Android自定義View的三種方式:繼承佈局,繼承原生控制元件,繼承View
自定義View非常的常用,也是Android開發的一項基本技能,自定義View有三種方式:繼承佈局,繼承原生控制元件,繼承View。
一、繼承佈局
先看效果圖:
程式碼實現:
1.在layout資料夾中建立佈局title_view.xml,這一步根據自己需要寫,本例中的佈局如下:
佈局程式碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="?actionBarSize" android:id="@+id/title_view" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/back" android:src="@drawable/ic_action_arrow_left" android:padding="16dp" android:adjustViewBounds="true" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/title" tools:text="Title" android:textColor="@android:color/black" android:textSize="24sp" android:gravity="center" app:layout_constraintLeft_toRightOf="@id/back" android:layout_marginLeft="8dp" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/menu" tools:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:padding="8dp" app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="match_parent" /> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
設定了一個返回圖示,一個標題,一個選單圖示。
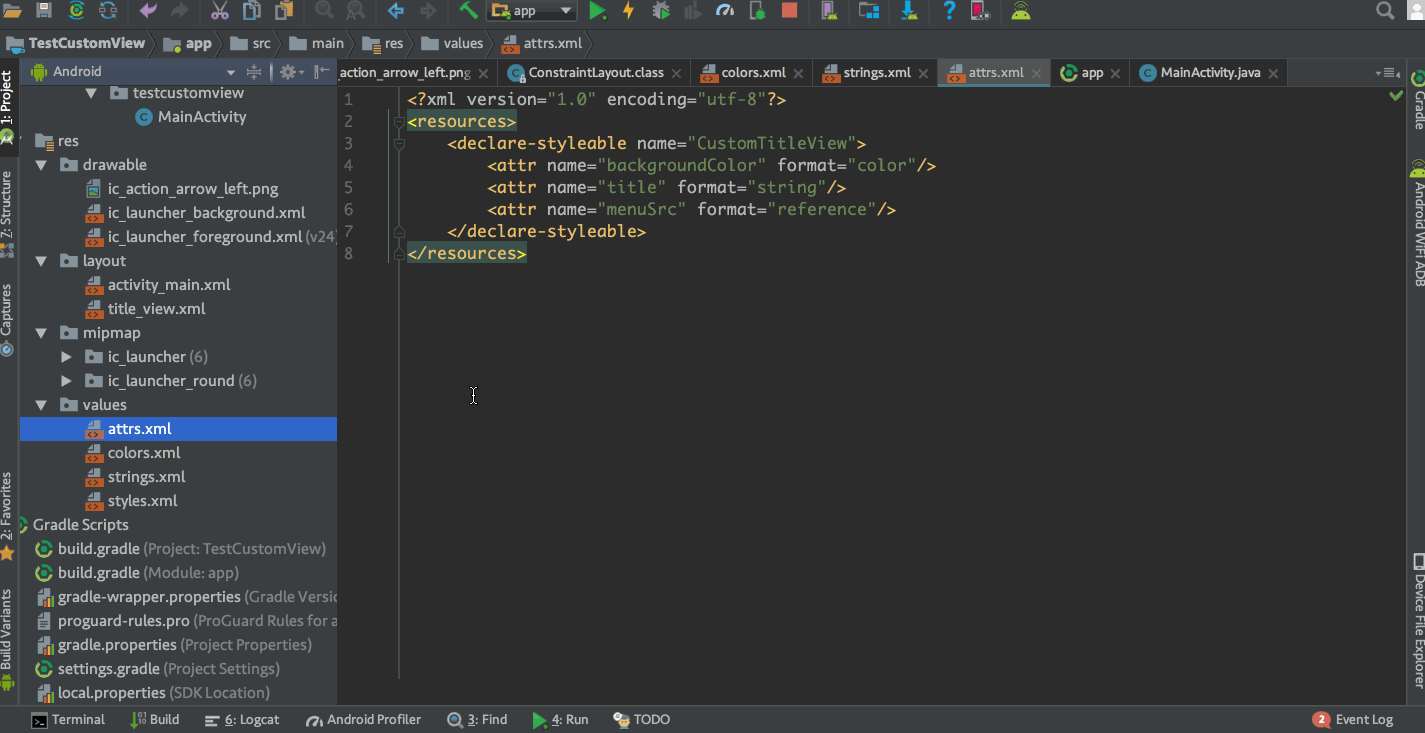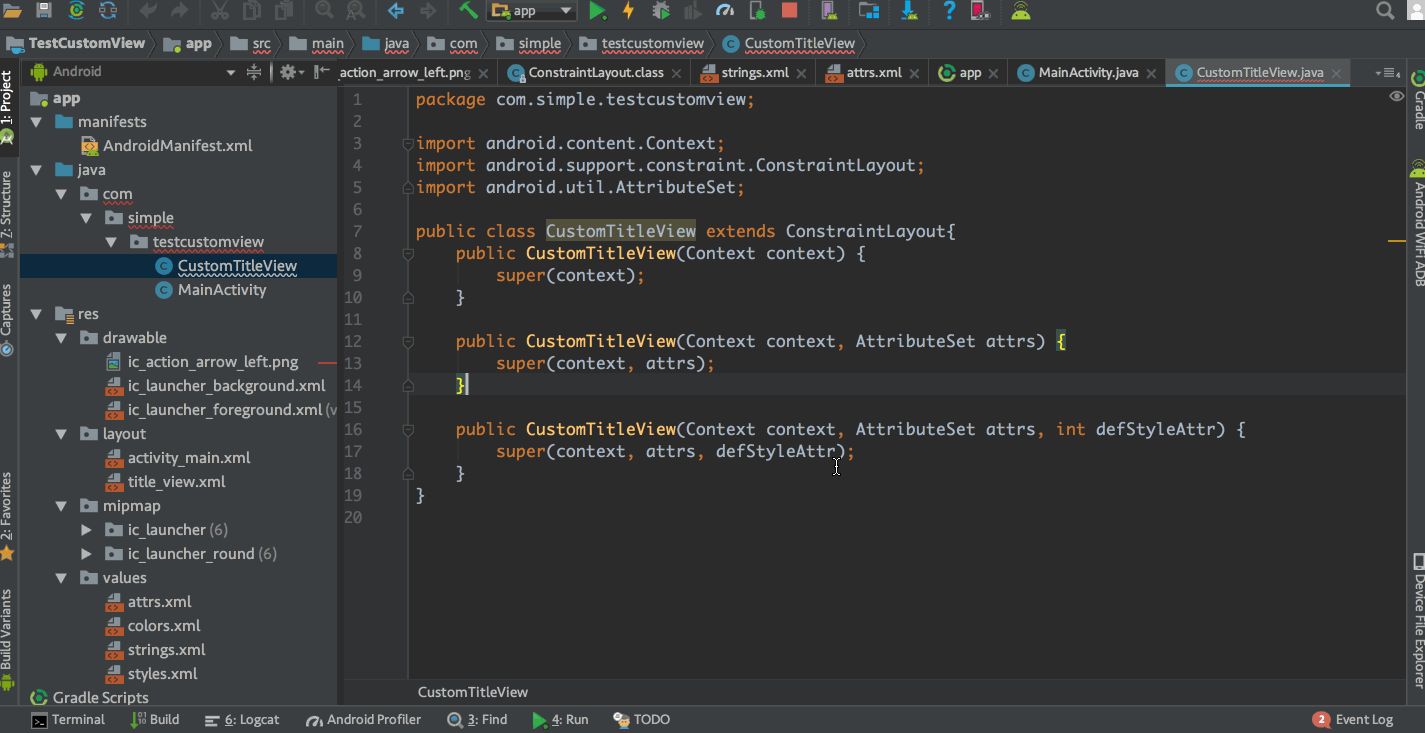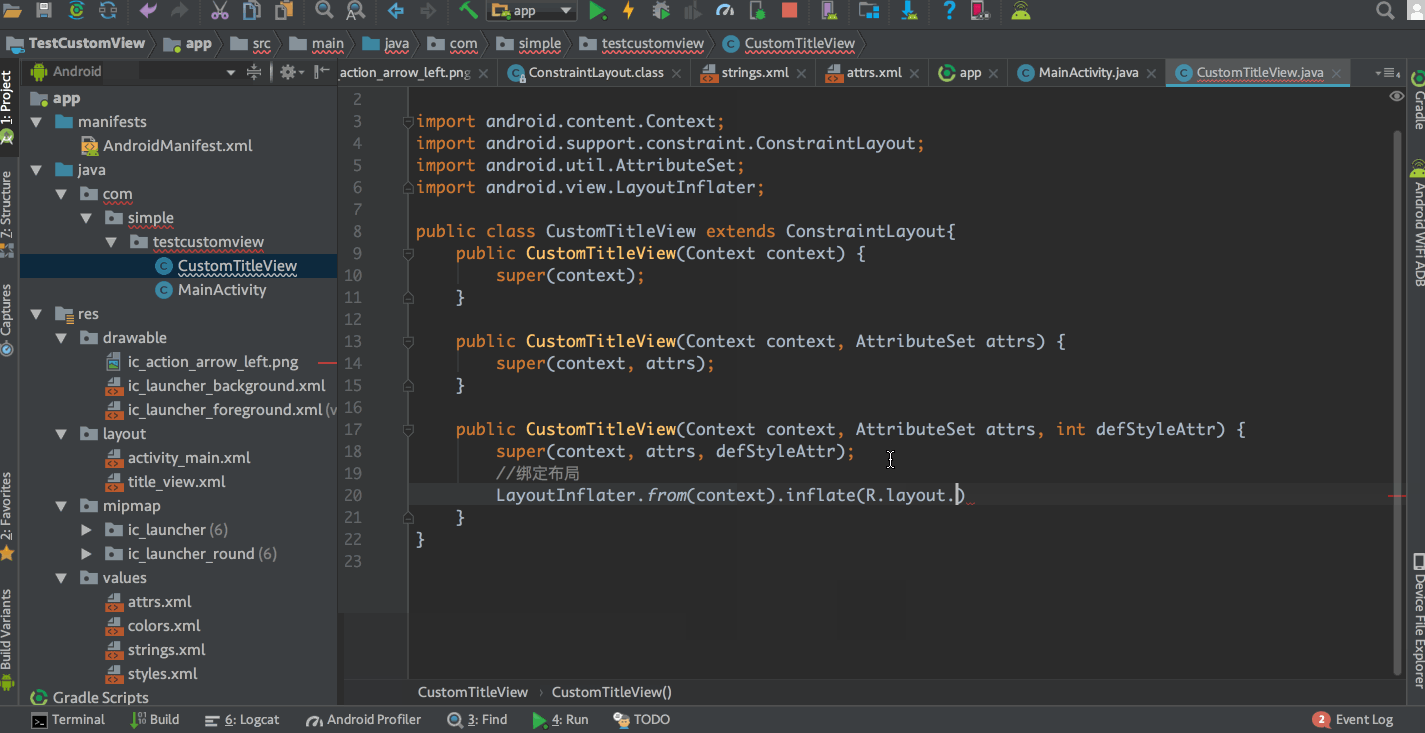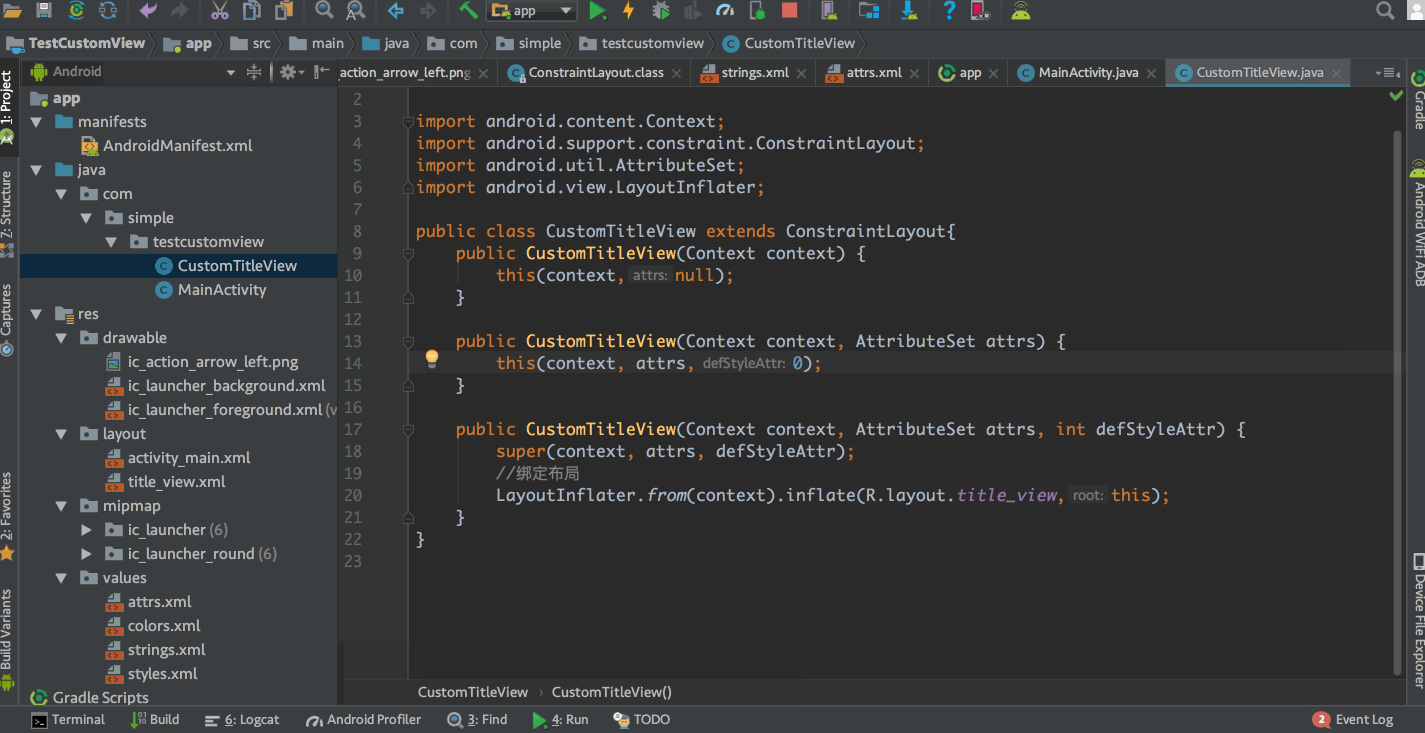
2.在values資料夾中新建attrs.xml,在其中宣告自定義屬性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <declare-styleable name="CustomTitleView"> <attr name="backgroundColor" format="color"/> <attr name="title" format="string"/> <attr name="menuSrc" format="reference"/> </declare-styleable> </resources>
本例中自定義了背景顏色,標題,選單資源三個屬性,format是指該屬性的取值型別,format取值一共有string,color,demension,integer,enum,reference,float,boolean,fraction,flag這幾種,其中reference是指引用資原始檔。
3.新建CustomTitleView檔案,並重寫三個構造方法,在public CustomTitleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)方法中繫結佈局,並將其他兩個構造方法修改成呼叫public CustomTitleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr)方法。這樣就實現了每個構造方法都會繫結我們剛才寫的佈局。當然這裡也可以在每個構造方法中都寫一遍繫結佈局。
4.找到控制元件並獲取屬性
public class CustomTitleView extends ConstraintLayout{ private ConstraintLayout clTitleView; private ImageView ivBack; private TextView tvTitle; private ImageView ivMenu; //背景色 private int backgroundColor; //標題 private String title; //選單圖片資源 private int menuSrc; public CustomTitleView(Context context) { this(context,null); } public CustomTitleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomTitleView(final Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //繫結佈局 LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.title_view,this); //找到控制元件 clTitleView = findViewById(R.id.title_view); ivBack = findViewById(R.id.back); tvTitle = findViewById(R.id.title); ivMenu = findViewById(R.id.menu); //獲取屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomTitleView,defStyleAttr,0); //獲取背景色屬性,預設透明 backgroundColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomTitleView_backgroundColor, Color.TRANSPARENT); //獲取標題屬性 title = typedArray.getString(R.styleable.CustomTitleView_title); //獲取選單圖片資源屬性,未設定選單圖片資源則預設為-1,後面通過判斷此值是否為-1決定是否設定圖片 menuSrc = typedArray.getResourceId(R.styleable.CustomTitleView_menuSrc,-1); //TypedArray使用完後需手動回收 typedArray.recycle(); //設定屬性 clTitleView.setBackgroundColor(backgroundColor); tvTitle.setText(title); if(menuSrc!=-1){ ivMenu.setImageResource(menuSrc); } //back圖示點選事件,點選關閉activity ivBack.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { ((Activity)getContext()).finish(); } }); } }
使用TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomTitleView,defStyleAttr,0);獲取所有屬性,再使用typedArray的getColor,getString,getResourceId方法分別獲取format為color,string,reference的自定義屬性。這些方法中有的需要傳入兩個引數,第二個引數就是沒有設定此屬性時的預設值,在繫結佈局後找到控制元件,然後為控制元件設定屬性。typedArray使用完之後需要手動呼叫typedArray.recycle()回收掉。
本例中我給返回圖示添加了一個點選事件,點選就會將這個TitleView所在的activity關閉
5.在佈局中使用CustomTitleView
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.sample.studycustomview.CustomTitleView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:backgroundColor="@color/colorPrimary" app:title="Title" app:menuSrc="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
這樣就完成了上面的效果圖
二、繼承原生控制元件
先看效果圖
程式碼實現
1.在values資料夾下的attrs.xml中,宣告自定義屬性
<declare-styleable name="CustomProgressBar"> <attr name="circleColor" format="color"/> <attr name="circleWidth" format="dimension"/> <attr name="startAngle" format="integer"/> <attr name="textSize" format="dimension"/> <attr name="textColor" format="color"/> </declare-styleable>
2.新建CustomProgressbar,繼承ProgressBar,重寫三個構造方法,並獲取自定義的屬性
