
建立執行緒
import threading
import _thread
import time
def job():
print('這是一個需要執行的任務')
#啟用的執行緒個數
print('當前執行緒的個數:',threading.active_count())
#列印當前執行緒的詳細資訊
print('當前執行緒資訊:',threading.current_thread())
time.sleep(10)
if __name__=='__main__':
job()
_thread模組建立多執行緒
import _thread import threading import time def job(name): print('這是一個需要執行的任務') #啟用的執行緒個數 print('啟用的執行緒個數:',threading.active_count()) #當前執行緒的資訊 print('當前執行緒資訊:',threading.current_thread()) print(name) time.sleep(10) if __name__=='__main__': #建立多個執行緒,但是沒有開始執行任務 _thread.start_new_thread(job,('thread1',)) _thread.start_new_thread(job,('thread2',)) # while True: job(job)
threading建立執行緒的方法
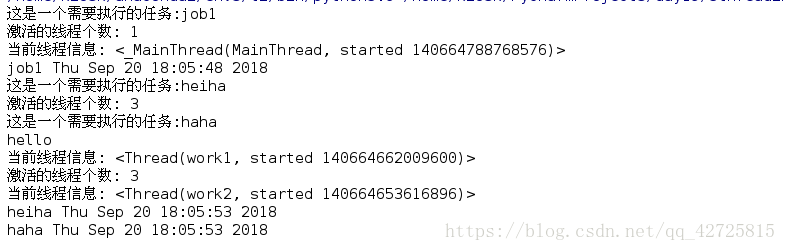
import _thread import threading import time def job(name): print('這是一個需要執行的任務:%s' %(name)) #啟用的執行緒個數 print('啟用的執行緒個數:',threading.active_count()) #執行緒資訊 print('當前執行緒資訊:',threading.current_thread()) time.sleep(5) print(name,time.ctime()) if __name__=='__main__': job('job1') #建立多個執行緒 t1=threading.Thread(target=job,name='work1',args=('heiha',)) t1.start() t2=threading.Thread(target=job,name='work2',args=('haha',)) t2.start() print('hello')
不使用多執行緒及多執行緒的join方法
不使用
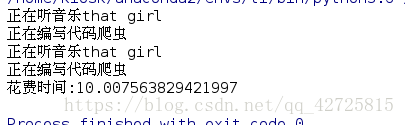
import time def music(name): for i in range(2): print('正在聽音樂%s' %(name)) time.sleep(3) def code(name): for i in range(2): print('正在編寫程式碼%s' %(name)) time.sleep(5) if __name__=='__main__': start_time=time.time() music('that girl') code('爬蟲..') print('花費時間:%s' %(time.time()-start_time))
使用join方法
import threading
import time
def music(name):
for i in range(2):
print('正在聽音樂%s' %(name))
time.sleep(3)
def code(name):
for i in range(2):
print('正在編寫程式碼%s' %(name))
time.sleep(5)
if __name__=='__main__':
start_time=time.time()
t1=threading.Thread(target=music,args=('that girl',))
t1.start()
t2=threading.Thread(target=code,args=('爬蟲',))
# t1.start()
t2.start()
#等待所有的子執行緒執行結束之後,繼續執行主執行緒的內容
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('花費時間:%s' %(time.time()-start_time))
_threading的set_daemon方法實現
#當主執行緒執行結束,讓沒有執行的執行緒強制結束;set_daemon
import threading
import time
#任務1
def music(name):
for i in range(2):
print('正在聽音樂%s' %(name))
time.sleep(3)
#任務2
def code(name):
for i in range(2):
print('正在編寫程式碼%s' %(name))
time.sleep(5)
if __name__=='__main__':
start_time=time.time()
t1=threading.Thread(target=music,args=('that girl',))
t2=threading.Thread(target=code,args=('爬蟲',))
#將t1執行緒設定為守護執行緒,如果設定為True,子執行緒啟動,當主執行緒執行結束,子執行緒也執行結束
#設定setDaemon必須在啟動執行緒之前設定
t1.setDaemon(True)
t2.setDaemon(True)
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('花費時間:%s' %(time.time()-start_time))
join的詳細理解
1. 管理執行緒的模組: _thread, threading
2. _thread建立多執行緒: _thread.start_new_thread(執行緒需要執行的任務,(任務需要的引數, 元組資料型別 ))
3. threading建立多執行緒第一種方式:例項化一個物件(Thread)
#t1 = threading.Thread(target=任務函式名, args=(x1,x2), name=‘threadName’)
4. 啟動執行緒: t.start()
5. join方法: 會等待, 直到t1執行緒執行結束;阻塞正在呼叫的執行緒
6. setDaemon:
import threading
import time
def job():
time.sleep(2)
print('job1')
# t1=threading.Thread(target=job)
# t1.start()
# t1.join() #會等待,直到t1執行緒執行結束;阻塞正在呼叫的執行緒(t2)
# t2=threading.Thread(target=job)
# t2.start()
# t2.join()#會等待,直到t2執行緒執行結束,阻塞正在呼叫的執行緒
t1=threading.Thread(target=job)
t1.start()
t2=threading.Thread(target=job)
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
print('main thread end')
threading建立執行緒方法2_任務無需引數和需要傳引數
無需引數
import threading
#類的繼承
