讓shell終端和goland控制檯輸出彩色的文字
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-24
終端輸出彩色文字
在終端輸出這段命令,將的到一個紅色背景、綠色文字,並不停閃爍的輸出。
sszxr:~ sszxr$ echo -e "\033[5;32;41mI ♡ You \033[0m"
I ♡ You
sszxr:~ sszxr$
雙引號中的反斜槓\表示轉義,033是識別符號,表示用來設定顏色,[表示開始顏色設定,m為顏色設定結束。[後面的5表示閃爍,分號後面的32表示前景色,也就是文字的顏色,為綠色;再後面41表示背景色,為紅色,到m為設定結束,後面是輸出的內容,最後為再一次設定顏色,0m表示取消顏色設定。
從括號[到m中間為顏色設定,以;號分隔。
樣式有【0,1,4,5,7,8】六種,分別是:
0 終端預設設定
1 高亮顯示
4 使用下劃線
5 閃爍
7 反白顯示
8 不可見
顏色有7中,分別為
前景 背景 顏色
30 40 黑色
31 41 紅色
32 42 綠色
33 43 黃色
34 44 藍色
35 45 紫紅色
36 46 青藍色
37 47 白色
3位前景色,也就是文字的顏色;4位背景色。
Go語言中的彩色輸出
樣式和顏色與上面一樣,只是識別符號不一樣,
fmt.Printf("%c[0;41;36m%s%c[0m\n", 0x1B, "testPrintColor", 0x1B)
識別符號為0x1B,具體設定也是在[
m之間,以分號;分隔。
另一種方式
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
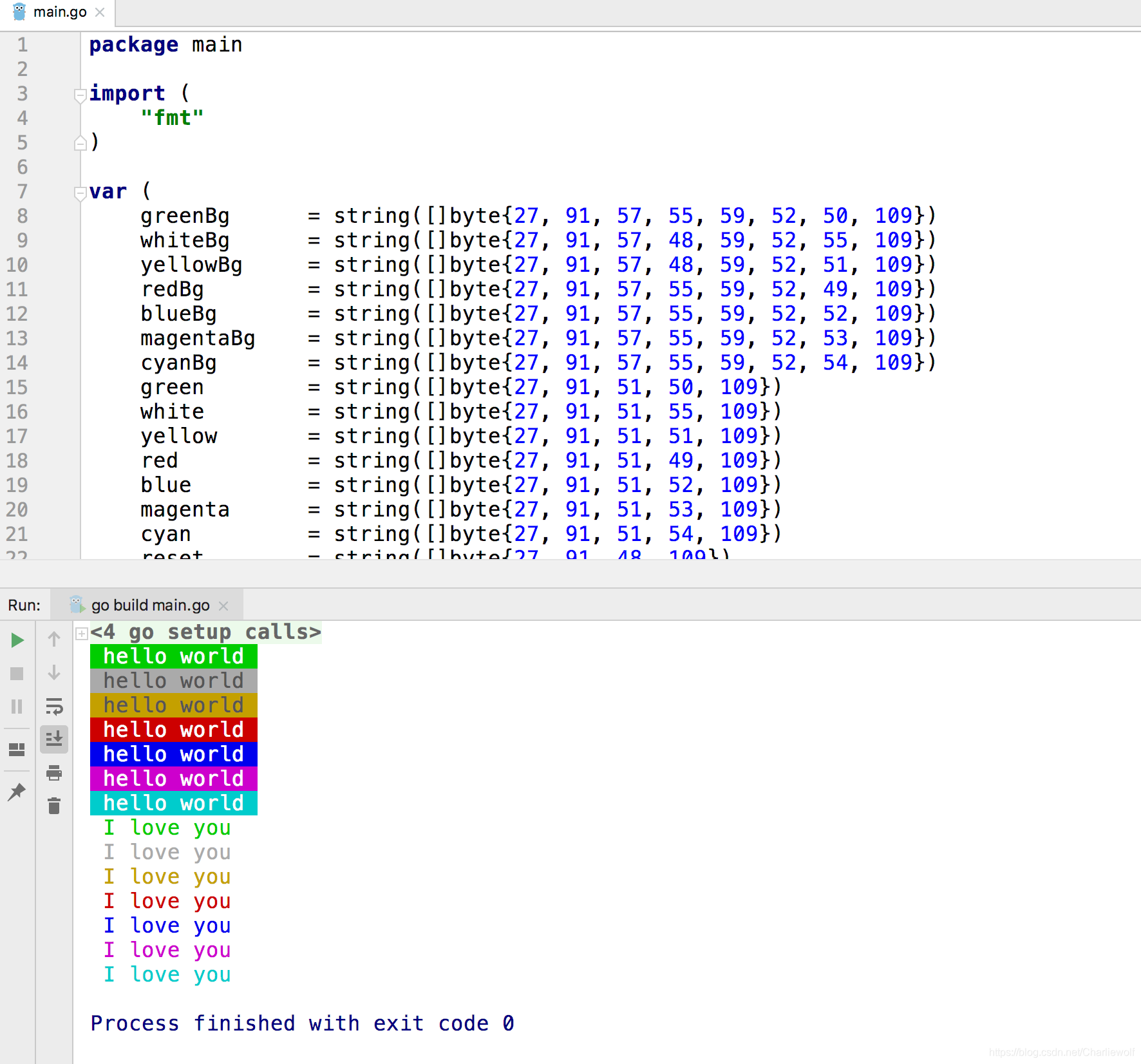
var (
greenBg = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 55, 59, 52, 50, 109})
whiteBg = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 48, 59, 52, 55, 109})
yellowBg = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 48, 59, 52, 51, 109})
redBg = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 55, 59, 52 執行結果
[]byte{}中那些數字是什麼意思
他們是0x1B [ ; m以及0-9的ASCII編碼
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Print(0x1B, '[', ';', 'm', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', "\n")
fmt.Printf("%#X\t%c\t%c\t%c\t", 27, 91, 59, 109)
