線索二叉樹建立及刪除
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-12-25
題目描述
線索二叉樹概念
1.定義
n個結點的二叉連結串列中含有n+1個空指標域。利用二叉連結串列中的空指標域,存放指向結點在某種遍歷次序下的前趨和後繼結點的指標(這種附加的指標稱為”線索”)。
這種加上了線索的二叉連結串列稱為線索連結串列,相應的二叉樹稱為線索二叉樹(Threaded BinaryTree)。根據線索性質的不同,線索二叉樹可分為前序線索二叉樹、中序線索二叉樹和後序線索二叉樹三種。
注意:
線索連結串列解決了二叉連結串列找左、右孩子困難的問題,出現了無法直接找到該結點在某種遍歷序列中的前趨和後繼結點的問題。
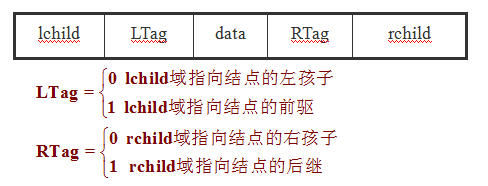
2.線索連結串列的結點結構
線索連結串列中的結點結構為:
其中:
ltag和rtag是增加的兩個標誌域,用來區分結點的左、右指標域是指向其左、右孩子的指標,還是指向其前趨或後繼的線索。
下面你的任務:首先根據輸入的序列建立二叉樹,然後對二叉樹進行線索化,最後中序遍歷二叉線索樹並輸出結果。
輸入要求
輸入的第一行包含單獨的一個數字T,表示測試序列的數目;
以下每一行為一個測試序列,測試序列是按先序序列輸入字元 ,如果節點沒有左或右孩子,則輸入用空格表示,最後用一個空格結束一行的輸入。
輸出要求
對應每個測試序列,採用中序遍歷二叉線索樹,輸出一行
假如輸入
2
ABC DE G F
-+a *b -c d /e f 應當輸出
CBEGDFA
a+b*c-d-e/f
寫了個線索二叉樹
Code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BTree
{
char data;
struct BTree *left,*right;
int ltag,rtag;
}BTree;
BTree *CreatBTree()
{
char ch=getchar();
if(ch==' ')
return NULL;
BTree *temp=(BTree *