public class CustomProgressBar extends ProgressBar{ private Paint mPaint; private int mCircleColor;//圓的顏色 private int mCircleWidth;//圓的粗細 private int mStartAngle;//起始角度 private int mTextSize;//文字大小 private int mTextColor;//文字顏色 public CustomProgressBar(Context context) { this(context,null,0); } public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //獲取屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomProgressBar,defStyleAttr,0); //獲取圓的顏色,預設黑色 mCircleColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_circleColor,Color.BLACK); //獲取圓的粗細,預設5dp mCircleWidth = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_circleWidth,FormatUtil.dp2px(context,5)); //獲取圓的起始角度,預設0度 mStartAngle = typedArray.getInteger(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_startAngle,0); //獲取文字大小,預設18sp mTextSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_textSize,FormatUtil.sp2px(getContext(),18)); //獲取文字顏色,預設黑色 mTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_textColor,Color.BLACK); typedArray.recycle(); mPaint = new Paint(); } }
3.重寫onMeasure,計算寬高
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //如果寬高為固定dp 或 match_parent 直接使用以上獲得的width和height即可,如果是wrap_content 需要單獨處理 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); //預設寬度60dp,預設高度60dp if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ width = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + FormatUtil.dp2px(getContext(),60); } if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ height = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + FormatUtil.dp2px(getContext(),60); } setMeasuredDimension(width,height); }
4.重寫onDraw,畫圓弧和文字
public class CustomProgressBar extends ProgressBar{ private Paint mPaint; private int mCircleColor;//圓的顏色 private int mCircleWidth;//圓的粗細 private int mStartAngle;//起始角度 private int mTextSize;//文字大小 private int mTextColor;//文字顏色 private RectF mRectF;//限制弧線的矩形 private Rect mBounds;//測量文字的邊緣 public CustomProgressBar(Context context) { this(context,null,0); } public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomProgressBar(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //獲取屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomProgressBar,defStyleAttr,0); //獲取圓的顏色,預設黑色 mCircleColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_circleColor,Color.BLACK); //獲取圓的粗細,預設5dp mCircleWidth = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_circleWidth,FormatUtil.dp2px(context,5)); //獲取圓的起始角度,預設0度 mStartAngle = typedArray.getInteger(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_startAngle,0); //獲取文字大小,預設18sp mTextSize = (int) typedArray.getDimension(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_textSize,FormatUtil.sp2px(getContext(),18)); //獲取文字顏色,預設黑色 mTextColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomProgressBar_textColor,Color.BLACK); typedArray.recycle(); mRectF = new RectF(); mBounds = new Rect(); mPaint = new Paint(); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //如果寬高為固定dp 或 match_parent 直接使用以上獲得的width和height即可,如果是wrap_content 需要單獨處理 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); //預設寬度60dp,預設高度60dp if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ width = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + FormatUtil.dp2px(getContext(),60); } if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ height = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + FormatUtil.dp2px(getContext(),60); } setMeasuredDimension(width,height); } @Override protected synchronized void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { //1.畫圓弧 mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); //設定只畫邊框模式 mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE); mPaint.setColor(mCircleColor); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(mCircleWidth); //限制圓弧的左、上、右、下座標 mRectF.set(getPaddingLeft(),getPaddingTop(),getWidth() - getPaddingRight(),getHeight() - getPaddingBottom()); //畫圓弧,傳入RectF,開始角度,掃過角度,是否連線中心,畫筆 canvas.drawArc(mRectF,mStartAngle,getProgress()*1.0f/getMax()*360,false,mPaint); //2.畫文字 String strProgress = getProgress()+"%"; mPaint.setTextSize(mTextSize); mPaint.setColor(mTextColor); mPaint.setStrokeWidth(FormatUtil.dp2px(getContext(),1)); //設定填充模式 mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL); //獲取文字邊緣 mPaint.getTextBounds(strProgress,0,strProgress.length(),mBounds); //畫文字,傳入文字內容,文字左下角座標,畫筆 canvas.drawText(strProgress ,(getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight() - mBounds.width())/2+getPaddingLeft() ,(getHeight() - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom() - mBounds.height())/2+getPaddingTop()+mBounds.height(),mPaint); } }