fmt.Printf("%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t%c\t", 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57)
}
執行結果
27 91 59 109 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57
0X1B [ ; m 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
27代表0x1B
91代表[
59代表;
109代表m
57代表9,表示設定字型顏色
52代表4,表示設定背景色
51代表3,表示設定前景色,也就是文字的顏色
90到97與30到37的效果一樣,一個是設定字型顏色,一個是設定前景色,所以57和51可以互換,效果完全一樣,
reset表示0x1B[0m,表示清除顏色設定。
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
var (
black = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 48, 109})
red = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 49, 109})
green = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 50, 109})
yellow = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 51, 109})
blue = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 52, 109})
magenta = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 53, 109})
cyan = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 54, 109})
white = string([]byte{27, 91, 57, 55, 59, 52, 48, 109})
reset = string([]byte{27, 91, 48, 109})
disableColor = false
)
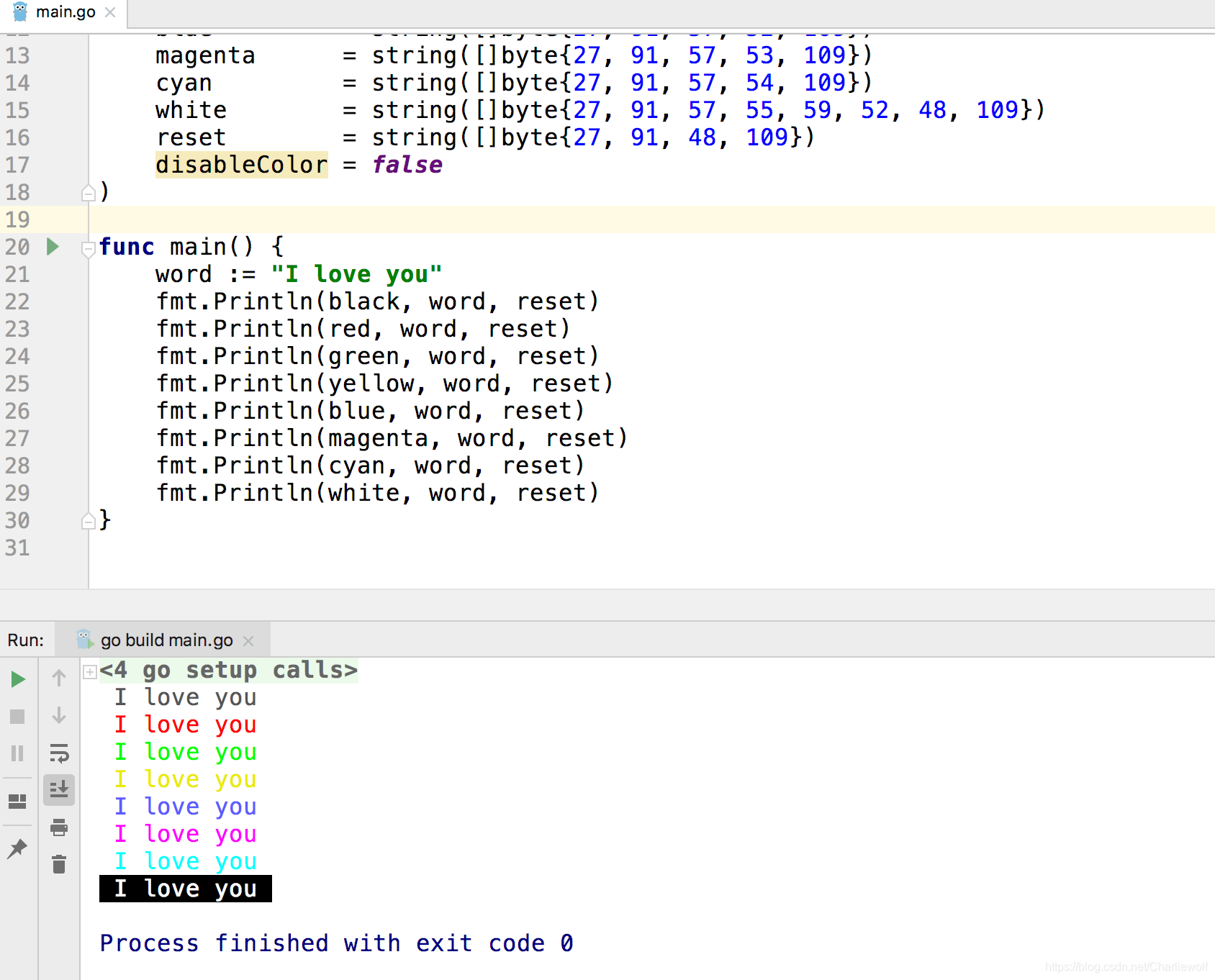
func main() {
word := "I love you"
fmt.Println(black, word, reset)
fmt.Println(red, word, reset)
fmt.Println(green, word, reset)
fmt.Println(yellow, word, reset)
fmt.Println(blue, word, reset)
fmt.Println(magenta, word, reset)
fmt.Println(cyan, word, reset)
fmt.Println(white, word, reset)
}