class IpThread(threading.Thread):
#重寫構造方法
def __init__(self,jobname):
super(IpThread, self).__init__()
self.jobname=jobname
#將多執行緒需要執行的任務重寫到run方法中
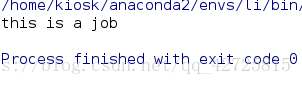
def run(self):
print('this is a job')
t1=IpThread(jobname='new job')
t1.start()
需要引數
import json
import threading
#類的繼承
from urllib.error import HTTPError
from urllib.request import urlopen
import time
class IpThread(threading.Thread):
#重寫構造方法;如果執行的任務需要傳遞引數;那將引數通過建構函式與self繫結
def __init__(self,jobname,ip):
super(IpThread, self).__init__()
self.jobname=jobname
self.ip=ip
#將多執行緒需要執行的任務重寫到run方法中
def run(self):
try:
#需要一個引數,傳ip
url="http://ip.taobao.com/service/getIpInfo.php?ip=%s" % (self.ip)
#根據url獲取網頁中的內容;並且解碼為utf-8格式,識別中文
text=urlopen(url).read().decode('utf-8')
except HTTPError as e:
print('Error:%s獲取地理位置網路錯誤' %(self.ip))
else:
#將獲取的字串型別轉換為字典,方便處理
d=json.loads(text)['data']
country=d['country']
city=d['city']
print('%s:' %(self.ip),country,city)
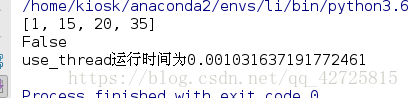
def use_thread():
start_time=time.time()
ips = ['172.25.254.250', '8.8.8.8',
'172.25.254.250']
threads = []
for ip in ips:
t = IpThread(jobname="爬蟲", ip=ip)
threads.append(t)
t.start()
# 等待所有的子執行緒執行結束
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
print("Success, 執行時間為%s" % (time.time() - start_time))
if __name__ == "__main__":
use_thread()
執行緒同步之執行緒鎖
import threading
def add(lock):
#2.操作變數之前進行加鎖
# lock.acquire()
global money
for i in range(1000000):
money+=1
#3.操作變數完成後進行解鎖
# lock.release()
def reduce(lock):
# 2.操作變數之前進行加鎖
# lock.acquire()
global money
for i in range(1000000):
money -= 1
# 3.操作變數完成後進行解鎖
# lock.release()
if __name__=='__main__':
money=0
#1,例項化鎖物件
lock=threading.Lock()
t1=threading.Thread(target=add,args=(lock,))
t2=threading.Thread(target=reduce,args=(lock,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
#等待所有子執行緒執行結束
t1.join()
t2.join()
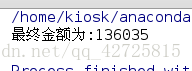
print('最終金額為:%s' %(money))
佇列與多執行緒
# 1). 理論上多執行緒執行任務, 會產生一些資料, 為其他程式執行作鋪墊;
# 2). 多執行緒是不能返回任務執行結果的, 因此需要一個容器來儲存多執行緒產生的資料
# 3). 這個容器如何選擇? list(棧, 佇列), tuple(x), set(x), dict(x), 此處選擇佇列來實現
import threading
from collections import Iterable
from mytimeit import timeit
from queue import Queue
def job(l,queue):
#將任務的結果儲存到佇列中
queue.put(sum(l))
@timeit
def use_thread():
#例項化一個佇列,用來儲存每個執行緒執行的結果
q=Queue()
#入隊
q.put(1)
li = [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], [2, 3, 4, 5, 6]]
threads=[]
for i in li:
t=threading.Thread(target=job,args=(i,q))
threads.append(t)
t.start()
#join方法等待所有子執行緒執行結束
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
#從佇列裡面拿出所有執行結果
result=[q.get() for _ in li]
print(result)
print(isinstance(q,Iterable))
if __name__=='__main__':
use_thread()
Threadpool執行緒池
# 注意: python3.2版本以後才可以使用;
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import time
#需要執行的任務
def job():
print('this is a job')
return 'hello'
if __name__=='__main__':
#例項化物件,執行緒池包含10個執行緒來處理任務
pool=ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10)
#往執行緒池扔需要執行的任務,返回一個物件
f1=pool.submit(job)
f2=pool.submit(job)
#判斷任務是否執行結束
print(f1.done())
time.sleep(3)
print(f2.done())
#獲取任務執行的結果
print(f1.result())
print(f2.result())
執行緒池執行多個迴圈執行任務多次
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from urllib.request import urlopen
"""
Name:06_多執行緒paramiko執行命令.py
Author: lvah
Date: 2018-09-15
Email: [email protected]
Desc:
這是一個python指令碼.