5.在佈局中使用CustomProgressBar
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <com.sample.studycustomview.CustomProgressBar android:progress="60" android:max="100" android:padding="16dp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:circleColor="@color/colorPrimary" app:circleWidth="3dp" app:startAngle="90" app:textSize="15sp" app:textColor="@color/colorPrimary"/> </android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
附上FormatUtil工具類,主要是為了dp、sp、px互相轉換
public class FormatUtil { private FormatUtil() { /* cannot be instantiated */ throw new UnsupportedOperationException("cannot be instantiated"); } /** * Value of dp to value of px. * * @param dpValue The value of dp. * @return value of px */ public static int dp2px(Context context,final float dpValue) { final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f); } /** * Value of px to value of dp. * * @param pxValue The value of px. * @return value of dp */ public static int px2dp(Context context,final float pxValue) { final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (pxValue / scale + 0.5f); } /** * Value of sp to value of px. * * @param spValue The value of sp. * @return value of px */ public static int sp2px(Context context,final float spValue) { final float fontScale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().scaledDensity; return (int) (spValue * fontScale + 0.5f); } /** * Value of px to value of sp. * * @param pxValue The value of px. * @return value of sp */ public static int px2sp(Context context,final float pxValue) { final float fontScale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().scaledDensity; return (int) (pxValue / fontScale + 0.5f); } }
這樣就完成了上面的效果圖
三、繼承View
先看效果圖:
程式碼實現:
1.在values資料夾下的attrs.xml中,宣告自定義屬性
<declare-styleable name="CustomAnimNumberView"> <attr name="number" format="string"/> <attr name="numberColor" format="color"/> <attr name="numberSize" format="dimension"/> <attr name="animDuration" format="integer"/> </declare-styleable>
2.新建CustomAnimNumberView,繼承View,重寫三個構造方法,並獲取自定義的屬性,其中用到的FormatUtil和上例中一樣:
public class CustomAnimNumberView extends View { private Paint paint; private int number;// private int numberColor;//文字顏色 private int numberSize;//文字大小 private int animDuration;//動畫時長 public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context) { this(context,null); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //獲取自定義屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView,defStyleAttr,0); number = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_number,0); numberColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberColor, Color.BLACK); numberSize = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberSize,FormatUtil.sp2px(context,18)); animDuration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_animDuration,1000); typedArray.recycle(); paint = new Paint(); } }
3.重寫onMeasure,計算寬高
public class CustomAnimNumberView extends View { private Paint paint; private int number;// private int numberColor;//文字顏色 private int numberSize;//文字大小 private int animDuration;//動畫時長 private Rect bounds;//文字邊緣 public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context) { this(context,null); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //獲取自定義屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView,defStyleAttr,0); number = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_number,0); numberColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberColor, Color.BLACK); numberSize = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberSize,FormatUtil.sp2px(context,18)); animDuration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_animDuration,1000); typedArray.recycle(); paint = new Paint(); paint.setTextSize(numberSize); paint.setColor(numberColor); bounds = new Rect(); paint.getTextBounds(String.valueOf(number),0,String.valueOf(number).length(),bounds); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //如果寬高為固定dp 或 match_parent 直接使用以上獲得的width和height即可,如果是wrap_content 需要單獨處理 int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); if(widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ width = getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight() + bounds.width(); } if(heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){ height = getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom() + bounds.height(); } setMeasuredDimension(width,height); } }