"""
# 基於ssh用於連線遠端伺服器做操作:遠端執行命令, 上傳檔案, 下載檔案
import threading
import paramiko
from paramiko.ssh_exception import NoValidConnectionsError, AuthenticationException
def connect(cmd, hostname, port=22, user='root'):
# ssh [email protected]
# 建立一個ssh物件;
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 返回一個私鑰物件
private_key = paramiko.RSAKey.from_private_key_file('id_rsa')
# 2. 解決問題:如果之前沒有;連線過的ip, 會出現
# Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
# 自動選擇yes
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
try:
# 3. 連線伺服器
client.connect(hostname=hostname,
port=port,
username=user,
pkey=private_key
)
# 4. 執行操作
stdin, stdout, stderr = client.exec_command(cmd)
except NoValidConnectionsError as e:
print("%s連線失敗" %(hostname))
except AuthenticationException as e:
print("%s密碼錯誤" %(hostname))
else:
# 5. 獲取命令的執行結果;
result = stdout.read().decode('utf-8')
print("%s執行結果:" %(hostname), result)
finally:
# 6. 關閉連線
client.close()
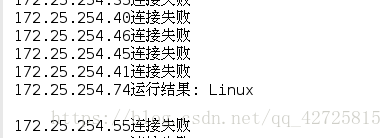
# ******************方法1: 每個ip使用一個執行緒來處理********************
# # 用來儲存建立的所有執行緒物件;
# threads = []
# for count in range(254):
# host = '172.25.254.%s' %(count+1)
# # print(host.center(50, '*'))
# t = threading.Thread(target=connect, args=('uname', host))
# threads.append(t)
# t.start()
#
#
# # join方法, 等待所有的子執行緒執行結束;
# _ = [thread.join() for thread in threads]
#
# print("任務執行結束........")
# ***********************方法2: 執行緒池只有50個執行緒處理所有的任務****************
# 建立執行緒池物件
pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=50)
# 依次向執行緒池提交任務
for count in range(254):
host = '172.25.254.%s' % (count + 1)
pool.submit(connect, 'uname', host)
執行緒池與map函式
from urllib.error import HTTPError
from urllib.request import urlopen
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from concurrent.futures import as_completed
import time
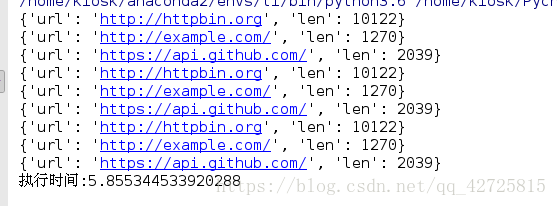
URLS = ['http://httpbin.org', 'http://example.com/',
'https://api.github.com/'] * 3
def get_page(url, timeout=3):
try:
content = urlopen(url).read()
return {'url':url, 'len':len(content)}
except HTTPError as e:
return {'url':url, 'len':0}
# 方法1: submit提交任務
start_time = time.time()
pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=20)
futuresObj = [pool.submit(get_page, url) for url in URLS]
# 注意: 傳遞的時包含futures物件的序列, as_complete, 返回已經執行完任務的future物件,
# 直到所有的future對應的任務執行完成, 迴圈結束;
# for finish_fs in as_completed(futuresObj):
# print(finish_fs.result() )
for future in futuresObj:
print(future.result())
print("執行時間:%s" %(time.time()-start_time))
# 方法2:通過map方式執行
# pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=20)
# for res in pool.map(get_page, URLS):
# print(res)