4.重寫onDraw,畫動畫的數字
public class CustomAnimNumberView extends View { private Paint paint; private int number;// private int numberColor;//文字顏色 private int numberSize;//文字大小 private int animDuration;//動畫時長 private ValueAnimator animation;//動畫 private Rect bounds;//文字邊緣 public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context) { this(context,null); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs,0); } public CustomAnimNumberView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); //獲取自定義屬性 TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView,defStyleAttr,0); number = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_number,0); numberColor = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberColor, Color.BLACK); numberSize = typedArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_numberSize,FormatUtil.sp2px(context,18)); animDuration = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.CustomAnimNumberView_animDuration,1000); typedArray.recycle(); paint = new Paint(); paint.setTextSize(numberSize); paint.setColor(numberColor); bounds = new Rect(); paint.getTextBounds(String.valueOf(number),0,String.valueOf(number).length(),bounds); } @Override protected void相關推薦
Android自定義View的三種方式:繼承佈局,繼承原生控制元件,繼承View
自定義View非常的常用,也是Android開發的一項基本技能,自定義View有三種方式:繼承佈局,繼承原生控制元件,繼承View。一、繼承佈局先看效果圖:程式碼實現:1.在layout資料夾中建立佈局title_view.xml,這一步根據自己需要寫,本例中的佈局如下:佈
【Android進度條】三種方式實現自定義圓形進度條ProgressBar
總結了3種方法: 1.多張圖片切換 2.自定義顏色 3.旋轉自定義圖片 其它: Android自定義控制元件NumberCircleProgressBar(圓形進度條)的實現:點選開啟連結 橫線帶數字進度條:點選開啟連結
【Android】一、Progress進度條實現的三種方式:主執行緒實現,Service載入,動態建立
前言 更新版本,上傳資料到服務端,都是需要進度顯示的,Android進度顯示兩種方式 ProgressDialog 和 ProgressBar 新版本中ProgressDialog不被推薦使用,所以專案採用ProgressBar 分為三種實現方式: 1、MainAct
Java中數組定義的三種方式
++ pan stat div 方式 clas 空間 inf bsp 方法一: 1.先聲明 2.分配空間 3.賦值 public class arr{ public static void main(String[] args){
函數定義的三種方式
ont {} var 構造函數 函數定義 字面量 size 構造 ros 1.關鍵字函數 function fnName(){} 2.字面量函數 var fn = function(){} 字面量可以暫時理解為右值,即等號右面的值 3.構造函數 var fn = new F
(轉)Linux中設置服務自啟動的三種方式
情況下 level httpd sysv kconfig clas mage com ssh 有時候我們需要Linux系統在開機的時候自動加載某些腳本或系統服務 主要用三種方式進行這一操作: ln -s 在/etc/rc.d/rc
細談 C++ 返回傳值的三種方式:按值返回、按常量引用返回以及按引用返回
一、引言 停滯了很久,最近又開始細細品味起《Data Structure And Algorithm Analysis In C++》這本書了。這本書的第一章即為非常好的 C++11 統領介紹的教材範文,可能對於 C++11 新手來說,作者這樣短篇幅的介紹或許有些蒼白晦澀,但是對於我
java斐波那契數列(Fibonacci sequence)的三種方式:遞迴,備忘錄,動態規劃
java斐波那契數列(Fibonacci sequence)的三種方式:遞迴,備忘錄,動態規劃 1.最常使用的是遞迴,就是從上往下尋找答案,然後在返回來。 2.備忘錄也是從上往下,只是去掉了遞迴中重複計算的部分,因為它使用一個容器來裝已經計算出的值,這裡就多一個判斷,如果計算過該式子,就直接
android解析XML的三種方式 DOM、SAX、PULL
第一種DOM是全部解析出來,消耗記憶體空間 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
php中字串定義的三種方式
三種定義方式 單引號 雙引號 定界符<<< 單引號與雙引號的區別: $name='張三'; echo $name; 輸出 張三 $name="張三"; echo $name; 輸出 張三
android圖片壓縮的三種方式
為了避免oom的出現,幾乎每個應用都會對大圖進行壓縮,我現在手頭做的產品就有很多地方用到,以前封裝工具類的時候,都是在網上找東找西,然後拼拼湊湊,有效果就行了,一直用的迷迷糊糊,這幾天工作比較閒,正好系統的總結梳理一下圖片壓縮方式: 圖片壓縮現在常見的有三種方式: 1、等比壓縮,等
Android呼叫巨集的三種方式
在工程專案中,為什麼vendor目錄下的platformconfigs.xml檔案可以對部分手機的屬性特性進行設定? 答:在framework目錄下,android.provider.Settings檔案為這種方式提供了可能。通過官方文件對其描述:“The Settings
運維團隊踐行的三種方式:簡、智、深
本文整理自 GOPS • 2017 北京站演講《運維團隊的一種選擇 簡、智、深》,高效運維社群致力於陪伴您的職業生涯,與您一起愉快的成長。 作者:趙建春 編輯:畢巨集飛 新時代下的網際網路運維正在經歷了一場場風雨洗禮,當前時代下有多少運維人處在迷茫和無助之中,交流和學習所積累下來的是更清晰,還是更
Linux中設定服務自啟動的三種方式
有時候我們需要Linux系統在開機的時候自動載入某些指令碼或系統服務 主要用三種方式進行這一操作: ln -s 在/etc/rc.d/rc*.d目錄中建立/etc/init.d/服務的軟連結(*代表0~6七個執行級別之一) chkonfig
Android 使用OpenCV的三種方式(Android Studio)
其實最早接觸OpenCV是很久很久之前的事了,大概在2013年的5,6月份,當時還是個菜逼(雖然現在也是個菜逼),在那一段時間,學了一段時間的android(並不算學,一個月都不到),之後再也沒接觸android,而是一直在接觸java web。那次接觸Open
C# 連線 Oracle 資料庫(三種方式:OracleClient、ODBC、OLEDB)
1、OracleClient //基於.NET 2.0,只有2.0中包含OracleClient using System; using System.Collections; using System.ComponentModel; using System.Data;
spring 配置的三種方式:XML配置,JAVA配置和註解配置
是否有了這些 IOC 註釋,我們就可以完全摒除原來 XML 配置的方式呢?答案是否定的。有以下幾點原因:註釋配置不一定在先天上優於 XML 配置。如果 Bean 的依賴關係是固定的,(如 Service 使用了哪幾個 DAO 類),這種配置資訊不會在部署時發生調整,那麼註釋配
Android退出程式的兩種方式:killProcess()和System.exit()
KillProcess() 呼叫 android.os.Process.killProcess(android.os.Process.myPid()) 可以殺死當前應用活動的程序,這一操作將會把所有該程序內的資源(包括執行緒全部清理掉)。當然,由於ActivityManag
Android 自定義Toast顯示多種方式
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(this.getApplicationContext,"This is a Toast including Image!", Toast.LENGTH_LONG); toast.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER, 0, 0); Lin
list集合(String字串)去重的三種方式:
方式一: List<String> listTemp = new ArrayList<String>(); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ if(!listTemp